Which Of The Following Would Affect An Employee's Net Pay
Payroll departments nationwide are scrambling to answer a critical question impacting millions: What factors directly influence an employee's net pay? The answer is complex, involving a variety of deductions and withholdings that ultimately determine the take-home amount.
This article breaks down the key elements affecting net pay, providing a clear and concise guide for employees and employers alike to understand where their money goes.
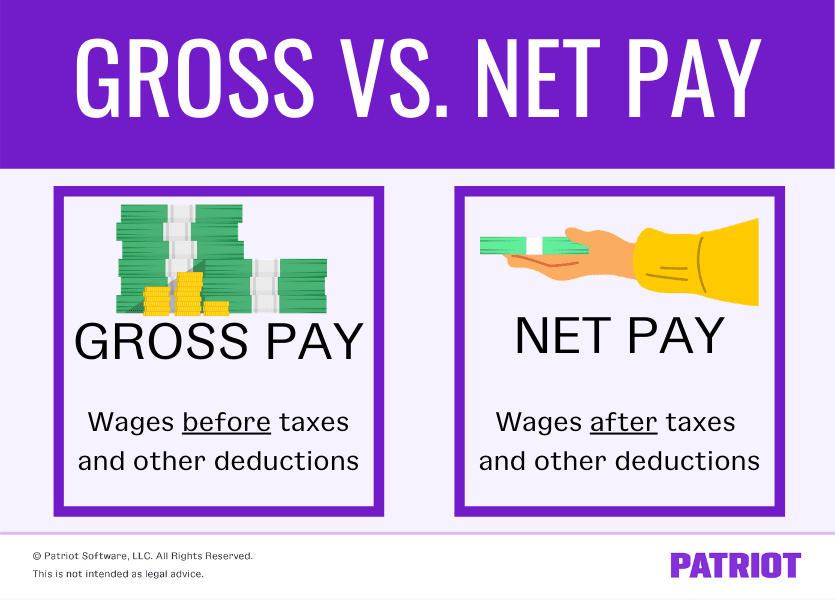
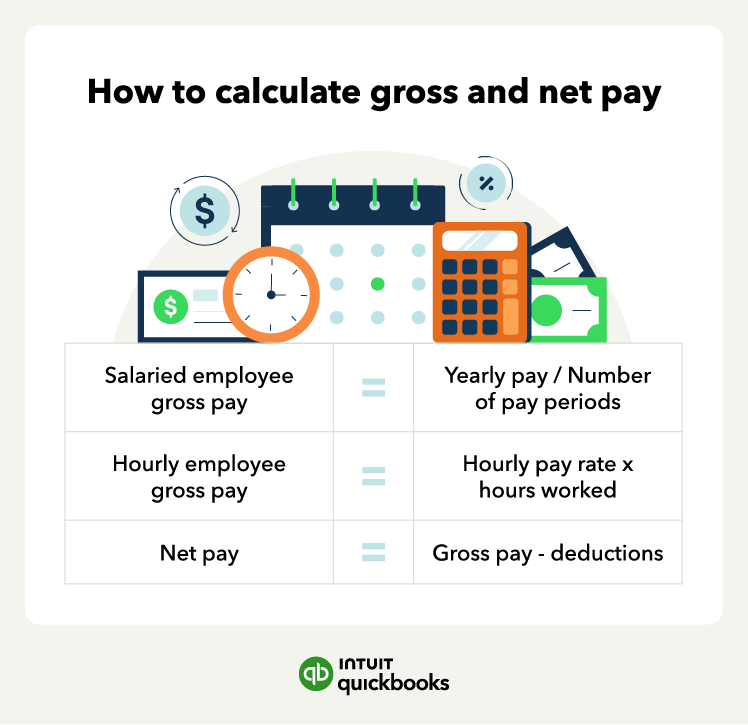
Understanding Gross Pay vs. Net Pay
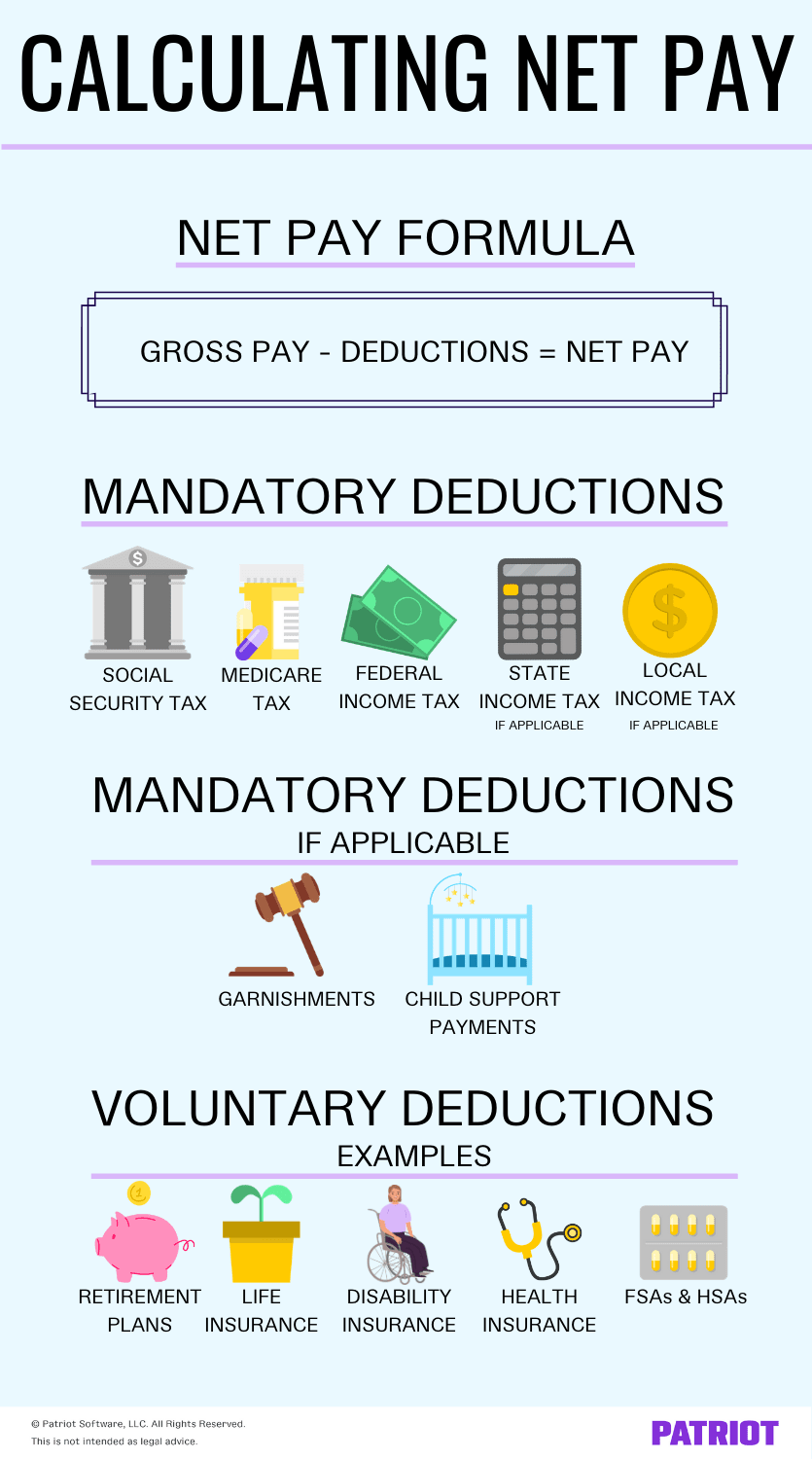
Gross pay is the total amount earned before any deductions. Net pay, often referred to as take-home pay, is what remains after these deductions are subtracted.
Federal Income Tax Withholding
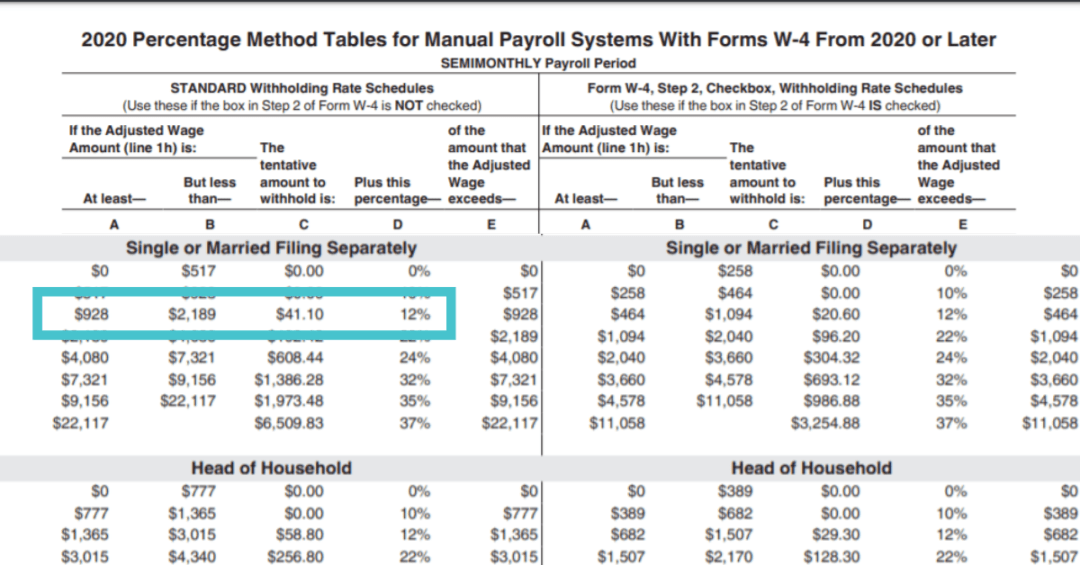
Federal income tax is a mandatory deduction calculated based on the employee's W-4 form. This form indicates filing status and any claimed allowances.
Changes in tax laws or personal circumstances (marriage, dependents) necessitate updating the W-4, directly impacting net pay.
Failure to accurately complete the W-4 can result in over- or under-withholding.
State Income Tax Withholding
Similar to federal income tax, state income tax is withheld based on state-specific forms and regulations. The amount varies depending on the state's tax structure and the employee's reported information.
Some states, like Florida and Texas, do not have state income tax, simplifying the net pay calculation for residents.
FICA Taxes: Social Security and Medicare
Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) taxes fund Social Security and Medicare. Social Security is withheld at a rate of 6.2% of gross wages up to a certain annual limit, and Medicare at a rate of 1.45% with no wage limit.
These deductions are mandatory for most employees and are a significant component of payroll withholdings.
Pre-Tax Deductions
Pre-tax deductions are subtracted from gross pay before taxes are calculated, reducing taxable income and potentially lowering overall tax liability.
Common examples include health insurance premiums, contributions to 401(k) or other retirement plans, and flexible spending account (FSA) contributions.
Increasing pre-tax deductions can significantly boost net pay by lowering taxable income.
Post-Tax Deductions
Post-tax deductions are subtracted from gross pay after taxes are calculated. These deductions do not reduce taxable income.
Examples include Roth 401(k) contributions, life insurance premiums, and charitable donations through payroll deductions.
Wage Garnishments
Wage garnishments are court-ordered deductions to repay debts, such as child support, unpaid taxes, or student loans. The amount garnished is legally determined and directly reduces net pay.
Employer-Sponsored Benefits
The cost of employer-sponsored benefits, even if partially subsidized, can impact net pay. Employee contributions to health insurance, dental insurance, and vision insurance are commonly deducted.
Changes in Salary or Wage
A raise or pay cut directly affects gross pay, subsequently impacting net pay after all applicable deductions are applied.
Overtime pay, bonuses, and commissions also increase gross pay and therefore net pay, although potentially placing the employee in a higher tax bracket.
Other Deductions
Miscellaneous deductions can include union dues, parking fees, or employee stock purchase plan (ESPP) contributions. The impact on net pay depends on the amount and frequency of these deductions.
The Impact of Life Changes
Significant life events frequently necessitate changes to tax withholdings and benefit elections, substantially affecting net pay. Marriage, the birth of a child, or a change in health insurance coverage all require adjustments.
Employees should regularly review their pay stubs and consult with their HR departments to ensure accuracy.
Moving Forward: Ensuring Accuracy
Employees are urged to proactively manage their W-4 forms and benefit elections to optimize their net pay. Employers should provide clear and accessible resources to help employees understand their pay stubs and make informed decisions.
The IRS offers various online tools and publications to assist taxpayers in understanding their tax obligations. Staying informed is crucial for financial well-being.