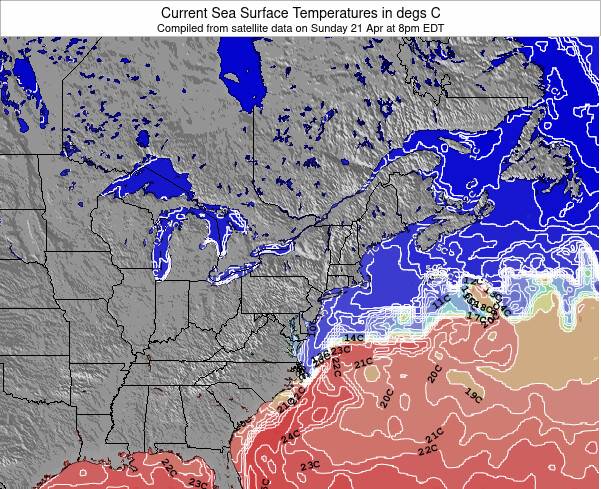
Water Temperature Atlantic City New Jersey
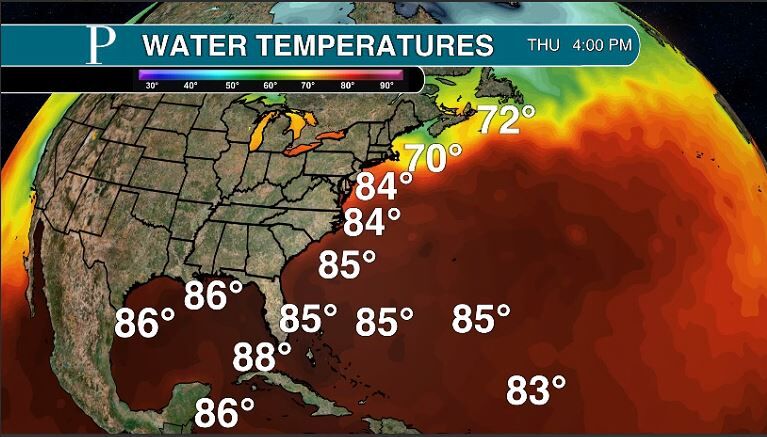
Atlantic City, NJ – Recent data indicates that water temperatures off the coast of Atlantic City are experiencing fluctuations, raising concerns among marine biologists, environmental advocates, and the local tourism industry. These temperature variations, observed over the past several weeks, could have far-reaching implications for the region’s delicate marine ecosystem and the economic activities dependent on it.
The Atlantic City region's ocean temperature is currently being closely monitored. These fluctuations require a thorough investigation, influencing everything from marine life distribution to potential weather patterns and impacting the livelihoods of fishermen and tourism operators.
Key Details of the Water Temperature Fluctuation
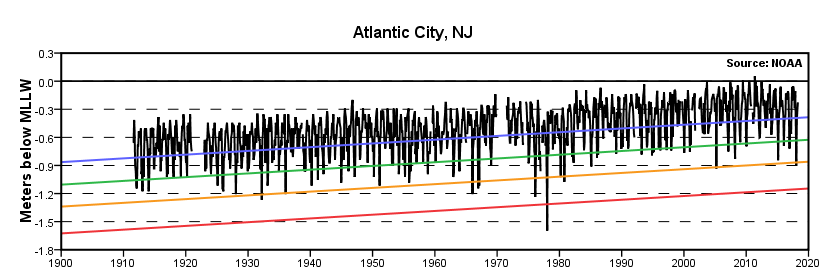
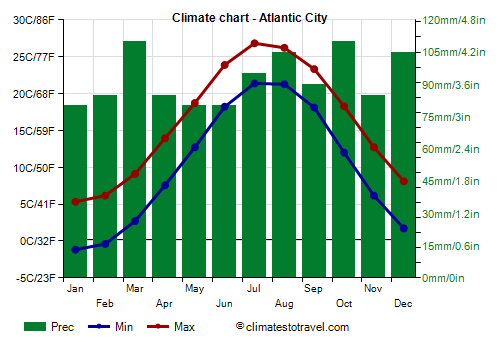
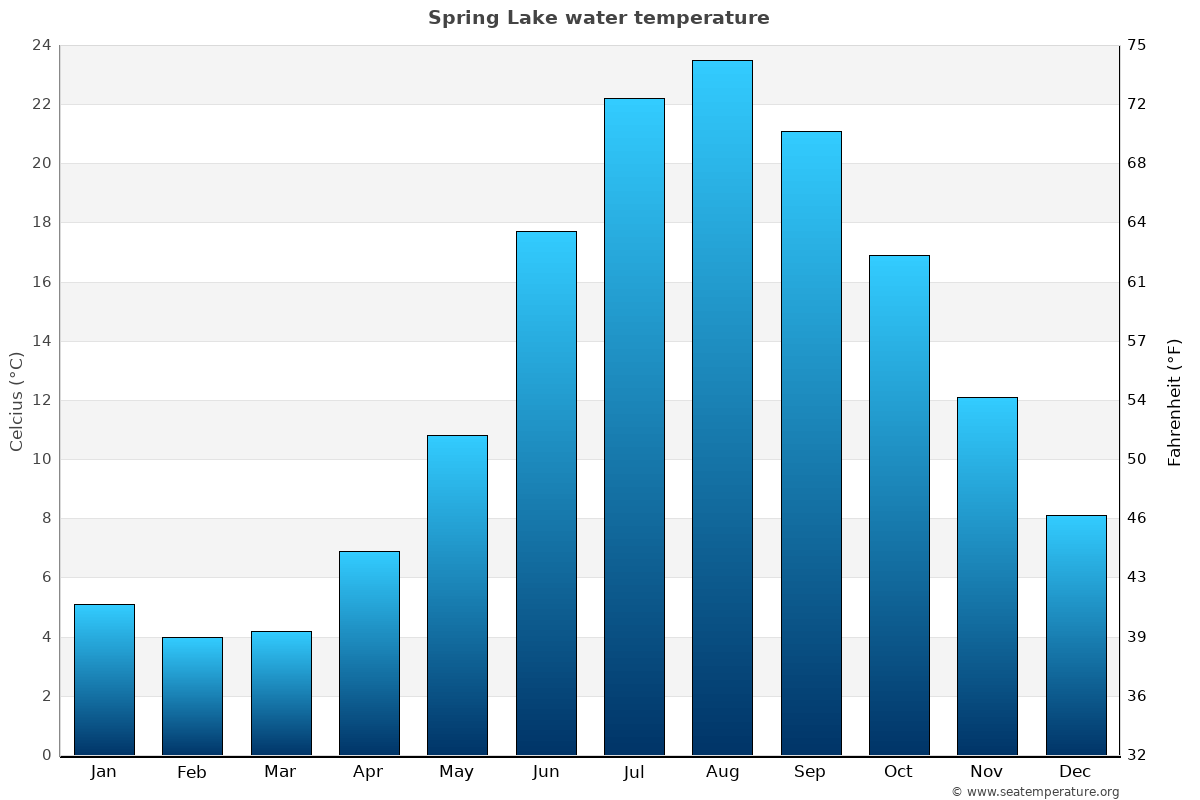
According to data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the average sea surface temperature (SST) off the coast of Atlantic City has shown both increases and decreases compared to historical averages for this time of year. This data is publicaly availble and accessible by anyone.
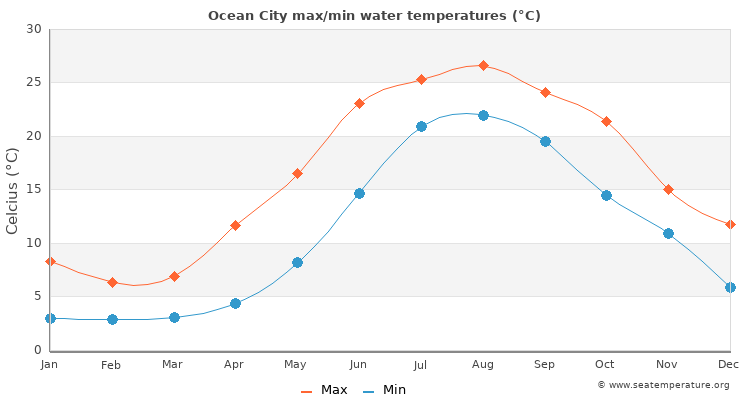
Specifically, readings taken over the past month reveal that the SST has, on average, varied by approximately 2-3 degrees Fahrenheit above and below the long-term mean.
The NOAA buoy located approximately 20 nautical miles offshore is a primary source of this data. This buoy continuously transmits real-time oceanographic information, including water temperature at various depths.
Factors Influencing the Temperature Changes
Several factors contribute to these observed temperature fluctuations. These factors range from natural weather patterns to potential long-term climate trends.
Ocean currents play a significant role, bringing in warmer or cooler water masses from other regions. Changes in wind patterns and atmospheric pressure systems can also influence surface water mixing and temperature distribution.
Scientists are also examining the potential influence of climate change on these temperature shifts. Long-term warming trends could be exacerbating natural variability, leading to more extreme temperature fluctuations.
Potential Impact on Marine Life
The fluctuating water temperatures can have a significant impact on the local marine ecosystem. This impact is direct and will affect the future of the ecosystem.
Many marine species are highly sensitive to temperature changes, and even small variations can disrupt their behavior, distribution, and reproductive cycles.
For example, changes in water temperature could affect the migration patterns of certain fish species. It can also impact the growth and survival of shellfish populations.
“These temperature swings can stress marine organisms, making them more susceptible to disease and less able to cope with other environmental stressors,” explains Dr. Emily Carter, a marine biologist at the Rutgers University Marine Field Station in Tuckerton, NJ. She specializes in estuarine and coastal ecology.
Economic Implications for Atlantic City
The tourism and fishing industries in Atlantic City are closely tied to the health of the marine environment. Changes in water temperature could have direct economic consequences for these sectors.
Warmer water, for instance, could attract different species of fish, potentially altering the composition of catches for local fishermen. These changes would directly affect fishermen and their livelihood.
Changes could also impact recreational activities such as swimming and surfing. Algal blooms, which are sometimes exacerbated by warmer water temperatures, can lead to beach closures and reduced tourism.
"We're keeping a close eye on these temperature changes and their potential impact on our fishing operations," says John Smith, a local fisherman who has been working the waters off Atlantic City for over 30 years. "A stable environment is crucial for our livelihoods."
Monitoring and Mitigation Efforts
Various organizations and agencies are actively monitoring water temperatures and assessing their potential impacts.
NOAA continues to provide real-time data and conduct research to better understand the dynamics of the Atlantic Ocean. State and local environmental agencies are also involved in monitoring water quality and implementing measures to protect marine resources.
Efforts to mitigate the impacts of climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, are also critical in addressing the underlying causes of long-term warming trends.
Ongoing research is being conducted to explore potential adaptation strategies. The strategies are intended to help marine ecosystems and coastal communities cope with the changing ocean environment.
These efforts range from developing more resilient aquaculture practices to implementing coastal management strategies that protect against rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Conclusion
The recent fluctuations in water temperatures off the coast of Atlantic City highlight the complex and interconnected nature of marine ecosystems. These fluctuations also highlight the importance of ongoing monitoring and research.
The potential impacts on marine life, the local economy, and the overall health of the ocean underscore the need for proactive measures. These measures are neede to mitigate climate change and protect coastal resources.
By continuing to monitor these trends and working collaboratively, scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders can strive to ensure the long-term sustainability of the Atlantic City region’s marine environment.