Weight Loss With Apple Cider Vinegar Recipe

A surge in interest surrounds apple cider vinegar (ACV) as a potential weight loss aid. Health experts are urging caution, emphasizing the need for more rigorous scientific research before widespread adoption.
This article dissects the claims, examines existing evidence, and outlines safe practices for those considering ACV as part of a weight management strategy. It prioritizes evidence-based information and highlights the importance of consulting healthcare professionals.
What's Driving the ACV Weight Loss Trend?
The purported benefits of apple cider vinegar for weight loss have gained traction through social media and anecdotal reports. Many individuals are sharing their experiences, claiming reduced appetite and increased fat burning.
These claims often center around the acetic acid content in ACV. Some studies suggest acetic acid may influence metabolism and appetite control.
The Science Behind ACV and Weight Loss: What the Research Says
While some studies show promise, the evidence supporting ACV for weight loss is limited and often conducted on small sample sizes.
A study published in the Journal of Functional Foods found that participants who consumed ACV daily experienced modest weight loss compared to a control group. However, the study cautioned against generalizing these findings.
Another study highlighted ACV's potential to improve blood sugar control, which could indirectly contribute to weight management in some individuals. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using ACV, especially if you have diabetes.
The "Recipe" and Recommended Dosage: Proceed with Caution
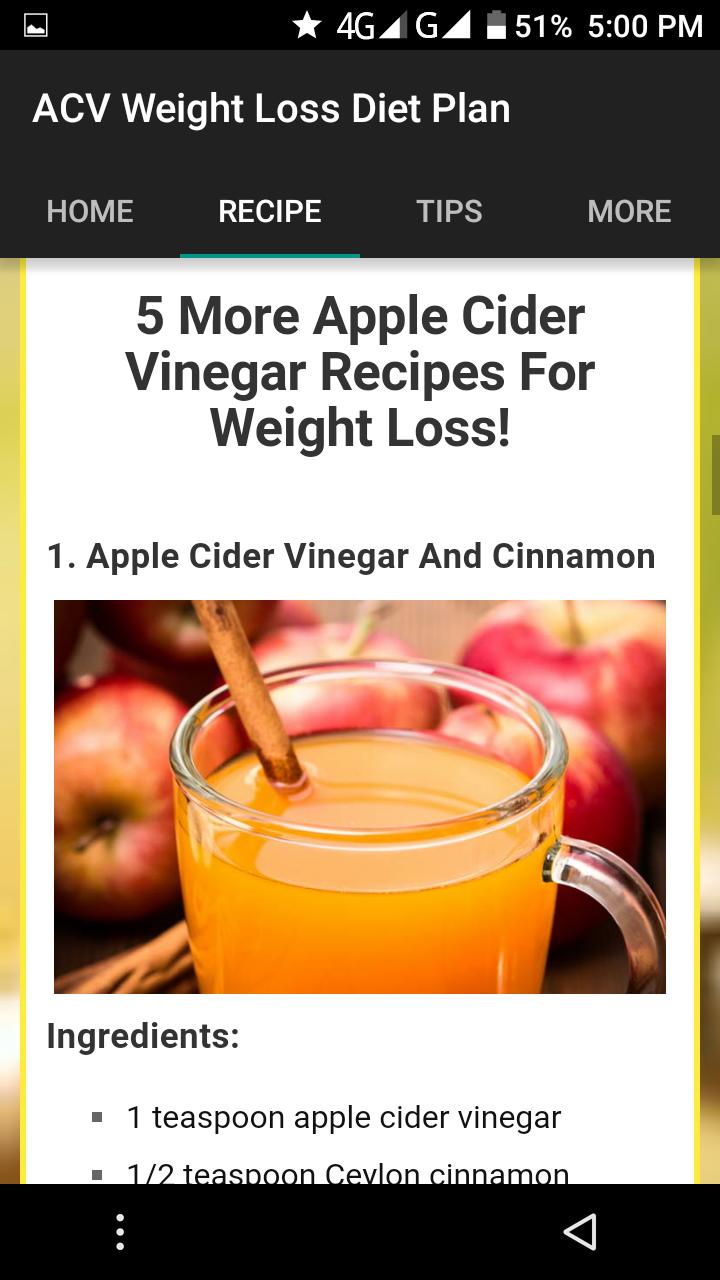
The commonly cited "ACV weight loss recipe" typically involves diluting 1-2 tablespoons of ACV in a glass of water. This mixture is often consumed before meals.
Experts warn against undiluted ACV consumption due to its high acidity, which can erode tooth enamel and irritate the esophagus. Always dilute ACV before consumption.
The maximum recommended daily intake is generally considered to be 1-2 tablespoons, diluted in water, spread throughout the day. Exceeding this dosage may increase the risk of adverse effects.
Potential Side Effects and Risks: Awareness is Key
Consuming ACV, especially in large quantities, can lead to several side effects. These include nausea, indigestion, and throat irritation.
ACV can also interact with certain medications, such as diuretics and diabetes medications. Consult your doctor before using ACV if you are taking any medications.
Long-term use of ACV may lower potassium levels in some individuals. Monitoring potassium levels is crucial, particularly for those with pre-existing health conditions.
Who Should Avoid ACV? Critical Considerations
Individuals with certain medical conditions should avoid ACV. This includes those with gastrointestinal issues like ulcers or acid reflux.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using ACV. There is limited research on the safety of ACV during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
People with kidney problems should also exercise caution, as ACV's acidity could potentially exacerbate their condition. It is important to discuss use with your healthcare provider first.
Debunking the Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Many claims surrounding ACV are not supported by scientific evidence. For instance, the idea that ACV can "melt fat" is a gross oversimplification.
While ACV might play a small role in appetite control or blood sugar regulation, it is not a magic bullet for weight loss. A balanced diet and regular exercise are essential for sustainable weight management.
Don't rely solely on ACV for weight loss. Incorporate it as a possible adjunct to a comprehensive healthy lifestyle, only after consulting a healthcare professional.
Integrating ACV Safely: Best Practices
If you choose to incorporate ACV into your routine, do so cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Always dilute ACV with water before consumption. Monitor your body's response and discontinue use if you experience any adverse effects.
Remember, ACV is not a replacement for a healthy diet and regular exercise. Prioritize a balanced approach to weight management for long-term success. Dr. Emily Carter, a registered dietitian, advises against relying solely on ACV for weight loss.
The Bottom Line: A Balanced Perspective
Apple cider vinegar may offer some potential benefits for weight management, but it is not a guaranteed solution. The current research is limited, and more rigorous studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Focus on evidence-based strategies like diet and exercise, and consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen.
Ongoing research will continue to explore the potential role of ACV in weight management. Stay informed and prioritize your health by seeking professional guidance. The National Institutes of Health is currently funding several studies examining ACV's effects.







+1.png)








