What Are The Four Conditions Of A Purely Competitive Market

Market stability hangs in the balance as economists dissect the core principles of pure competition. Understanding these conditions is crucial for navigating the current volatile economic landscape.
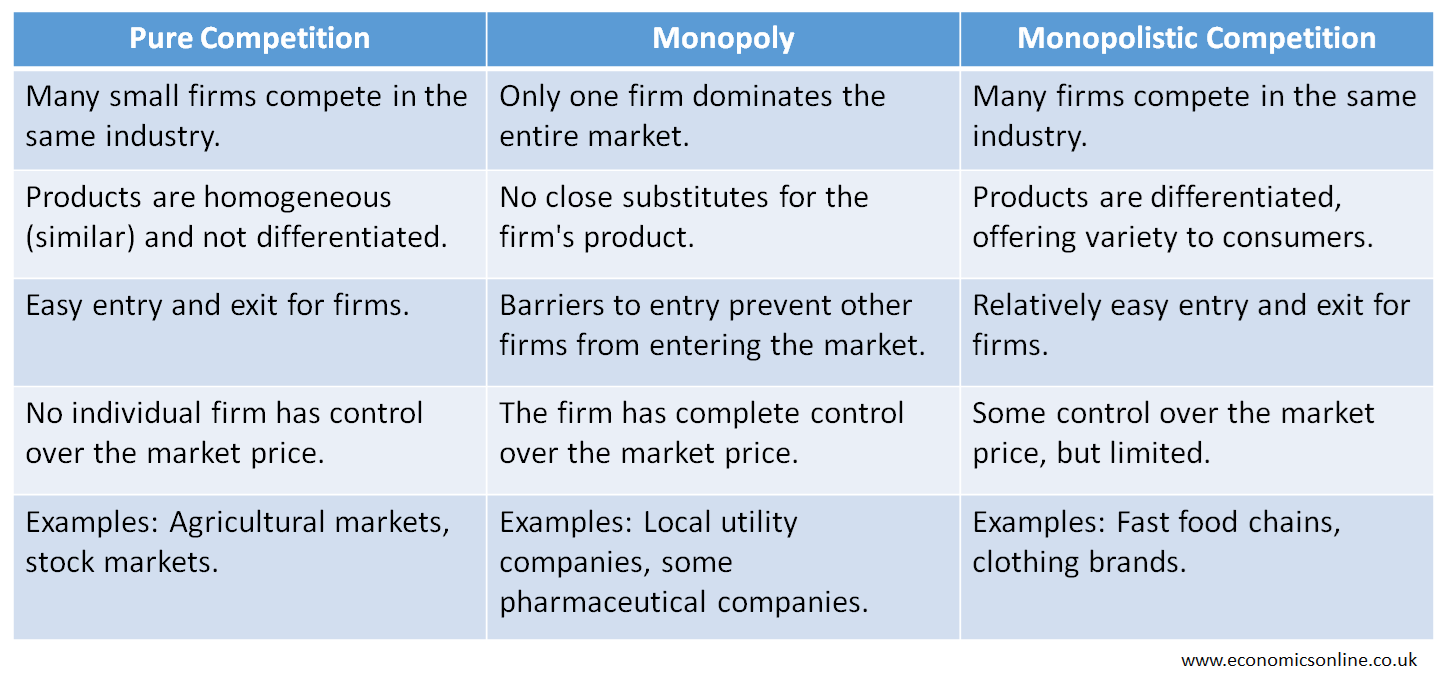
At its heart, pure competition, also known as perfect competition, represents an idealized market structure. It rarely exists in its purest form, but serves as a benchmark for evaluating real-world markets. This article will break down the four essential conditions, highlighting their importance and implications.
Homogeneous Products: The Foundation of Price Sensitivity
One crucial condition is homogeneous products. This means that the goods or services offered by all sellers are essentially identical.
Consumers perceive no difference between products from different suppliers. Therefore, price becomes the sole determining factor in their purchasing decisions.
For instance, agricultural commodities like wheat or raw milk often approximate this condition. Buyers select based on price alone.
Large Number of Buyers and Sellers: Diluting Market Power
A second key condition involves a large number of both buyers and sellers. No single participant can significantly influence the market price.
Each firm is a price taker, accepting the prevailing market price. This absence of market power prevents monopolies or oligopolies from forming.
According to Investopedia, in perfectly competitive markets, firms are too small relative to the overall market to individually impact prices.
Free Entry and Exit: Ensuring Market Responsiveness
Free entry and exit is a vital element for a purely competitive market. Businesses can enter or leave the market without facing significant barriers.
This ease of movement ensures that markets respond quickly to changing economic conditions. It also prevents firms from earning excessive profits in the long run.
High barriers to entry, such as significant startup costs or government regulations, can hinder competition. It ultimately distort market outcomes.
Perfect Information: Leveling the Playing Field
The condition of perfect information demands that all buyers and sellers have complete access to relevant market information. This include prices, product quality, and production techniques.
This transparency ensures that everyone makes informed decisions. It promotes efficient resource allocation.
Imperfect information can lead to market failures, as consumers and producers may make suboptimal choices due to lack of knowledge.
Real-World Implications and Deviations
While pure competition rarely exists perfectly, it serves as a valuable theoretical model. It helps us understand how competitive forces shape market behavior.
Most real-world markets deviate from these conditions to some extent. Products are often differentiated, information is imperfect, and barriers to entry exist.
However, understanding the principles of pure competition provides a framework for analyzing and addressing market imperfections.
The Role of Government Regulation
Government regulations can play a crucial role in promoting competition. This include measures to reduce barriers to entry and ensuring access to information.
Antitrust laws, for example, prevent monopolies and other anti-competitive practices. Regulations aimed at consumer protection can improve information transparency.
However, excessive regulation can also stifle innovation and reduce market efficiency. Striking the right balance is essential.
Economist Milton Friedman argued that government intervention should be limited. He believed that free markets are the most efficient way to allocate resources.
Deregulation, on the other hand, can lead to increased competition and lower prices in some industries.
The Future of Competition
In an increasingly globalized and technologically driven economy, the nature of competition is constantly evolving. New business models are emerging.
These models challenge traditional market structures. Furthermore, regulators are struggling to keep pace with these rapid changes.
Monitoring these developments is critical for maintaining fair and competitive markets.
Ongoing research and analysis will be essential to understand the impact of technological advancements.
Economists are actively studying the effects of artificial intelligence and automation. They also assess how these advancements will affect competition in various industries.
Next Steps: Continued Monitoring and Analysis
Ongoing monitoring of market structures and competitive dynamics is crucial. This includes assessing the impact of new technologies and regulations.
Policymakers and businesses must adapt to the evolving landscape to ensure fair competition. This leads to ultimately benefit consumers and promote economic growth.
Further research is needed to understand the long-term implications of these changes and to develop effective strategies for promoting competition in the 21st century.



![What Are The Four Conditions Of A Purely Competitive Market [ 4.1 ] Pure Competition. - ppt download](https://slideplayer.com/slide/12775285/77/images/7/Price%2C+Output%2C+and+Purely+Competitive+Markets.jpg)




+PURE+COMPETITION.jpg)