What Are The Two Key Ingredients To Natural Selection
Imagine a vibrant meadow, teeming with wildflowers in every imaginable hue. Bees buzz lazily from blossom to blossom, butterflies flutter in the sun, and a chorus of crickets chirps in the tall grass. Look closer, though, and you’ll see a subtler drama unfolding, a constant struggle for survival playing out among the plants and creatures that call this place home. It's a story of adaptation, of resilience, and of the relentless engine of evolution itself: natural selection.
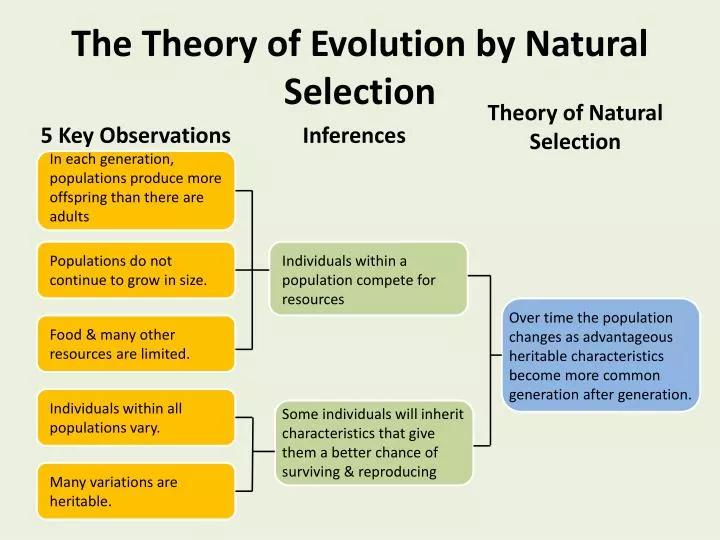
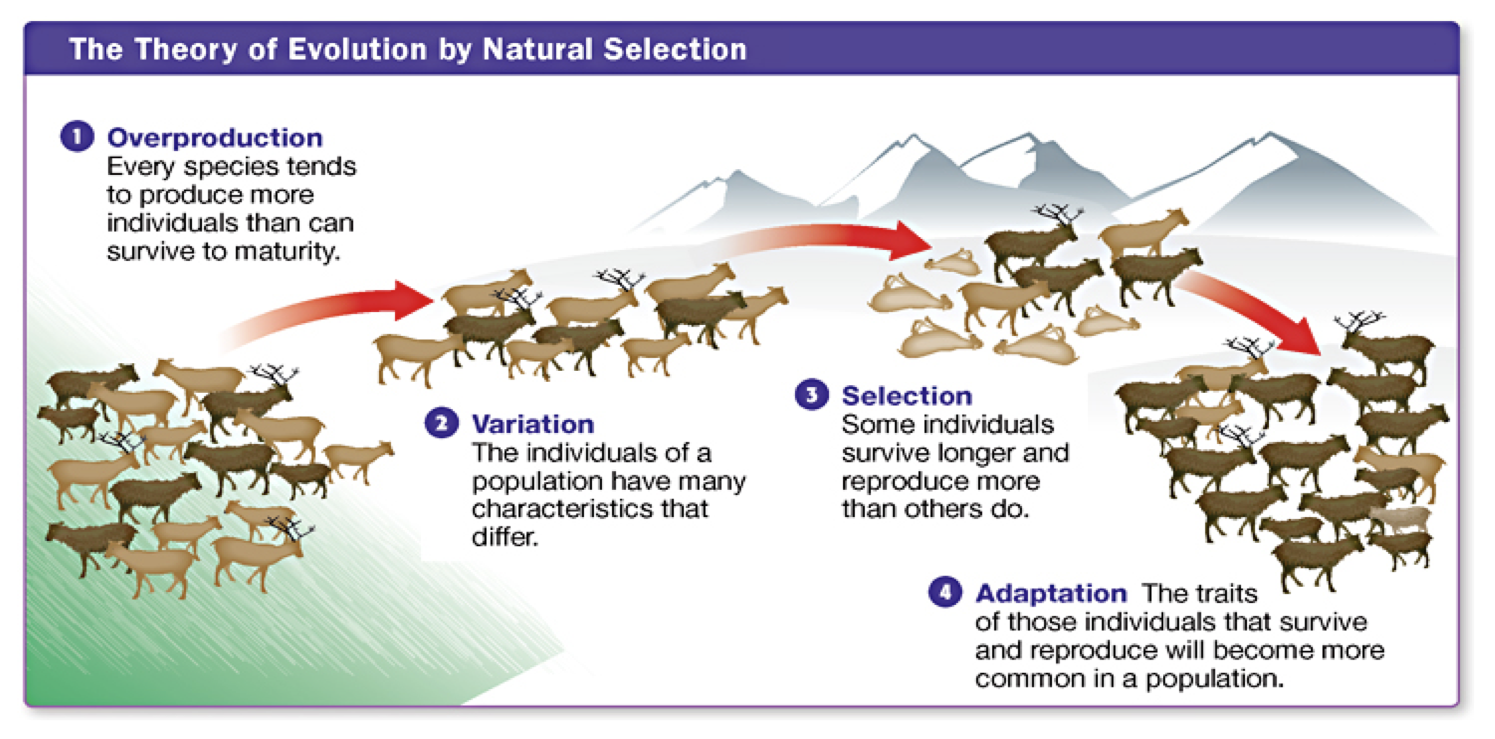
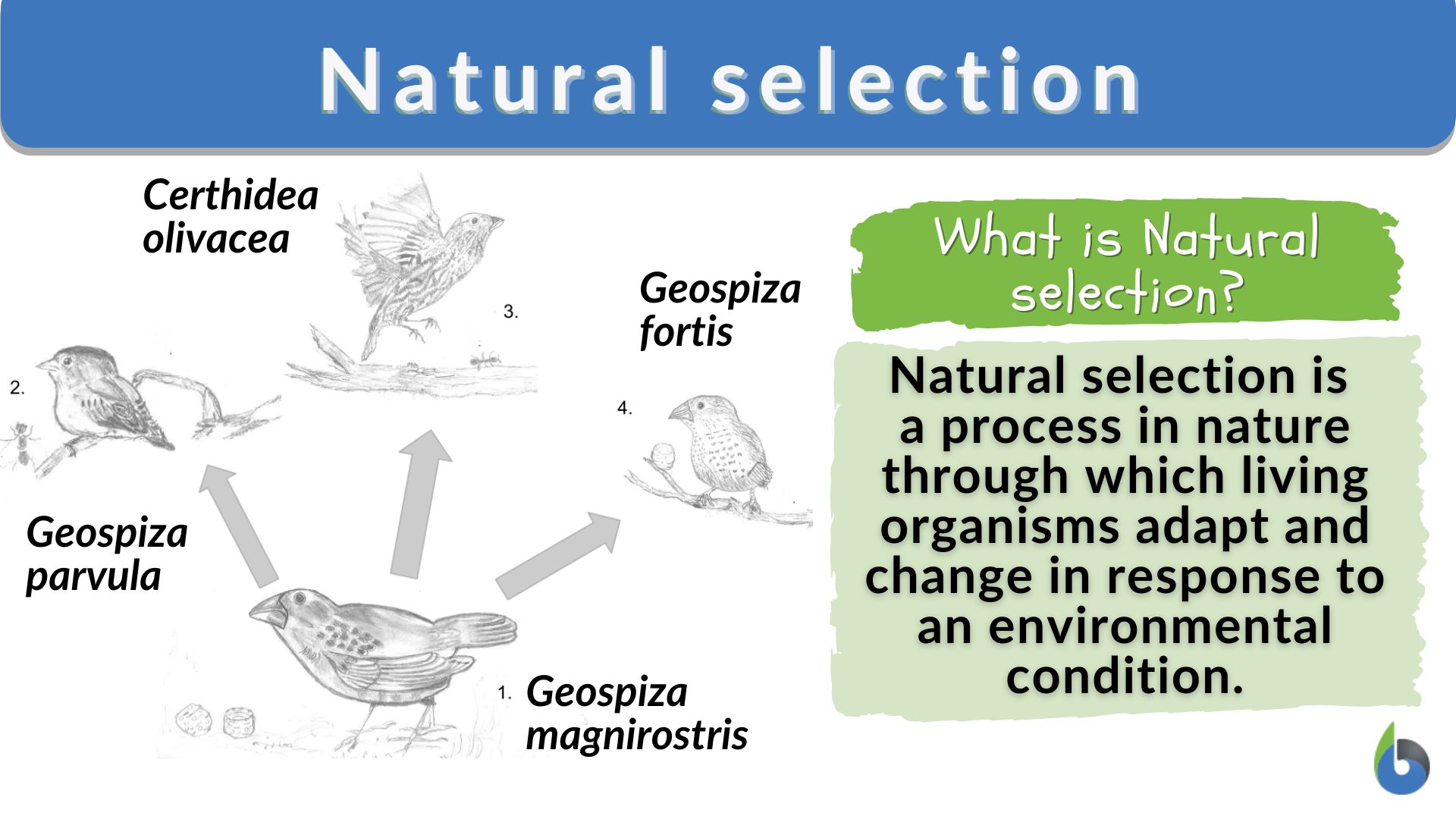
At its heart, natural selection, the driving force behind evolution, relies on two key ingredients: variation and differential reproduction. Without these, the process simply grinds to a halt. Understanding these two concepts is crucial to grasping how life on Earth has diversified into the astonishing array of forms we see today.
The Foundation: Variation
Think of a litter of puppies. While they share the same parents, each one possesses a unique combination of traits: some might be larger, some smaller; some might have darker fur, others lighter; some might be more playful, others more reserved.
This inherent variation is the raw material upon which natural selection acts. Without it, there would be no differences to select from, and evolution would be impossible.
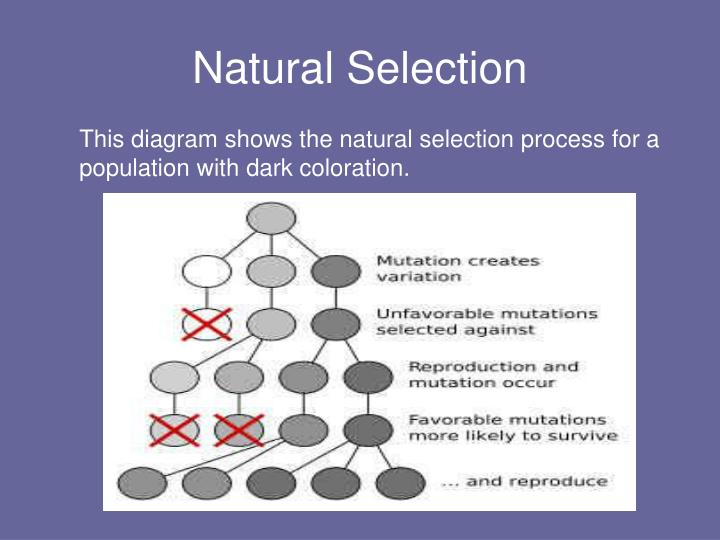
Variation arises primarily through two mechanisms: mutation and sexual reproduction. Mutation introduces new genetic material into a population, altering the DNA sequences that code for various traits. Sexual reproduction, on the other hand, shuffles existing genes during the creation of sperm and egg, resulting in offspring with novel combinations of characteristics.
According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, "A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence...Mutations can result from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or infection by viruses." This constant, albeit often subtle, alteration of the genetic code provides the fuel for evolutionary change.
This variation isn't always immediately visible or beneficial. Many mutations are neutral, having no discernible effect on an organism. Some can even be harmful, decreasing its chances of survival and reproduction. However, occasionally, a mutation arises that confers an advantage, increasing an organism's fitness in its particular environment.
The Selector: Differential Reproduction
The second key ingredient is differential reproduction, also known as "survival of the fittest". This doesn't necessarily mean the strongest or fastest individuals survive, but rather those best suited to their environment.
Organisms with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success are more likely to pass those traits on to their offspring. Those with less advantageous traits are less likely to reproduce, and their genes become less common in the population over time.
Consider a population of moths living in a forest. Originally, most of the moths are light-colored, blending in well with the lichen-covered trees. However, due to industrial pollution, the trees become darker, coated in soot. Suddenly, the light-colored moths are easily spotted by predators, while darker moths, perhaps arising from a rare mutation, are better camouflaged.
As the environment changes, the selective pressures favor the darker moths. They survive and reproduce more successfully, passing on their genes for dark coloration. Over time, the population shifts towards a higher proportion of dark moths, demonstrating natural selection in action.
The process of differential reproduction isn't always about direct competition. Factors like access to resources, resistance to disease, and even mate selection can all influence an organism's reproductive success. Organisms that can acquire food more efficiently, avoid predators more effectively, or attract more mates are more likely to leave behind a larger number of offspring.
The Interplay of Variation and Differential Reproduction
It's crucial to understand that variation and differential reproduction are inextricably linked. Without variation, there would be no differences for natural selection to act upon. Without differential reproduction, advantageous traits would not spread through the population, and evolution would stagnate.
These two forces work together in a continuous feedback loop, driving the adaptation of organisms to their environments over countless generations. Variation introduces new possibilities, and differential reproduction sifts through those possibilities, favoring the traits that enhance survival and reproduction.
The University of California, Berkeley's Understanding Evolution website explains it succinctly: "Evolution by natural selection is not random, because the survival and reproductive success of an individual is directly related to the attributes its possesses." This non-random process, guided by environmental pressures, leads to the remarkable diversity and complexity of life we see around us.
The Broader Significance
Understanding the principles of natural selection is not just an academic exercise. It has profound implications for a wide range of fields, from medicine and agriculture to conservation biology and climate change.
In medicine, for example, the principles of natural selection are crucial for understanding the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. As we overuse antibiotics, we create selective pressures that favor bacteria with resistance genes. These resistant bacteria survive and reproduce, leading to the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections.
In agriculture, natural selection can be harnessed to develop crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, or that are better adapted to changing climate conditions. By carefully selecting and breeding plants with desirable traits, we can accelerate the process of evolution to meet our needs.
Conservation biology relies heavily on understanding how natural selection shapes the adaptations of species to their environments. As habitats are destroyed and ecosystems are disrupted, species face new selective pressures. By understanding these pressures, we can develop strategies to help species adapt and survive in the face of environmental change.
The ongoing climate crisis underscores the importance of understanding natural selection. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, species are forced to adapt, migrate, or face extinction. The ability of species to adapt to these rapid changes will depend on the amount of variation present in their populations and the strength of the selective pressures they face.
Looking ahead, a deeper understanding of natural selection will be crucial for addressing some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity. By applying the principles of evolution to fields like medicine, agriculture, and conservation, we can develop more sustainable and resilient solutions to the problems of the 21st century.
A Continuing Story
The story of natural selection is not a static one; it is a continuous and ongoing process, shaping the evolution of life on Earth every moment of every day. From the smallest bacterium to the largest whale, every organism is subject to the forces of variation and differential reproduction.
As we learn more about the intricacies of genetics and the complexities of ecosystems, our understanding of natural selection will continue to evolve. By embracing this knowledge, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of life and our role in shaping its future.
So, the next time you find yourself in a vibrant meadow, or observing the diversity of life around you, remember the two key ingredients that have shaped it all: variation and differential reproduction. They are the driving forces of evolution, the architects of adaptation, and the foundation upon which the amazing tapestry of life is woven.