What Are The Two Phases Of The Business Cycle
Economic storm clouds are gathering. Understanding the two phases of the business cycle is now crucial for businesses and individuals alike.
This article cuts through the jargon to deliver a rapid-fire breakdown of the business cycle’s two primary phases: expansion and contraction. Grasping these dynamics is essential for navigating the turbulent economic waters ahead.
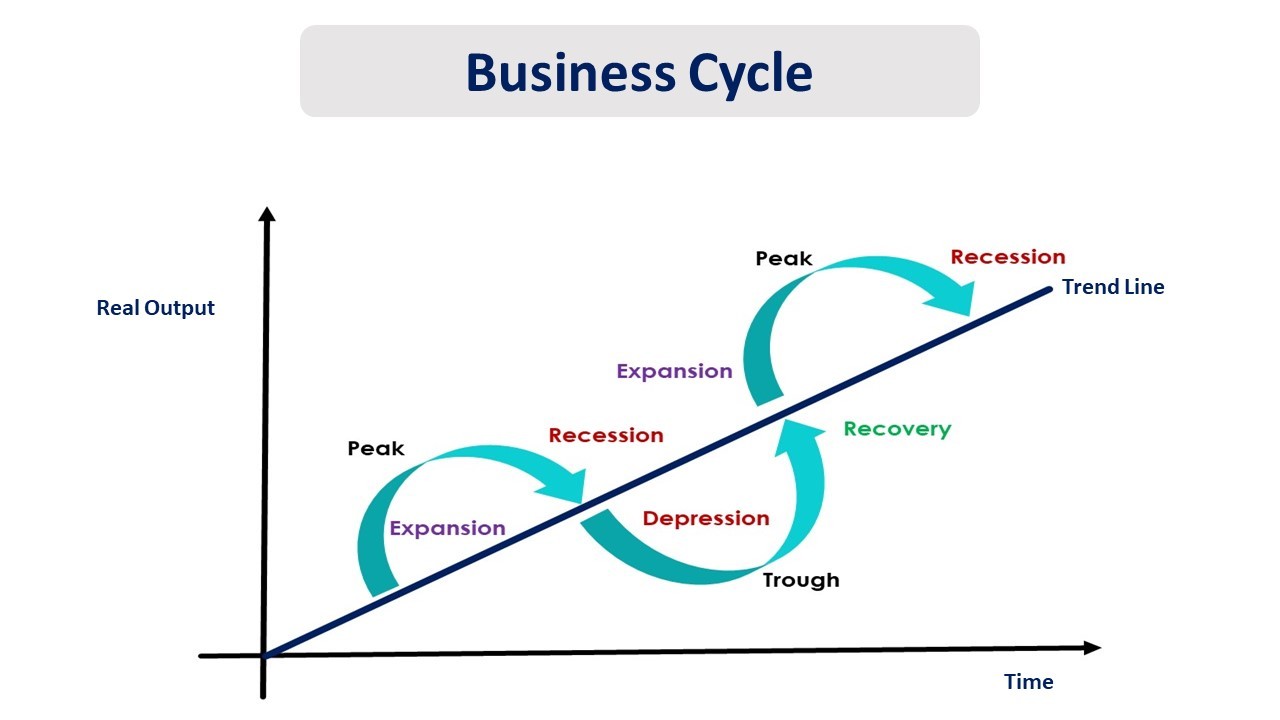
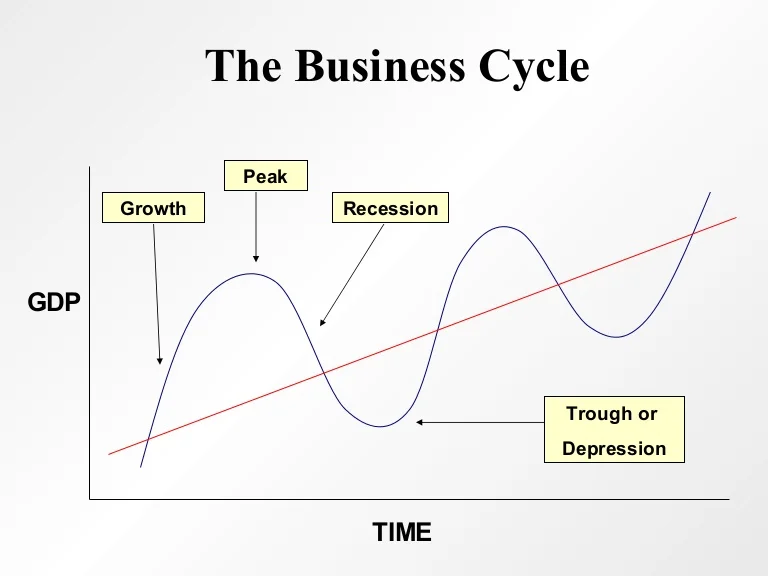
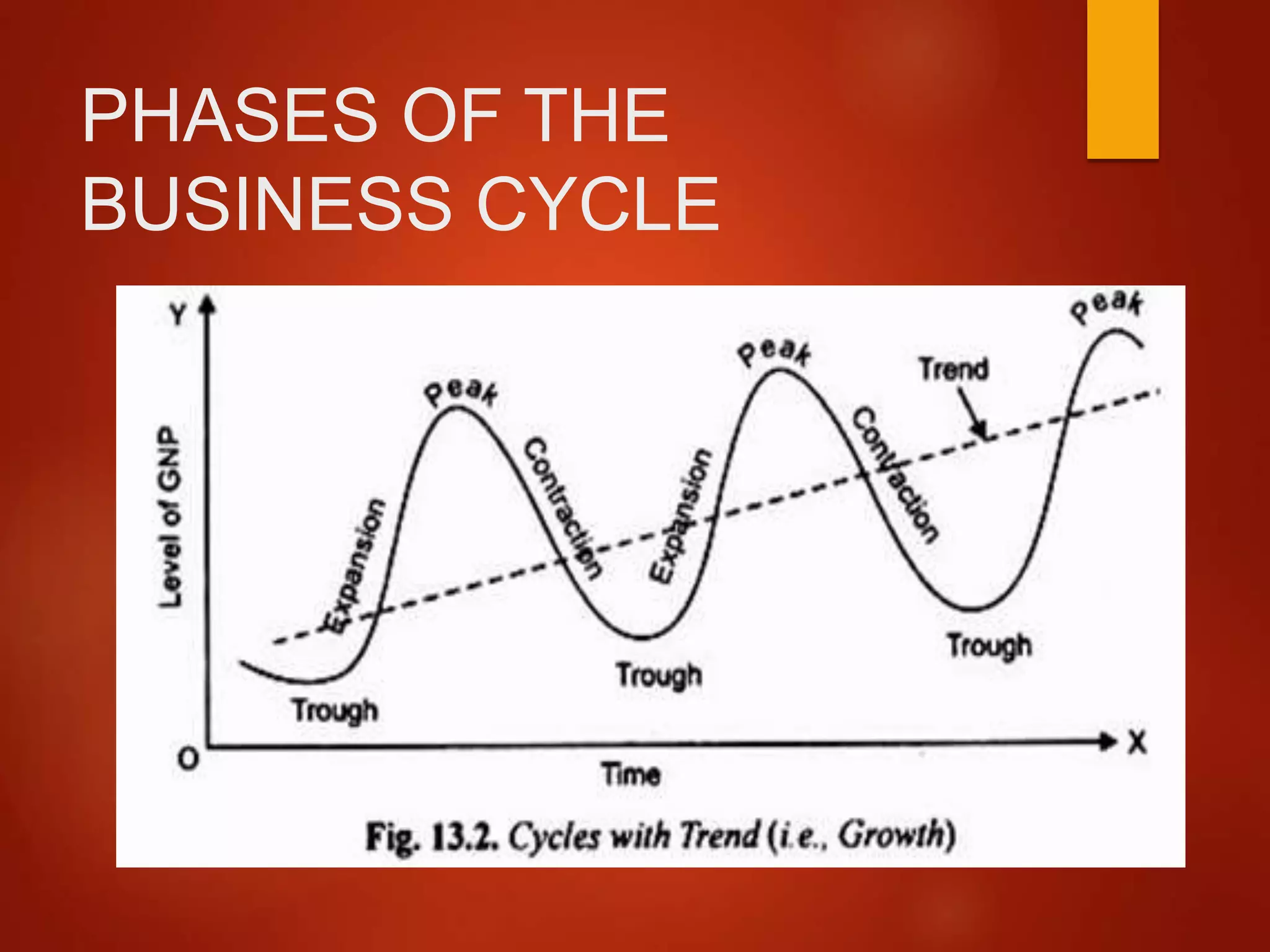
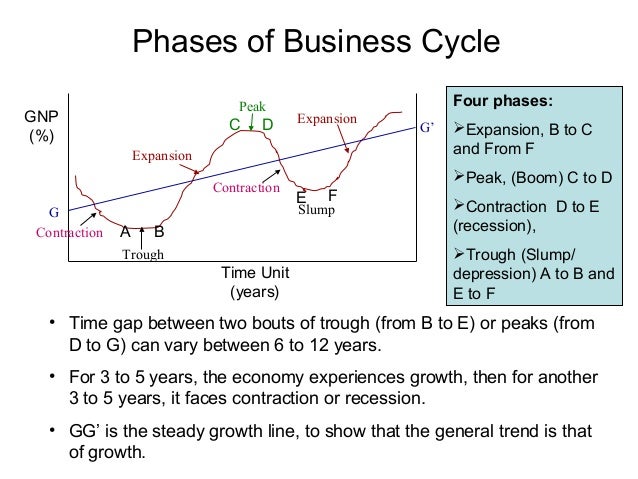
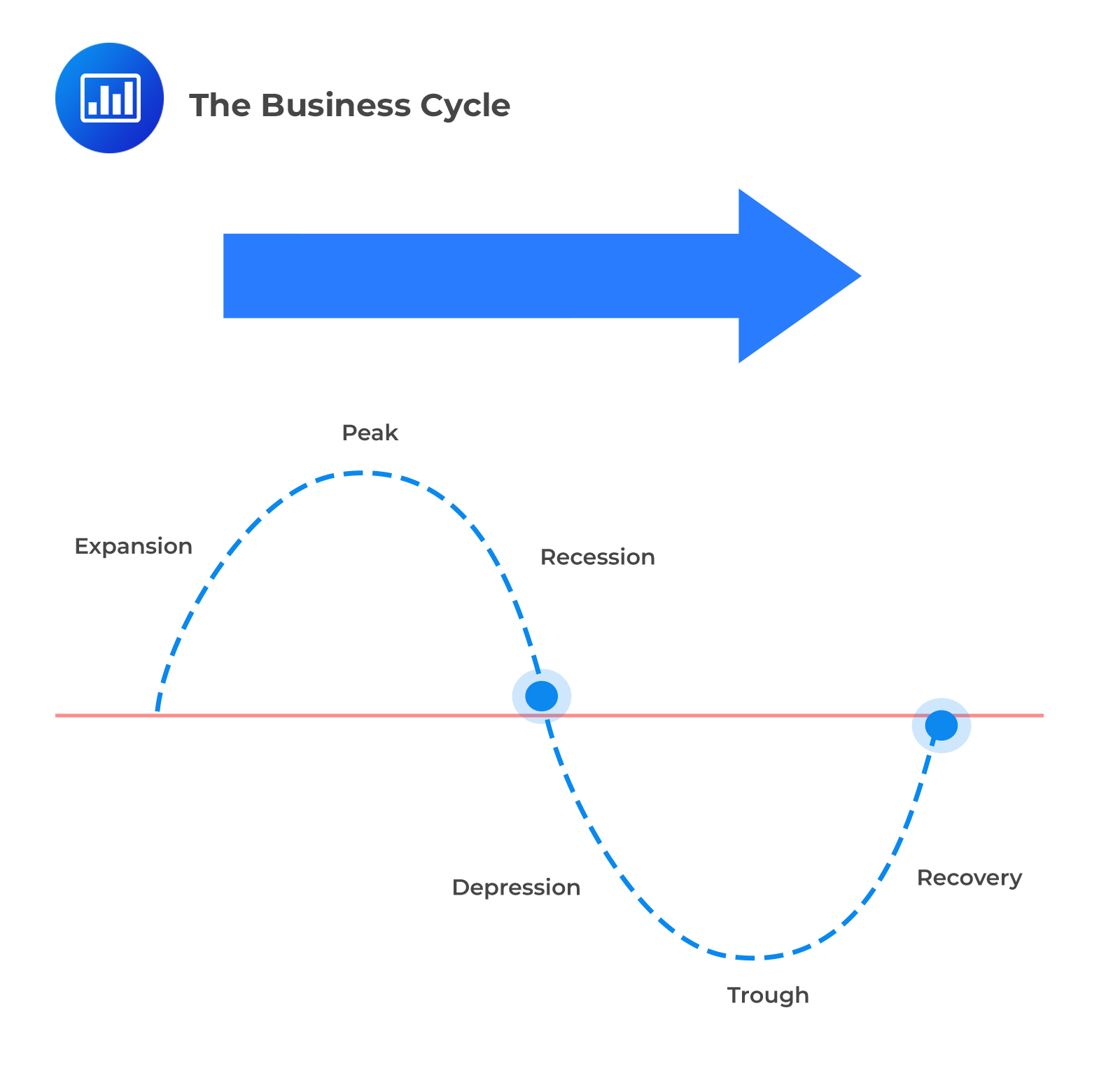
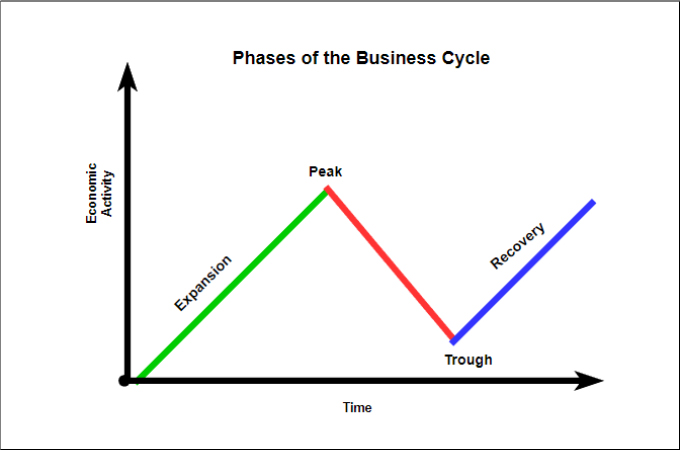
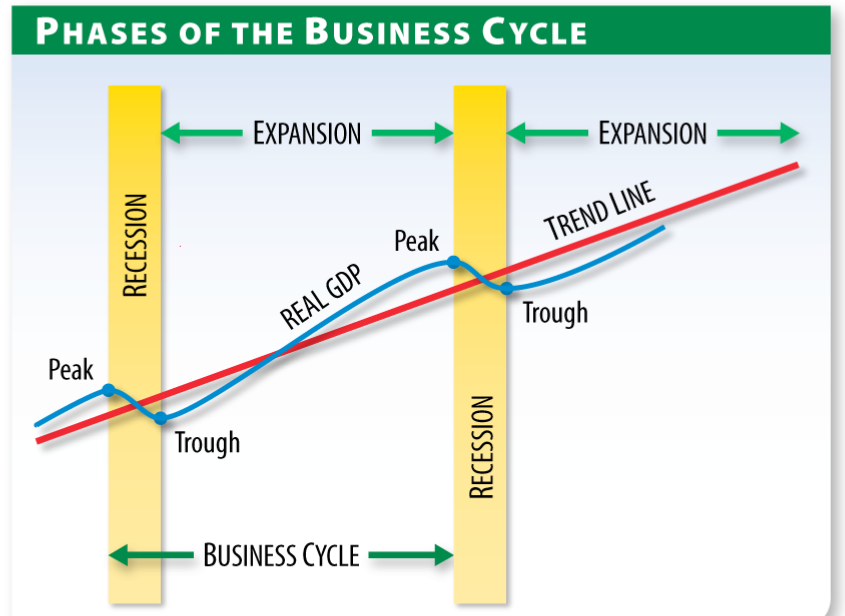
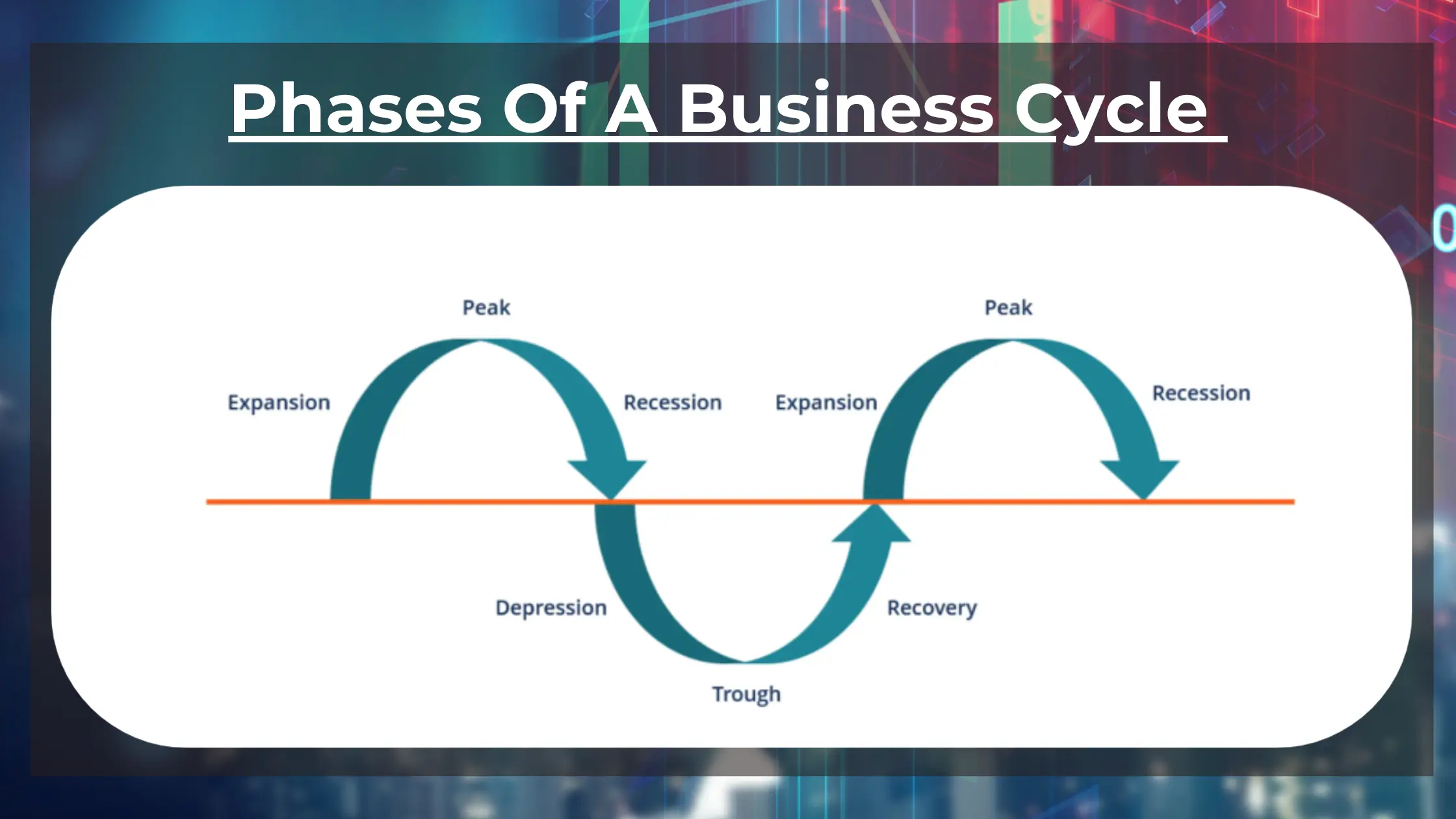
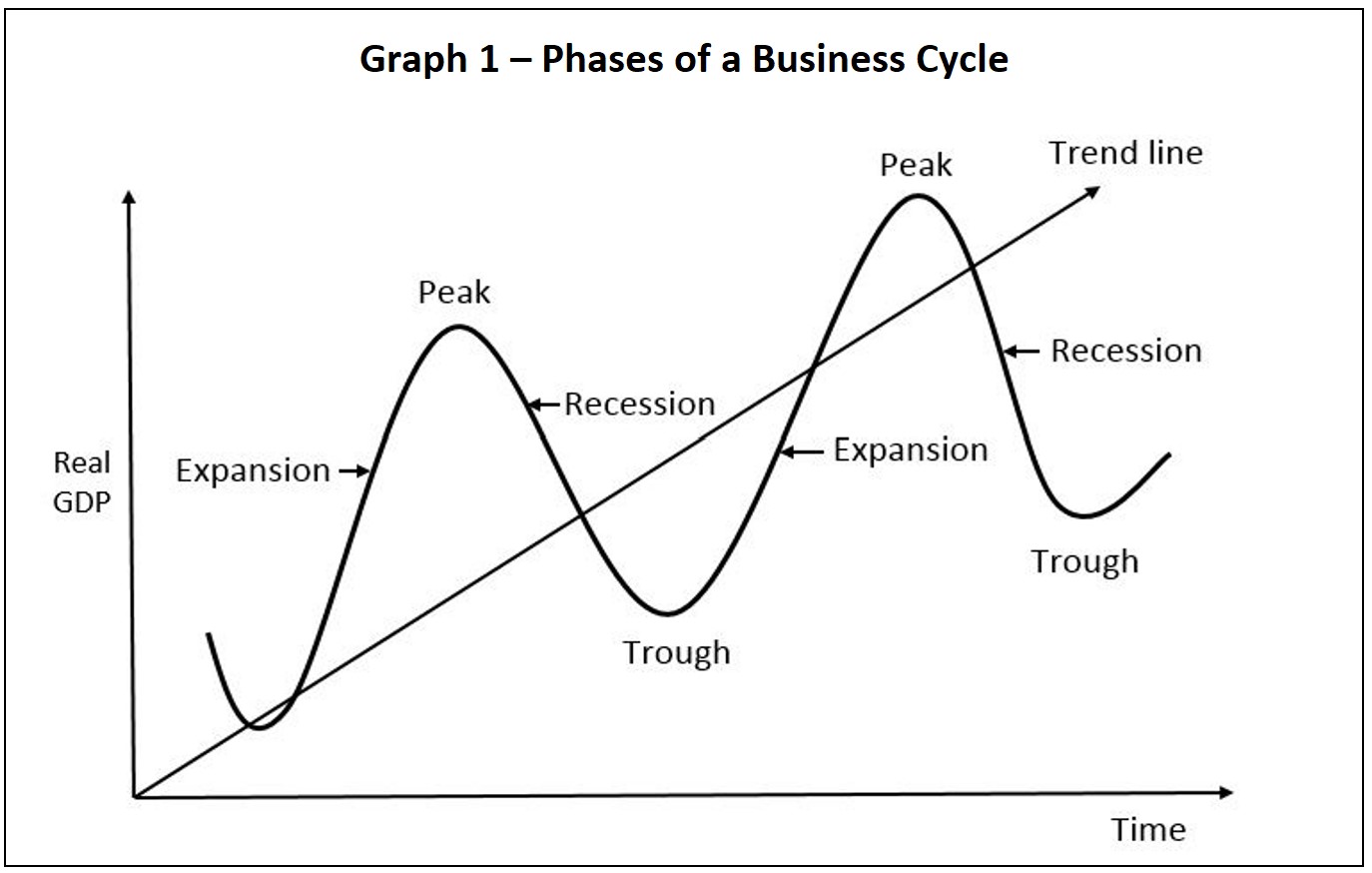
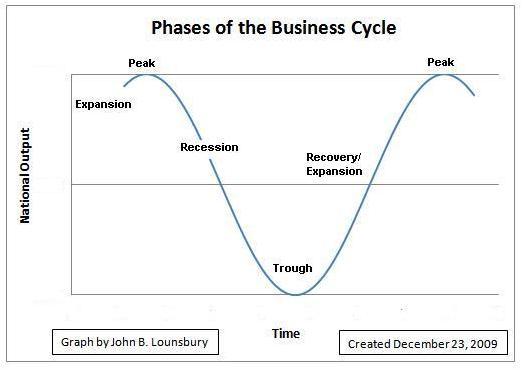
The Two Phases: A Clear Breakdown
Phase 1: Expansion (Boom)
The expansion phase, also known as the boom, is characterized by robust economic growth. This period sees increased employment, consumer spending, and business investment.
During expansion, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) rises steadily. Confidence is high, fueling further economic activity.
Think of the period between 2009 and 2020 in the US. This was a decade-long expansion, fueled by low interest rates and technological innovation, with unemployment rates reaching historic lows around 3.5% in early 2020 (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Phase 2: Contraction (Recession)
The contraction phase, conversely, marks a period of economic decline. This phase is often referred to as a recession.
Decreased spending, rising unemployment, and reduced business activity are hallmarks of contraction. GDP shrinks, signaling economic hardship.
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a sharp contraction in early 2020. Businesses closed, unemployment soared to 14.7% in April 2020 (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics), and GDP plummeted (Bureau of Economic Analysis).
Key Indicators to Watch
Several indicators signal which phase the economy is in. Monitoring these provides crucial insights.
GDP growth or decline is a primary indicator. Consumer spending and business investment trends also offer valuable clues.
Unemployment rates and inflation rates are crucial. Rising unemployment often signals contraction, while unchecked inflation can precede it.
Who is Affected?
The business cycle impacts everyone. Businesses face fluctuating demand, affecting profitability and hiring decisions.
Individuals experience job security during expansion. Conversely, they fear job losses during contraction.
Governments grapple with managing fiscal policy. They navigate to mitigate the effects of both booms and busts.
Where and When?
These phases occur globally. The timing and severity can vary across countries.
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) officially dates US business cycles. The NBER serves as the definitive authority.
The Path Forward
Understanding the two phases is crucial for informed decision-making. Prepare for potential shifts in the economic landscape.
Businesses should develop contingency plans. Individuals should manage their finances prudently.
Staying informed and adaptable is key. Monitor economic indicators and adjust strategies accordingly. Further updates will follow as the economic situation unfolds; consult reputable sources like the Federal Reserve and NBER for the latest data.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phasesofthebusinesscycle-c7cb7a3ce6894e86a3e44d5b0fe4d5e2.jpg)

/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)
