What Are The Two Reasons That Inventory Must Be Estimated

Businesses face critical junctures where knowing the precise value of their inventory becomes impossible. Estimating inventory is therefore a necessity for financial accuracy and operational continuity.
Inventory estimation is crucial primarily when physical counts are impractical or impossible due to events like disasters or when interim financial statements are required without disrupting operations for a full inventory count. It ensures that financial records remain accurate and decision-making isn't hampered by outdated information.
The Imperative of Inventory Estimation
The reasons for estimating inventory boil down to two primary situations: unavoidable physical count disruptions and the need for timely financial reporting.
Reason 1: When Physical Counts Are Impossible
Disasters can render physical inventory counts impossible. Events like fires, floods, or even large-scale theft can destroy or make inaccessible significant portions of a company's stock.
Without the ability to physically verify inventory, estimations become crucial for insurance claims and financial reporting. Estimating losses quickly and accurately is paramount in securing compensation and resuming operations.
The Retail Inventory Method and the Gross Profit Method are commonly used to estimate inventory in these scenarios.
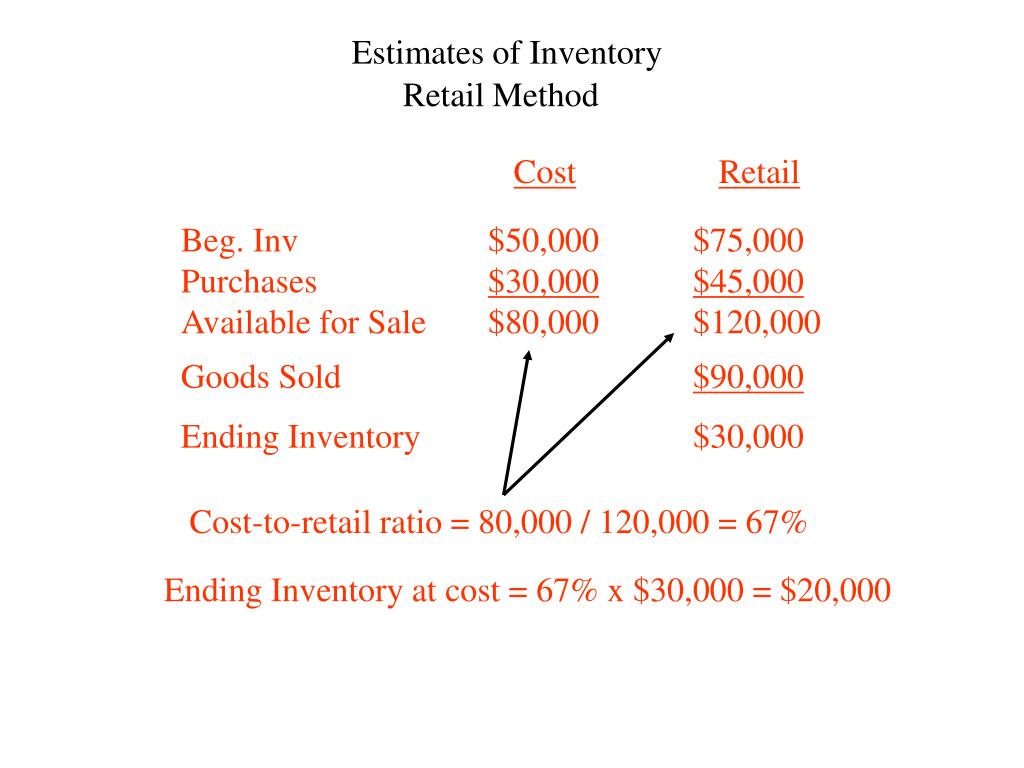
The Retail Inventory Method uses the relationship between the cost and retail price of goods to estimate ending inventory. This method involves tracking both the cost and retail value of purchases, sales, and markups.
The Gross Profit Method leverages historical gross profit margins to estimate the cost of goods sold and, consequently, the value of ending inventory.
For example, a fire at a warehouse owned by Acme Corp destroyed a substantial amount of inventory. Unable to conduct a physical count, Acme Corp's accounting team relied on the Gross Profit Method to estimate the value of the lost inventory for insurance purposes, and financial reporting.
Reason 2: For Interim Financial Reporting
Companies often need to prepare financial statements more frequently than their typical year-end reports. Monthly or quarterly reporting cycles require inventory values, but a full physical count each period would be prohibitively expensive and disruptive.
Estimating inventory offers a practical solution. It allows businesses to generate accurate interim financial statements without halting operations for extensive stocktaking.
The Gross Profit Method is often preferred for interim reporting due to its relative simplicity and ease of application. Companies can maintain ongoing business activities while still adhering to reporting deadlines.
GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) permits the use of estimation methods when physical counts are impractical or impossible, provided the method is consistently applied and adequately disclosed.
For instance, Beta Industries, a manufacturing company, uses the Gross Profit Method to estimate its inventory for quarterly financial reports. This ensures timely dissemination of financial information to investors without disrupting production schedules.
Consequences of Inaccurate Estimates
Inaccurate inventory estimations can have significant financial repercussions. Overstated inventory values inflate profits, potentially leading to tax liabilities and misleading investors.
Conversely, understated inventory can reduce reported profits, impacting investor confidence and potentially leading to missed opportunities. Either scenario can damage a company’s reputation and financial standing.
Regularly reconciling estimated inventory with physical counts and refining estimation methods are crucial for minimizing discrepancies.
Moving Forward
Businesses must develop robust inventory estimation procedures. These procedures should incorporate detailed records of purchases, sales, and historical gross profit margins.
Periodic physical inventory counts are essential to validate the accuracy of estimations and identify any discrepancies. Regular audits can also ensure that estimation methods are consistently and appropriately applied.
The development and consistent application of appropriate estimation techniques are critical for maintaining financial integrity and enabling informed decision-making.












![What Are The Two Reasons That Inventory Must Be Estimated SOLVED: Problem 3-4 Calculating Inventory Turnover [LO 2] A7X](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/5cbfe1d95e2d44e8860a2de639b75b5c.jpg)



