What Does It Cost To Start A Small Business
The dream of owning a small business is a powerful motivator for many, but the path to entrepreneurship is often paved with financial considerations. Understanding the costs associated with launching a venture is crucial for potential business owners to assess feasibility, secure funding, and set realistic expectations.
This article will delve into the multifaceted costs involved in starting a small business, drawing on data from reputable sources such as the Small Business Administration (SBA) and industry reports to provide a comprehensive overview. It aims to equip aspiring entrepreneurs with the knowledge necessary to navigate the financial landscape of launching a successful enterprise.
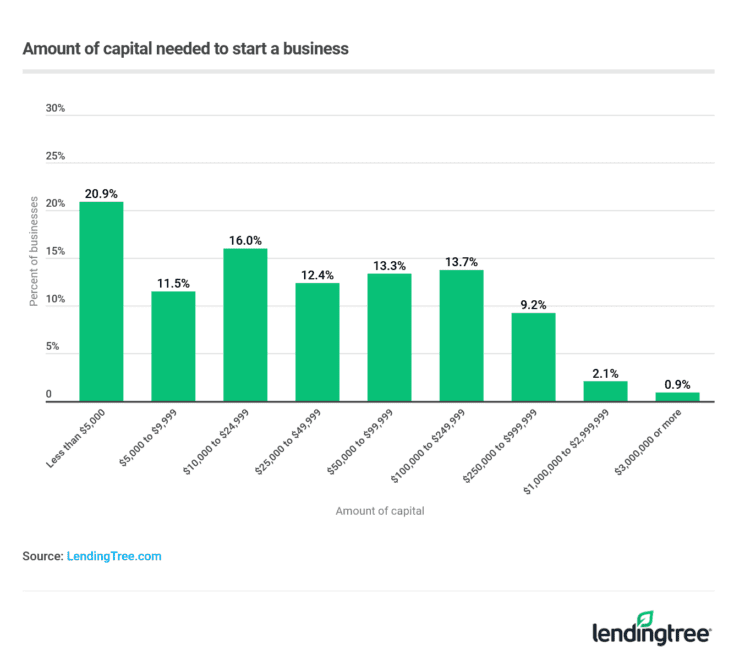
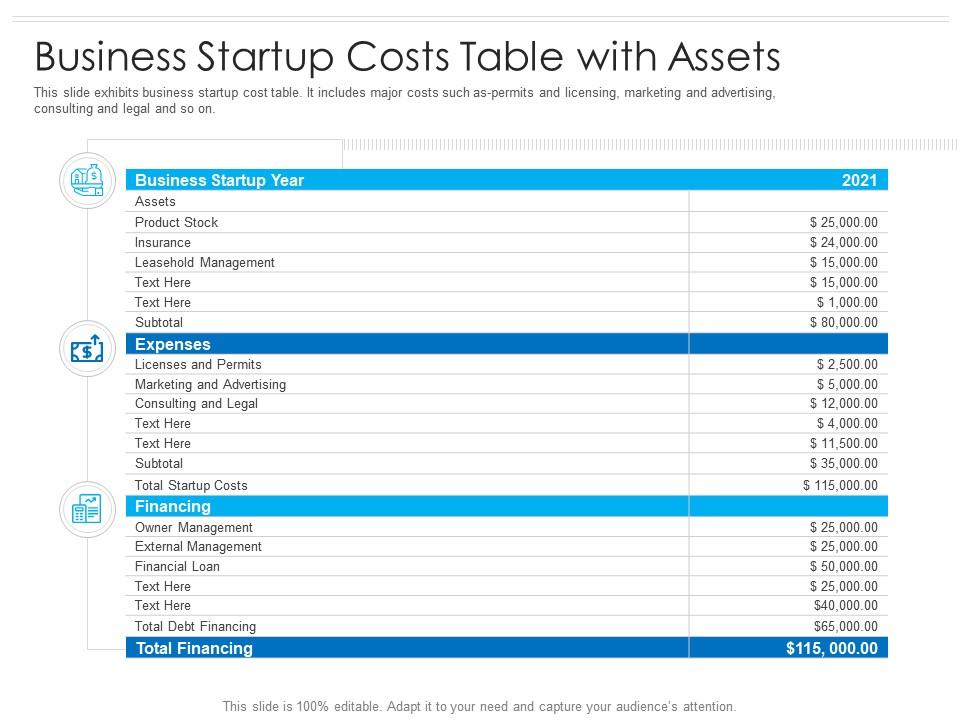
Startup Costs: A Breakdown
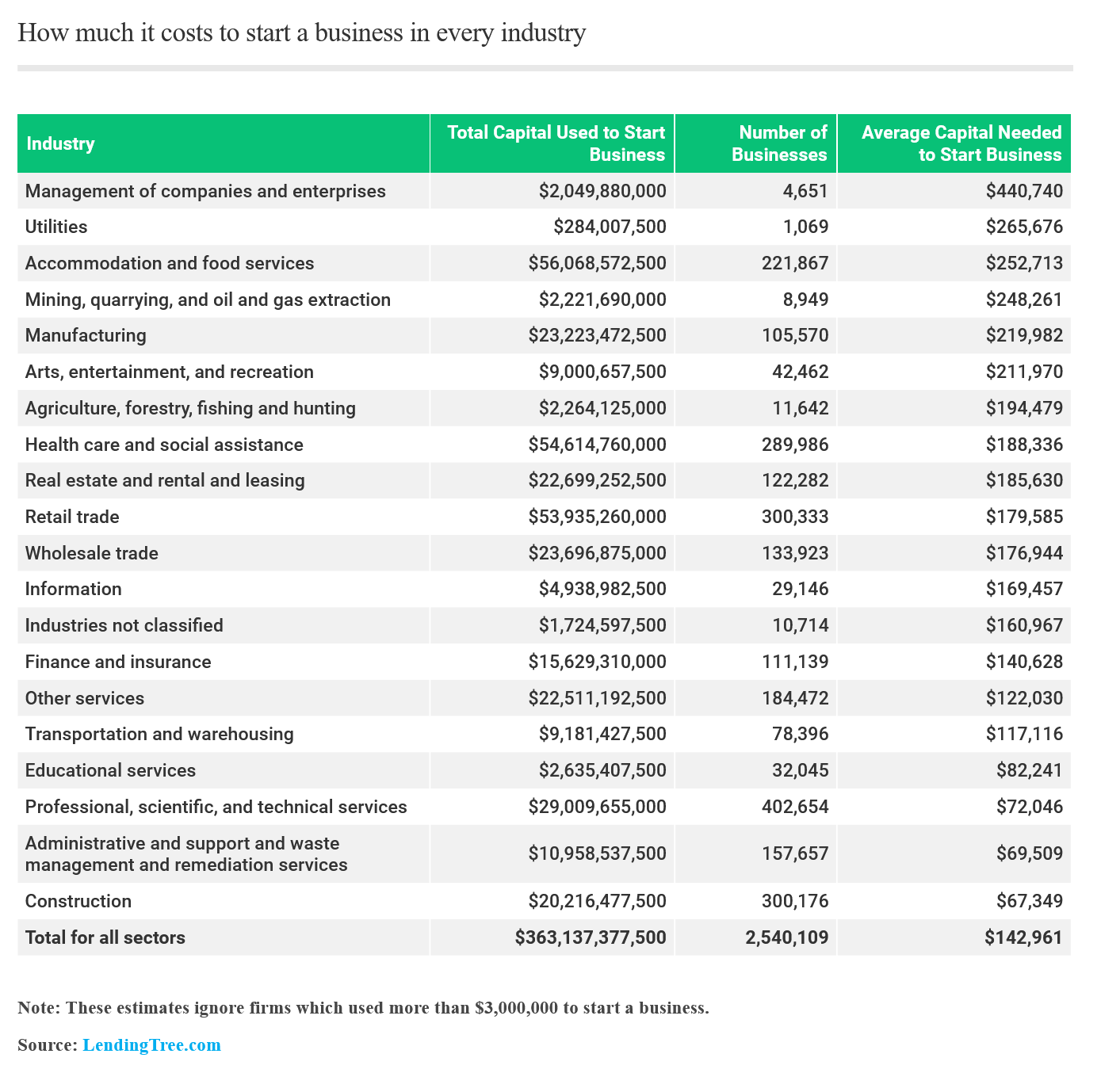
Startup costs can vary significantly depending on the industry, location, and business model. These costs can be broadly categorized into initial investments and operating expenses.
Initial Investments
Business Registration and Licensing: Fees associated with registering the business name, obtaining necessary licenses and permits can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the locality and industry regulations.
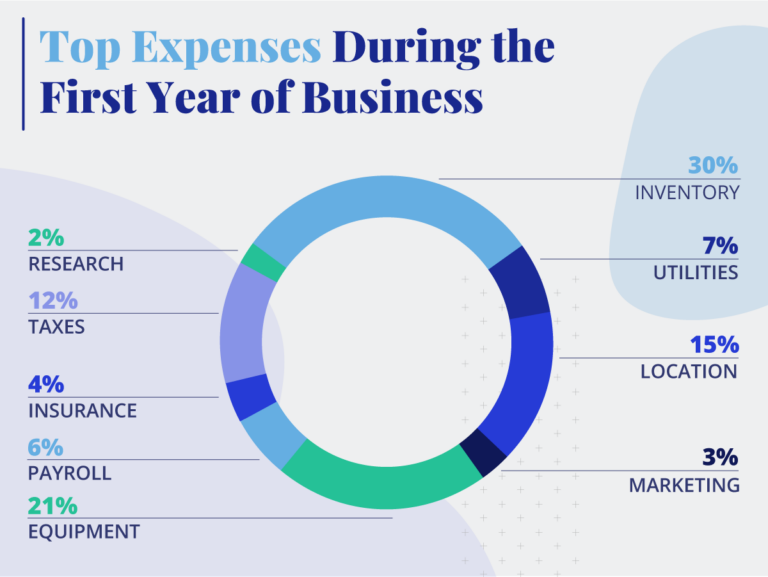
Equipment and Supplies: Purchasing or leasing equipment such as computers, machinery, furniture, and inventory is a major upfront expense. The cost can vary from a few thousand dollars for a home-based service business to hundreds of thousands for a manufacturing facility.
Real Estate: Renting or purchasing office space or a storefront is another significant cost. Location significantly impacts the price, with prime locations commanding higher rents.
Marketing and Advertising: Creating a brand identity, developing a website, and running initial marketing campaigns are essential for attracting customers. Experts often allocate at least 5% of expected revenue to marketing, especially in the initial stages.
Legal and Professional Fees: Engaging lawyers, accountants, and consultants for business setup, legal compliance, and financial planning can incur substantial costs.
Operating Expenses
Rent and Utilities: Ongoing expenses for rent, utilities (electricity, water, internet), and property maintenance are crucial for business operations.
Salaries and Wages: Paying employees, including salaries, wages, and benefits, is a significant recurring cost. Owners may also forgo salary or take reduced pay in initial stages.
Inventory and Supplies: Continuously restocking inventory and purchasing necessary supplies is essential for businesses that sell goods.
Insurance: Business insurance, including liability, property, and workers' compensation, is crucial for protecting the business from potential risks.
Marketing and Advertising (Ongoing): Consistent marketing efforts are necessary for maintaining brand visibility and attracting new customers.
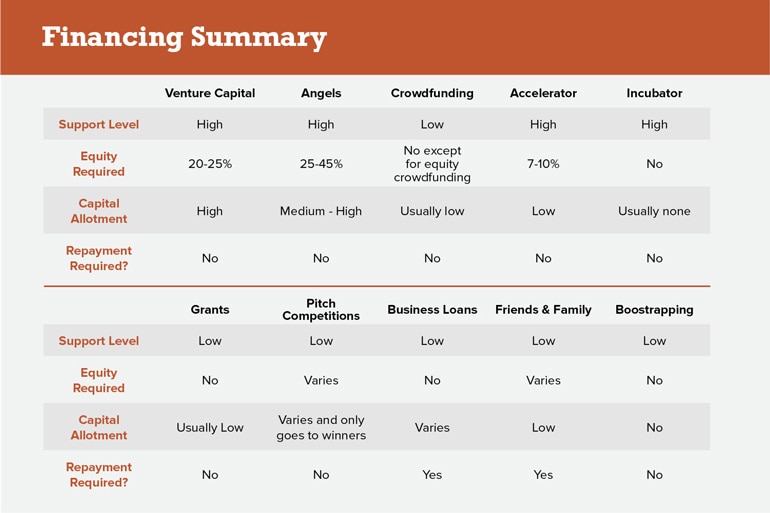
Funding Options
Many small business owners rely on a combination of personal savings, loans, and grants to finance their ventures. The SBA offers various loan programs designed to support small businesses, providing access to capital at competitive interest rates.
Venture capital and angel investors may also be an option for startups with high growth potential. Crowdfunding platforms are another alternative for raising capital from a larger pool of investors.
The Human Cost
Beyond the financial costs, aspiring entrepreneurs should also consider the personal sacrifices involved. Starting a business often requires long hours, reduced income, and significant personal investment.
One example is Maria Rodriguez, a former marketing manager who launched her own artisanal bakery. She initially worked 16-hour days, foregoing personal time and relying on family support to keep her business afloat. Despite the challenges, she eventually built a thriving business with loyal customers.
Planning and Preparation
A detailed business plan is essential for estimating startup costs, projecting revenue, and securing funding. A well-researched plan helps entrepreneurs identify potential challenges and develop strategies for overcoming them.
Seeking advice from experienced business owners and mentors can also provide invaluable insights and guidance. Numerous organizations offer free or low-cost business counseling and training programs.
Conclusion
The cost of starting a small business is a significant investment, but with careful planning, realistic expectations, and access to funding, aspiring entrepreneurs can successfully launch their ventures. Understanding the financial landscape and preparing for the challenges ahead are crucial for building a sustainable and thriving business.


![What Does It Cost To Start A Small Business [Infographic] Small Business Startup Costs – Canada Small Business](https://www.canadastartups.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/startupbuddy.com_.png)