What Does It Take To Charge A Tesla

The allure of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly those bearing the Tesla logo, has surged in recent years, fueled by environmental consciousness and technological advancements. However, the seemingly simple act of replenishing a Tesla's battery – its lifeblood – is a multifaceted process with considerations that extend far beyond plugging it into a wall.
Understanding the intricacies of Tesla charging is crucial for prospective buyers and current owners alike. This includes delving into charging levels, infrastructure availability, costs, and the impact on battery health. A deeper understanding empowers drivers to make informed decisions optimizing convenience, efficiency, and long-term vehicle performance.
Charging Levels: A Spectrum of Speed
Tesla charging isn't a one-size-fits-all affair. Charging speeds vary significantly depending on the charging level and the specific Tesla model.
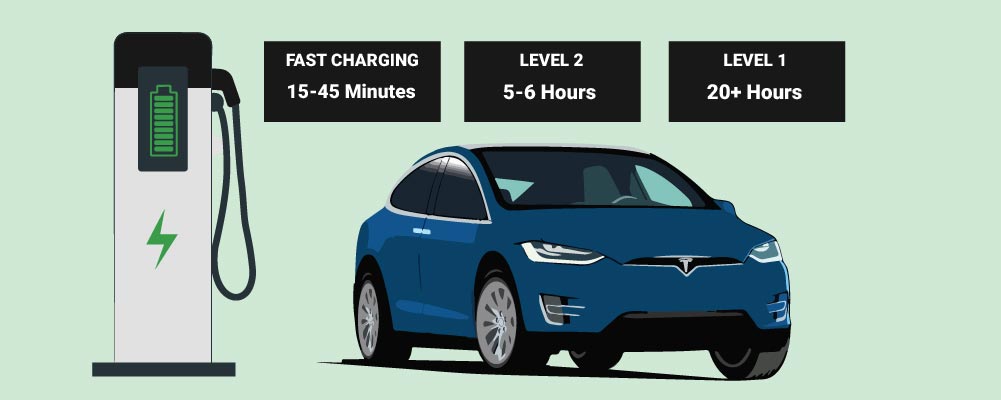
Level 1 Charging: The Slowest Sip
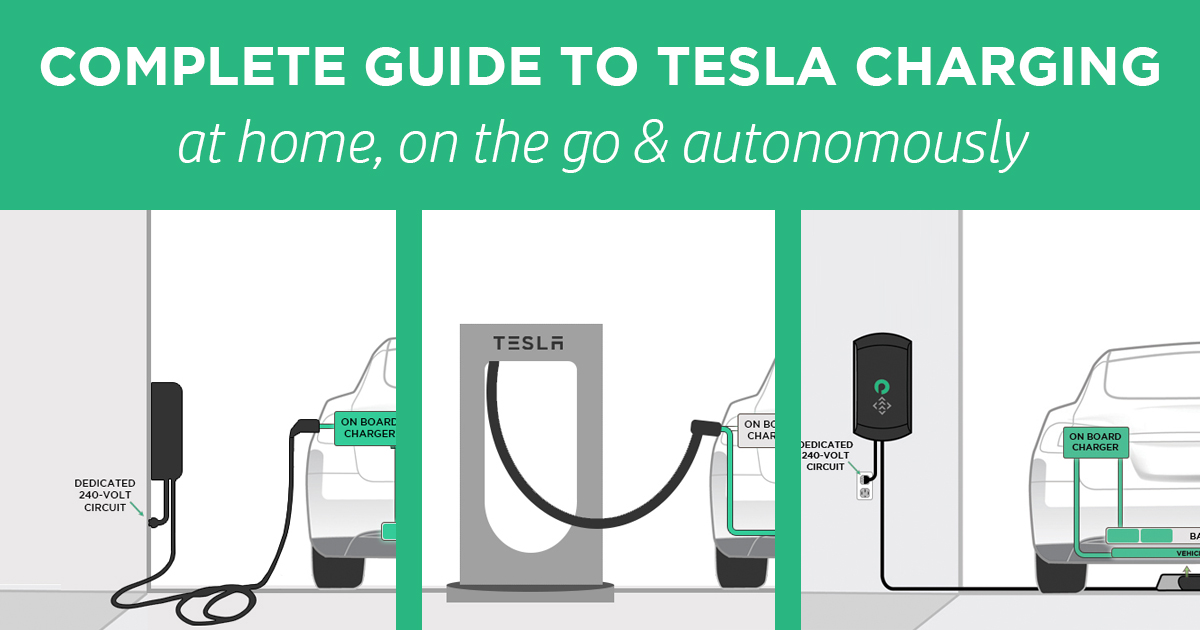
Level 1 charging, using a standard 120V household outlet, is the slowest method. It typically adds only 2-5 miles of range per hour. This method is best suited for overnight charging or as a supplemental option when faster alternatives aren't available.
Level 2 Charging: The Home Advantage
Level 2 charging, employing a 240V outlet, offers a considerably faster charging rate. This is the most common method for home charging and is also available at public charging stations, adding 20-40 miles of range per hour.
Installation of a dedicated 240V circuit and a Tesla Wall Connector is usually recommended for efficient home charging.
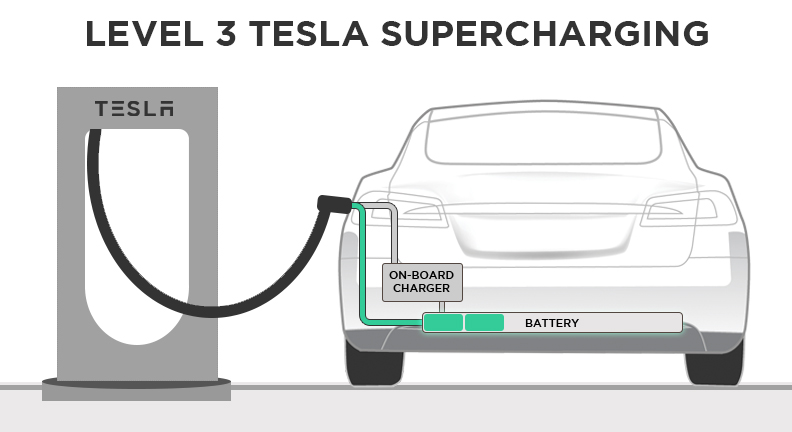
DC Fast Charging: On-the-Go Power
DC Fast Charging, also known as Level 3 charging, represents the fastest charging option. Tesla's Supercharger network utilizes this technology, delivering up to 200 miles of range in about 30 minutes.
This method is ideal for long-distance travel and situations where a quick charge is needed.
Infrastructure: A Growing Network
The availability of charging infrastructure is a critical factor for Tesla owners. Tesla has invested heavily in building its Supercharger network.
These stations are strategically located along major highways and in urban areas. However, the Supercharger network isn't the only option.
Third-party charging networks, such as ChargePoint and Electrify America, also offer DC Fast Charging and Level 2 charging options, though their compatibility and pricing may vary.
Cost Considerations: From Home to Highway
The cost of charging a Tesla varies depending on the charging location and electricity rates. Home charging is generally the most cost-effective option. The cost is only your home electricity costs.
Public charging, particularly DC Fast Charging, can be more expensive, with prices typically ranging from $0.25 to $0.50 per kWh.
Some Tesla owners also opt for subscription plans with charging networks to access discounted rates.
Battery Health: A Balancing Act
Charging habits can impact the long-term health and lifespan of a Tesla's battery. While Tesla batteries are designed to withstand frequent charging, certain practices can accelerate degradation.
Avoid consistently charging to 100% or frequently depleting the battery to 0%. Tesla recommends keeping the battery between 20% and 90% for daily use.
Using DC Fast Charging sparingly can also help minimize battery degradation over time.
The Future of Charging: Innovation on the Horizon
Tesla and other EV manufacturers are continually innovating to improve charging technology and infrastructure. Wireless charging, battery swapping, and higher voltage charging systems are among the advancements being explored.
These innovations promise to make charging faster, more convenient, and more accessible for EV owners in the future.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of Tesla charging empowers owners to maximize their vehicle's potential. As technology evolves and infrastructure expands, the journey towards seamless and efficient EV charging continues.