What Does Substrate Concentration Refer To
The term "substrate concentration" is frequently encountered in scientific disciplines ranging from biochemistry to environmental science. It describes the amount of a specific substance present and available for a reaction, often a biological or chemical process. Understanding substrate concentration is crucial for analyzing and predicting the rates and outcomes of these reactions.
At its core, substrate concentration refers to the measure of the amount of substrate present in a solution or system. The substrate is the molecule upon which an enzyme acts, or the substance that is transformed in a chemical reaction.
What is Substrate Concentration?
Substrate concentration is typically expressed in units of concentration such as moles per liter (M), millimoles per liter (mM), or micrograms per milliliter (µg/mL). These units quantify the amount of substrate dissolved in a given volume.
The higher the substrate concentration, the more substrate is available to interact with the enzyme or participate in the reaction. Conversely, a lower substrate concentration means less substrate is available.
Michaelis-Menten kinetics, a fundamental model in enzyme kinetics, directly incorporates substrate concentration to explain reaction rates. It’s fundamental to understanding its role.
The Role of Substrate Concentration in Enzyme Kinetics
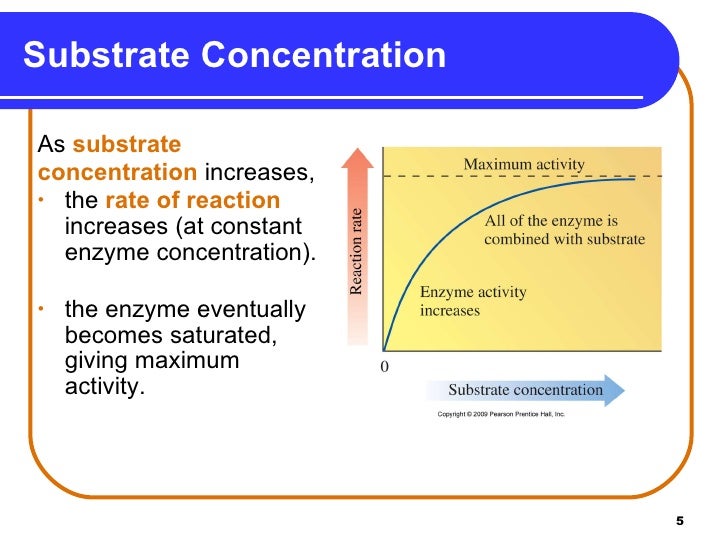
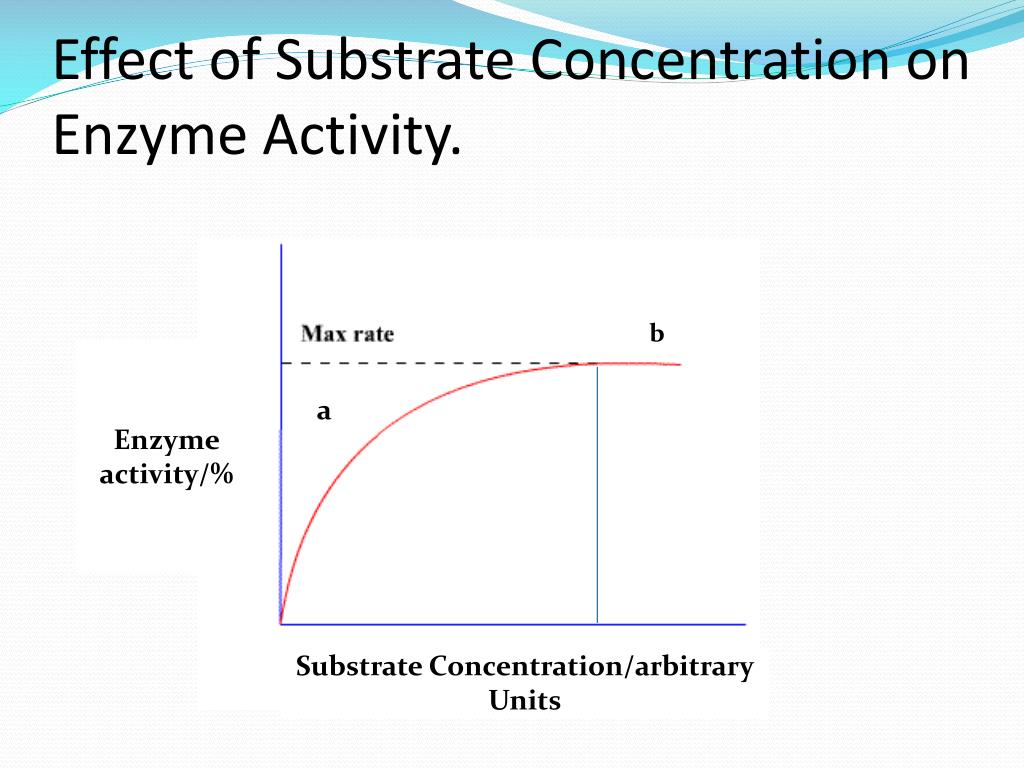
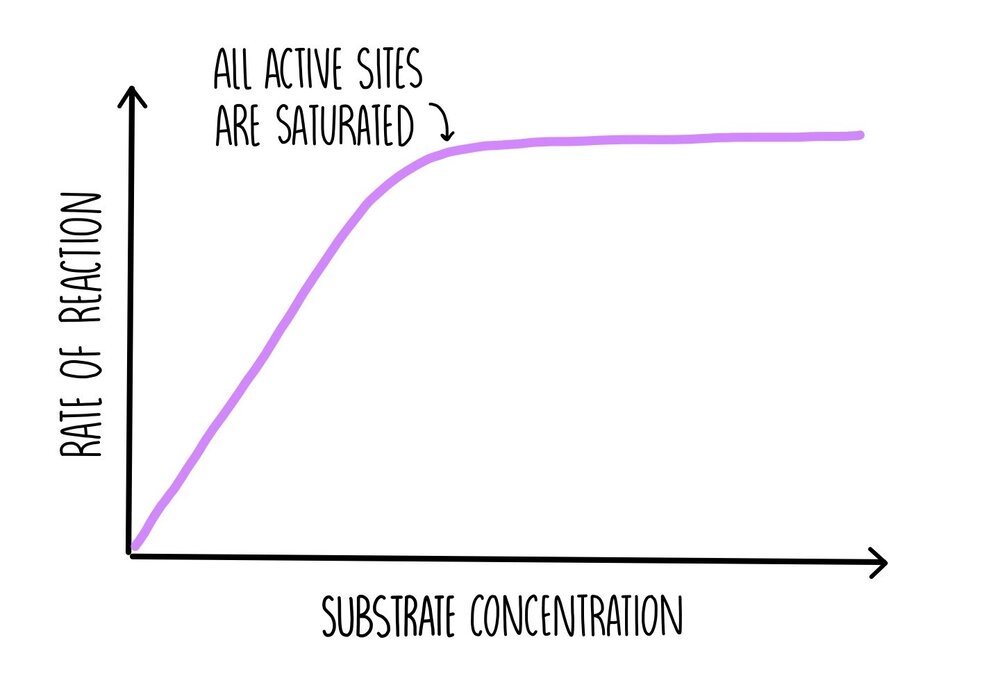
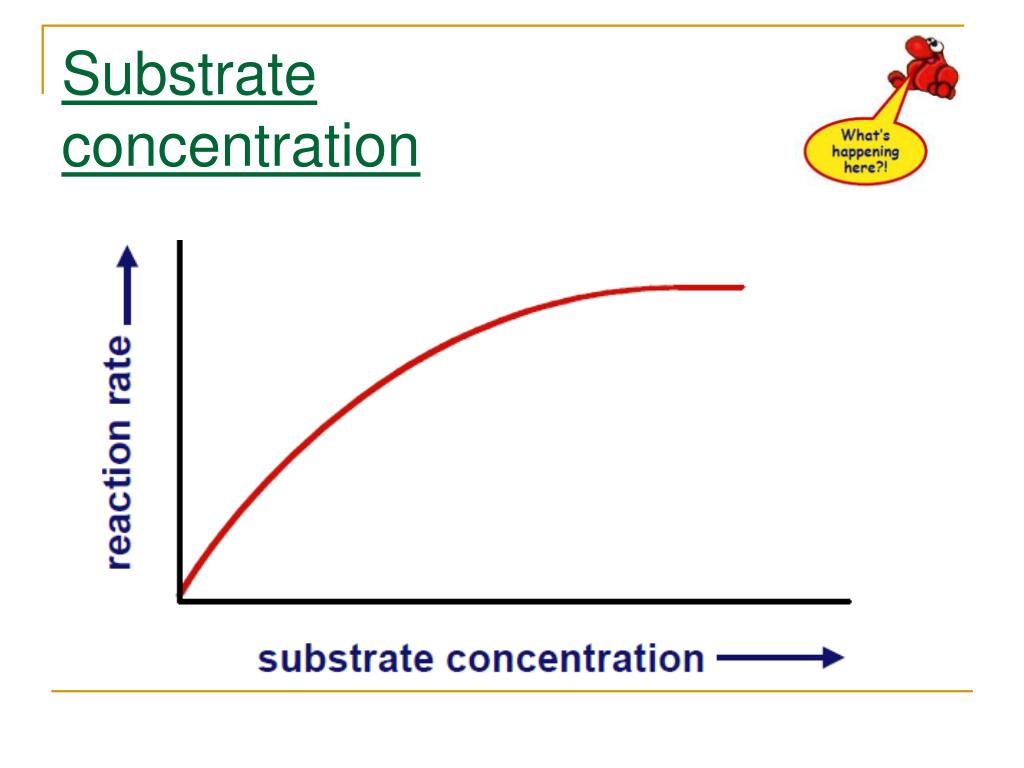
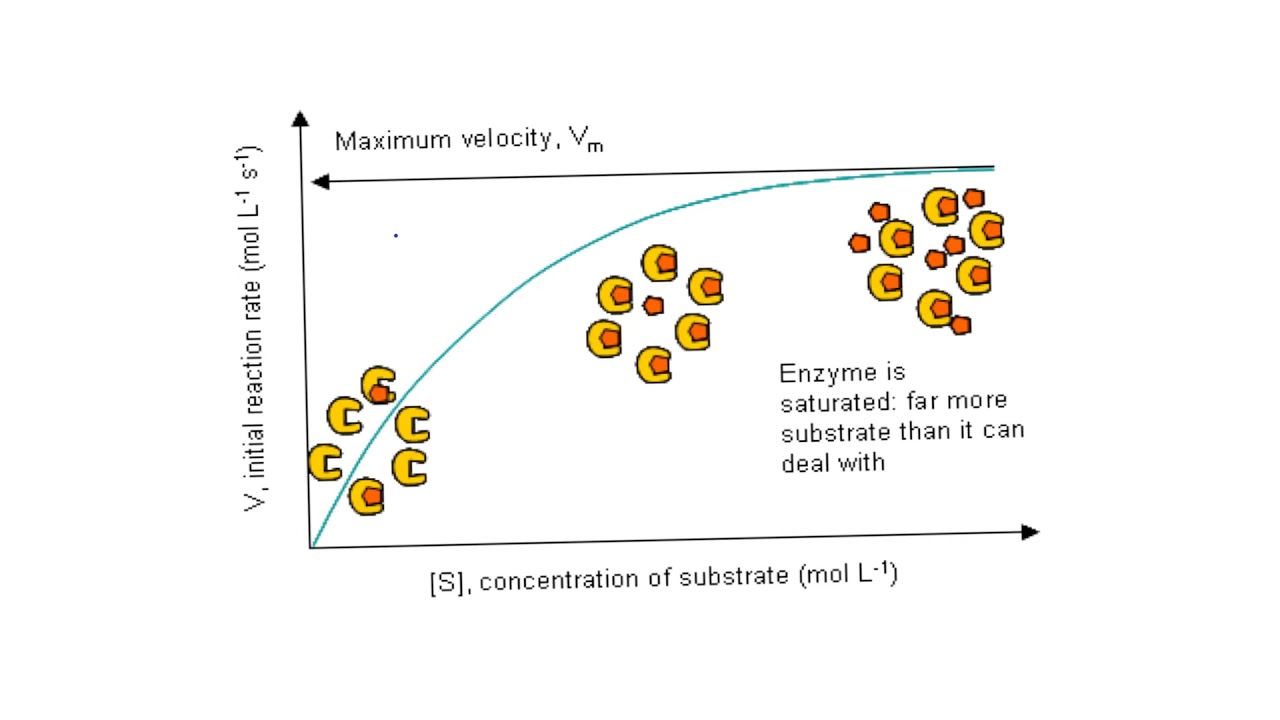
In enzymatic reactions, the rate at which the enzyme converts the substrate into product is heavily influenced by the substrate concentration. The relationship between substrate concentration and reaction rate is not linear, but follows a characteristic curve.
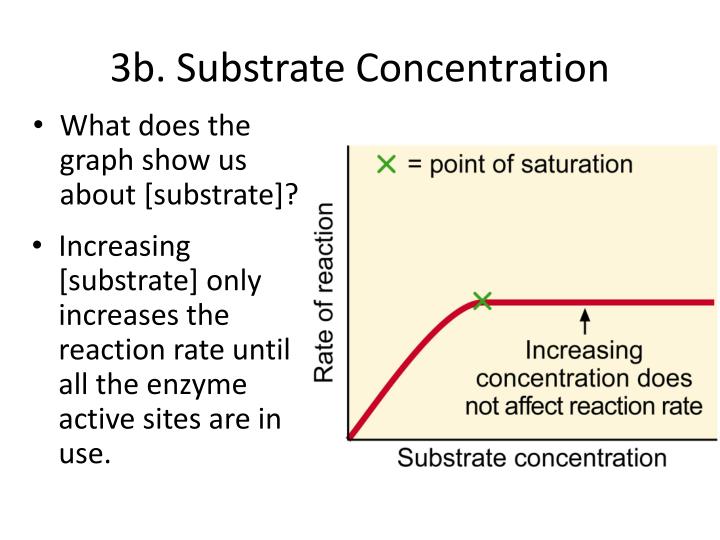
At low substrate concentrations, the reaction rate increases almost linearly with increasing substrate concentration. This is because there are plenty of active sites available on the enzyme molecules to bind to the substrate.
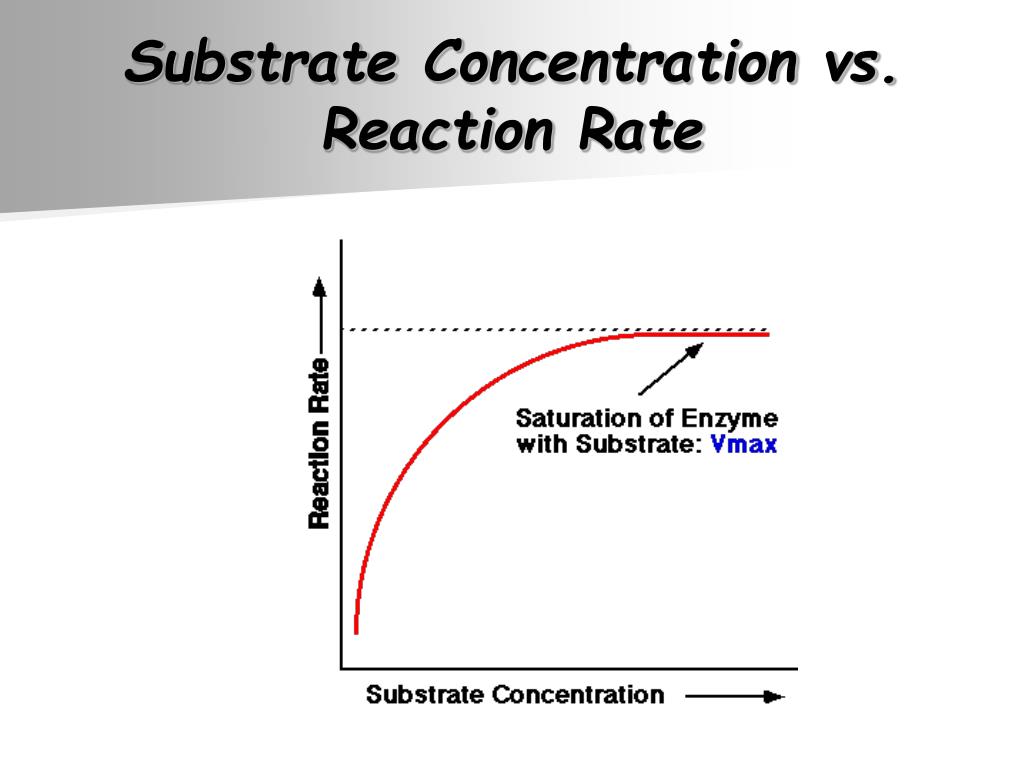
As the substrate concentration increases further, the reaction rate begins to plateau. This is because the active sites on the enzyme molecules become saturated with substrate, reaching a maximum velocity (Vmax).
Beyond the Vmax, increasing the substrate concentration further does not significantly increase the reaction rate. This plateau is a key aspect of Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
The Michaelis constant (Km) is another important parameter. It represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax. Km provides an indication of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate.
Applications of Substrate Concentration
Understanding substrate concentration has wide-ranging applications in various fields. These includes biochemistry, biotechnology, environmental science, and medicine.
Biochemistry and Biotechnology
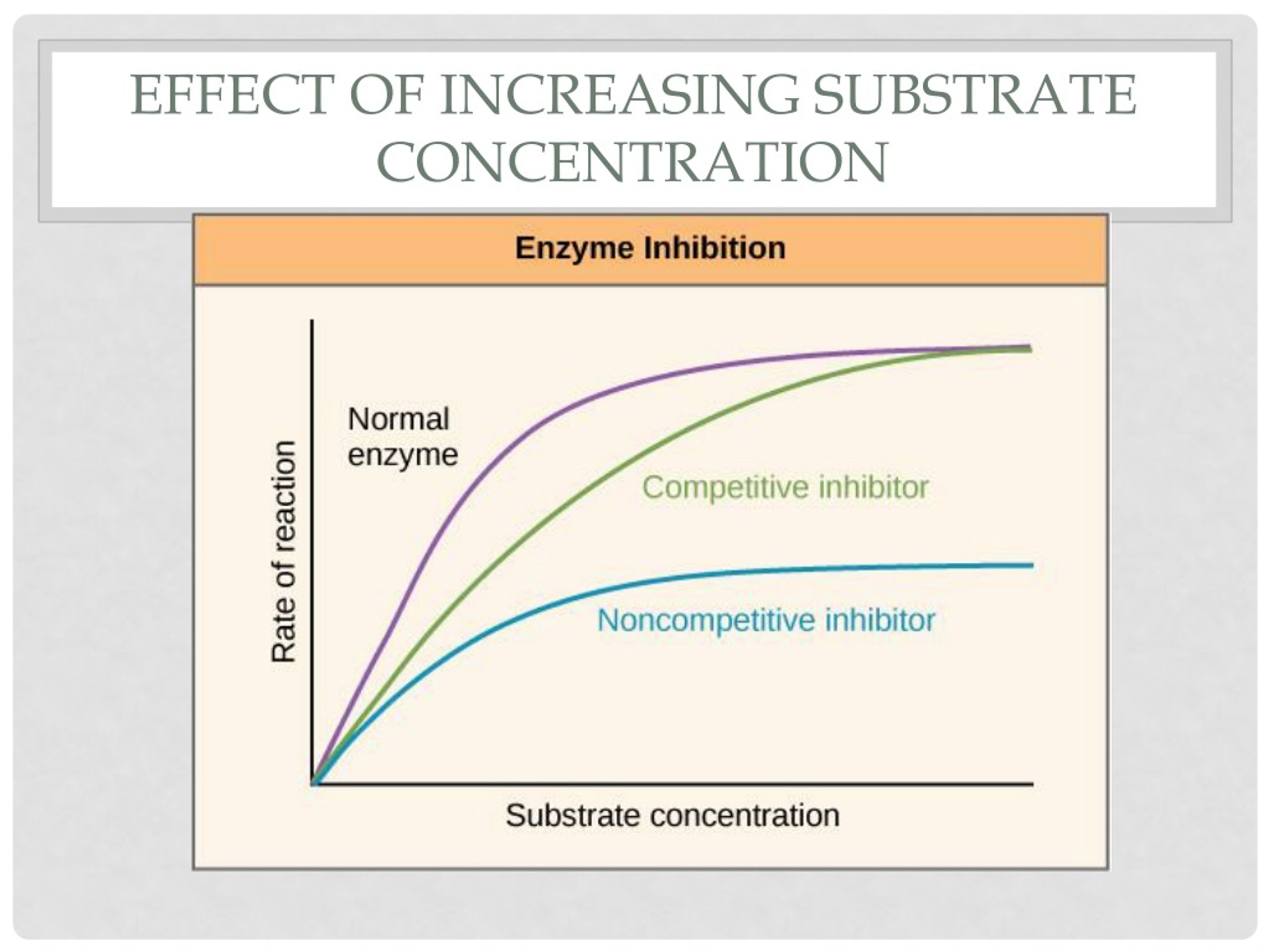
In biochemistry, substrate concentration is crucial for studying enzyme activity and designing enzyme assays. Researchers manipulate substrate concentrations to investigate the effects of inhibitors and activators on enzyme function.
In biotechnology, substrate concentration is optimized to maximize product yields in industrial processes involving enzymes or microorganisms. This is particularly relevant in the production of pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and food additives.
Environmental Science
In environmental science, substrate concentration plays a critical role in determining the rates of biodegradation of pollutants. Microorganisms in the environment utilize pollutants as substrates, and the concentration of these pollutants affects the speed and efficiency of their degradation.
For example, the concentration of organic matter in wastewater influences the rate at which microorganisms break down these pollutants during wastewater treatment.
Medicine
In medicine, substrate concentration is important for understanding metabolic disorders. These include conditions where the levels of certain substrates are abnormally high or low.
For example, in phenylketonuria (PKU), a genetic disorder, the substrate phenylalanine accumulates in the body due to a deficiency in the enzyme that metabolizes it. Monitoring and controlling substrate levels are essential for managing the disease.
Factors Affecting Substrate Concentration
Several factors can influence substrate concentration in a system. These factors depend on the context, such as whether the system is a controlled laboratory experiment or a complex environmental setting.
The initial amount of substrate added to the system is a direct determinant of substrate concentration. The rate of substrate production or degradation also affects substrate availability.
In biological systems, transport processes such as diffusion and active transport can influence substrate concentration at specific locations. Environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators can also alter substrate concentration.
Conclusion
Substrate concentration is a fundamental concept that underlies many biological and chemical processes. Its influence on reaction rates, enzyme activity, and metabolic pathways makes it a critical consideration in various fields.
By understanding and manipulating substrate concentration, scientists and engineers can optimize reactions, develop new technologies, and gain insights into the complexities of life. Further research will continue to unravel the intricacies of substrate-enzyme interactions.
Ultimately, a thorough grasp of substrate concentration is essential for advancing our knowledge and addressing challenges in biochemistry, biotechnology, environmental science, and medicine.






![What Does Substrate Concentration Refer To Untitled Document [www.ucl.ac.uk]](https://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucbcdab/enzass/images/subs5.png)