What Grade Is A 10 Out Of 13

A score of 10 out of 13 equates to a 77% grade, typically corresponding to a C+ or B- depending on the grading scale. The precise letter grade varies slightly across educational institutions, prompting confusion among students and parents.
This article breaks down the conversion of a 10/13 score to a letter grade, addressing the widespread ambiguity in grading systems. We'll explore the different interpretations and their implications for academic performance.
Understanding Percentage Conversion
The first step is to convert the fraction 10/13 into a percentage. This is achieved by dividing 10 by 13, resulting in approximately 0.7692.
Multiplying 0.7692 by 100 gives us 76.92%, which can be rounded to 77%. This percentage is the core numerical representation of the score.
Letter Grade Equivalents
Now, we need to determine what letter grade corresponds to 77%. This is where the discrepancy often arises, as different schools and even different instructors may use varying grading scales.
Generally, a 77% falls within the C+ to B- range. The exact placement depends on the specific grading rubric employed.
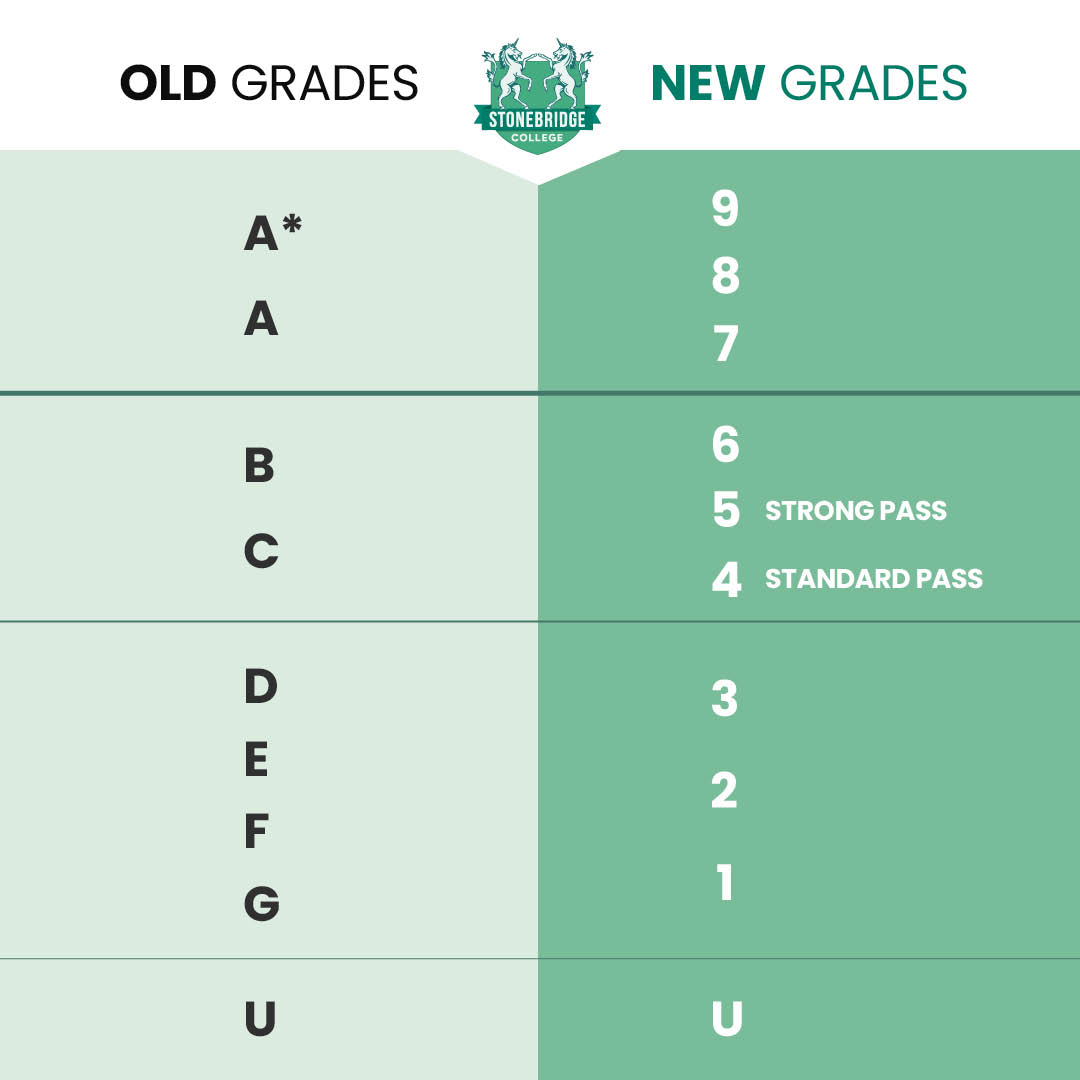
Common Grading Scales: A Comparison
Let's examine a few common grading scales to illustrate the potential variations.
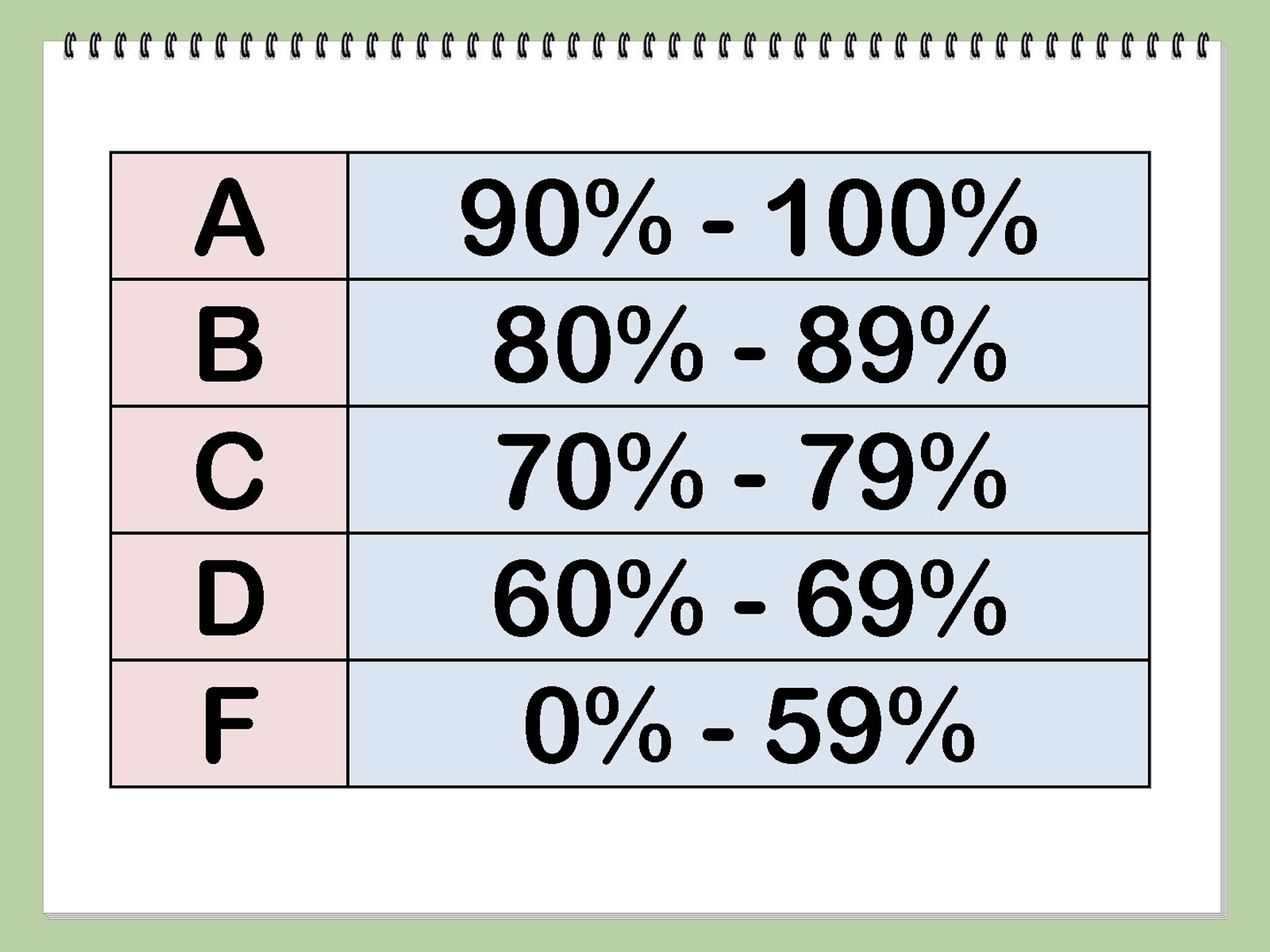
Scale 1: A (90-100%), B (80-89%), C (70-79%), D (60-69%), F (0-59%)
Under this scale, 77% is firmly a C. It would be considered average performance.
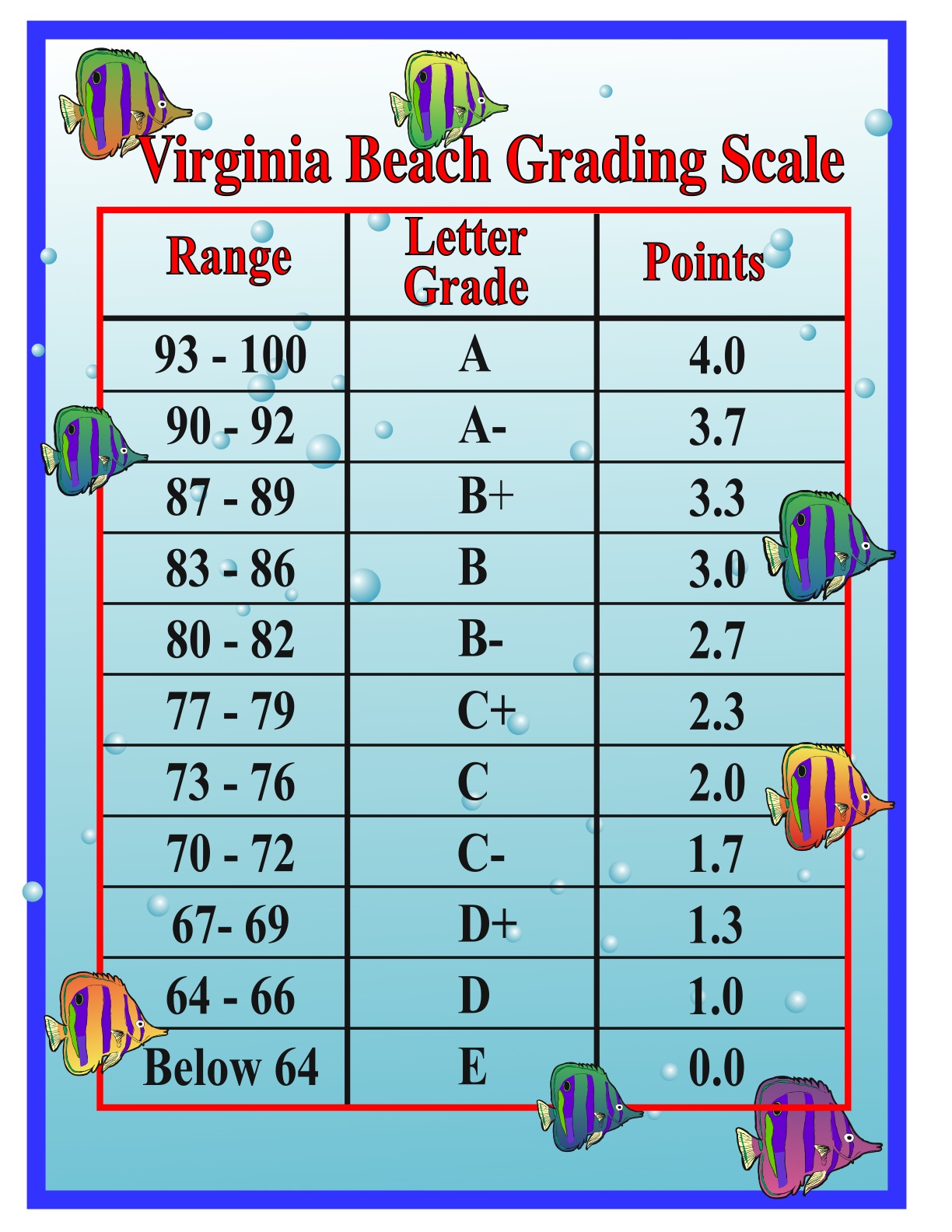
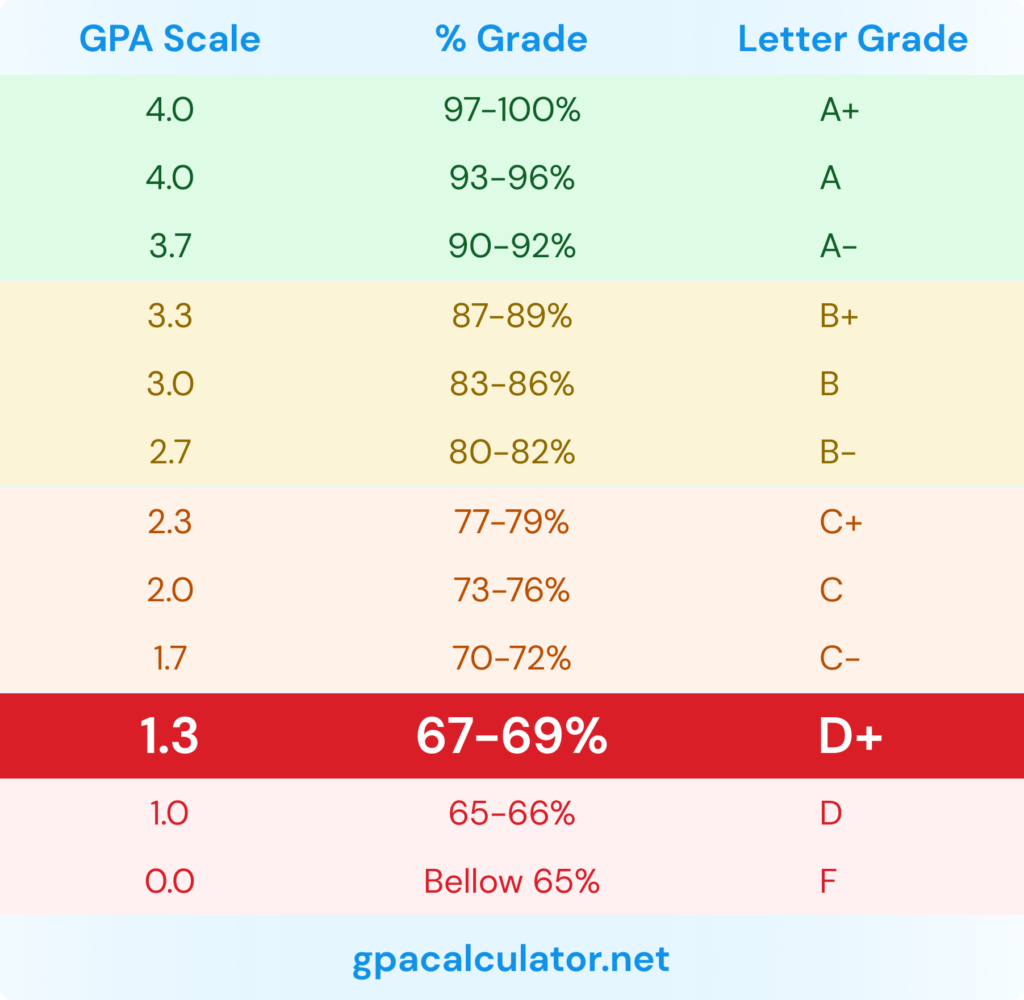
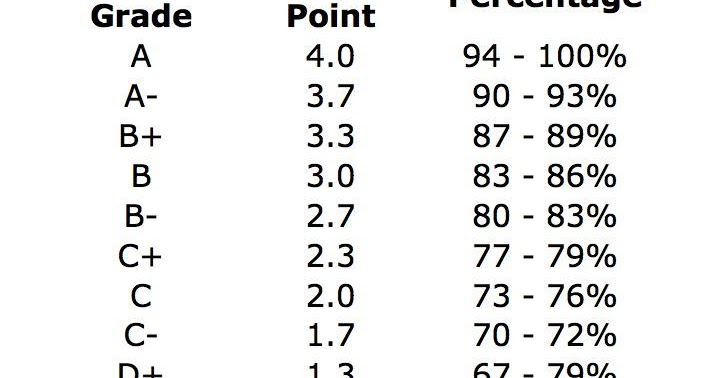
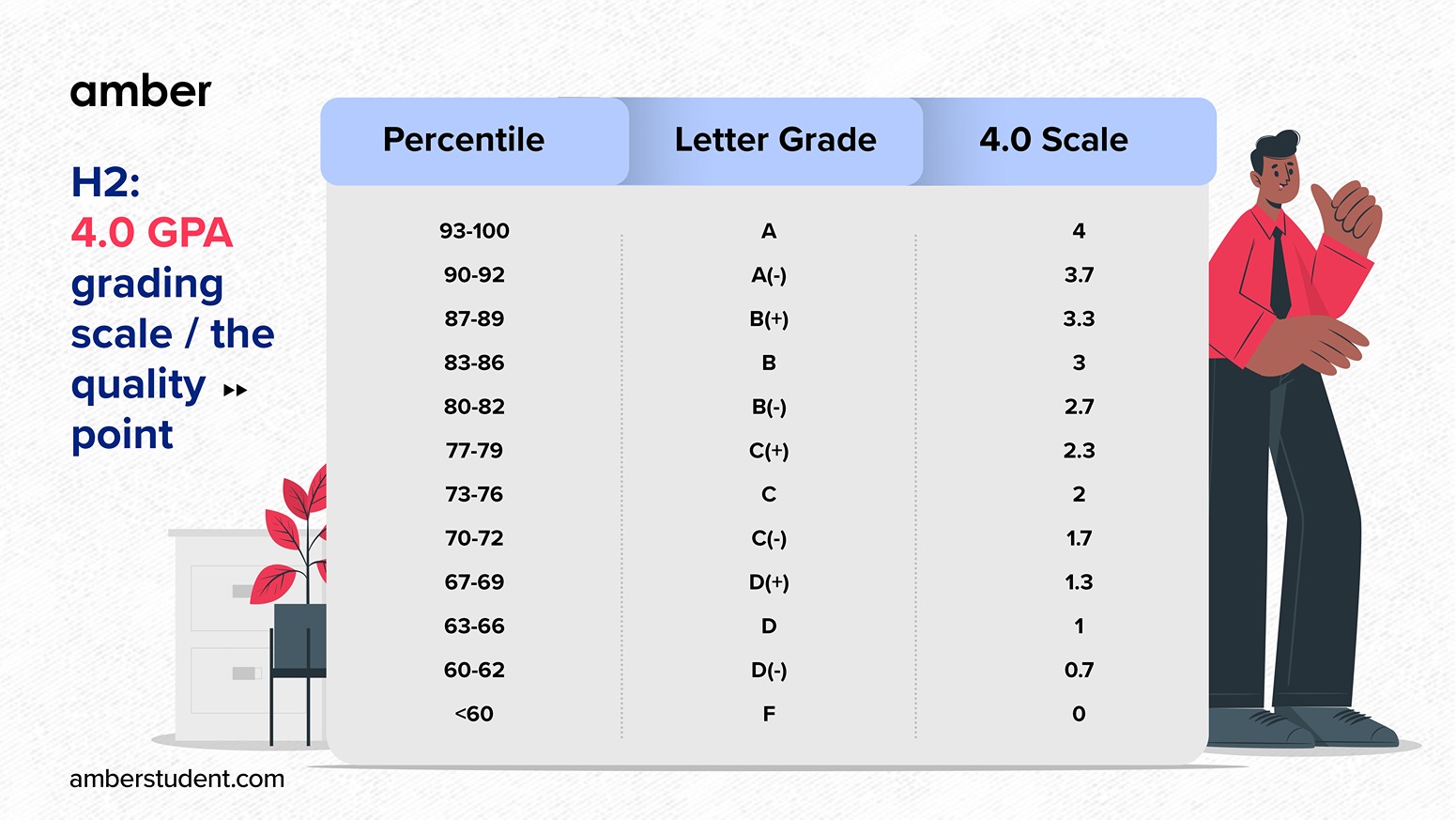
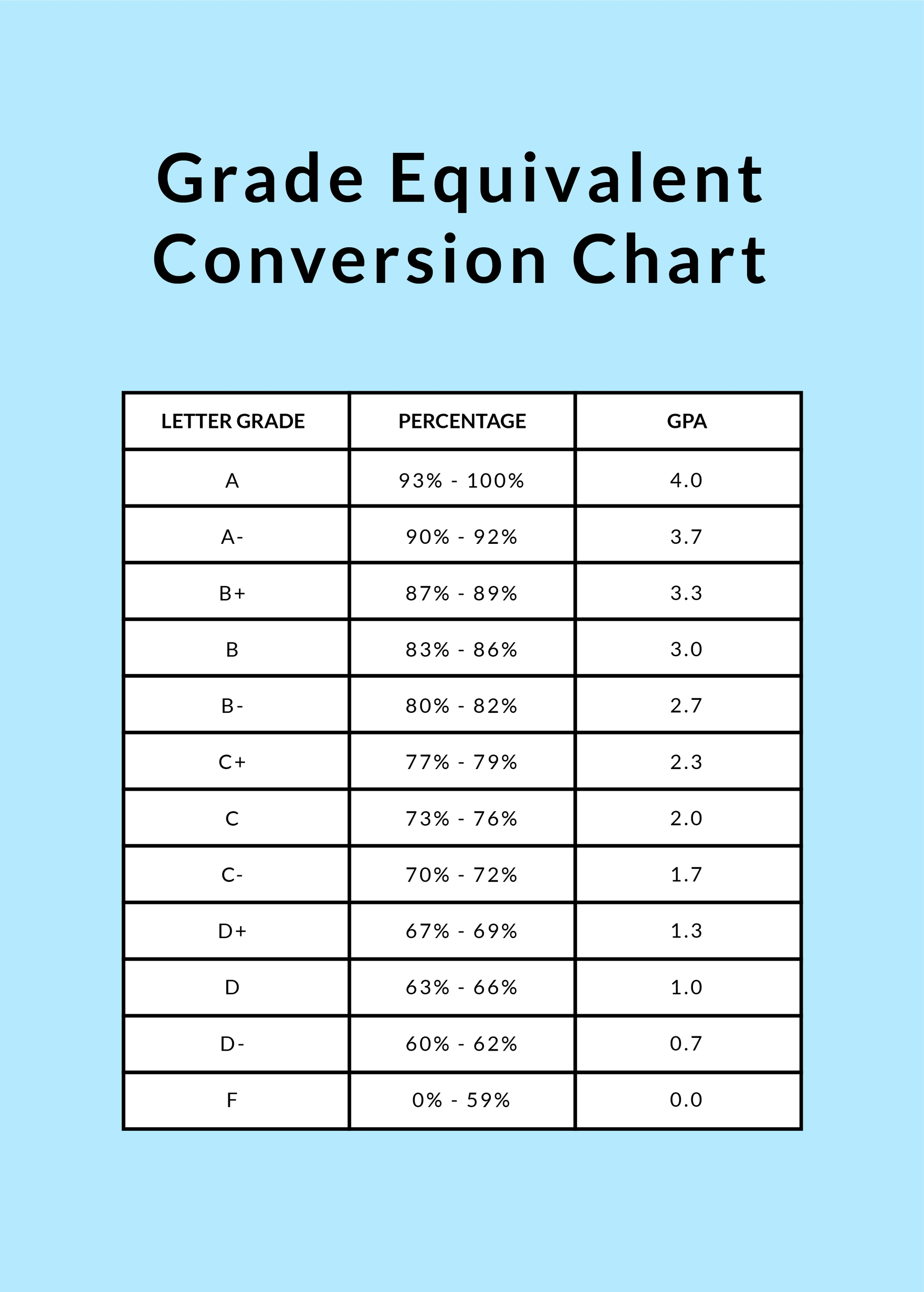
Scale 2: A (93-100%), A- (90-92%), B+ (87-89%), B (83-86%), B- (80-82%), C+ (77-79%), C (73-76%), C- (70-72%), D+ (67-69%), D (63-66%), D- (60-62%), F (0-59%)
Here, a 77% lands squarely on a C+. This scale offers more granular distinctions within each letter grade.
Scale 3: A (90-100%), B (80-89%), C (75-79%), D (65-74%), F (0-64%)
In this scenario, 77% is a C, but it's at the higher end of the C range. It's just shy of a B.
These examples highlight the subjectivity in grading. It's crucial to consult the specific grading policy for each class or institution.
Impact on Academic Standing
The letter grade assigned to a 10/13 score can have varying impacts on a student's academic standing. A C+ or B- may affect GPA and eligibility for certain programs or scholarships.
Students should be proactive in understanding their instructors' grading policies. They should also seek clarification if they are unsure about how their grades are calculated.
Expert Opinions
Dr. Emily Carter, an education professor at State University, emphasizes the need for transparency in grading. "Instructors should clearly communicate their grading rubrics to students at the beginning of the course," she states.
John Davis, a high school guidance counselor, advises students to focus on understanding the material, not just the grade. "A strong understanding of the concepts will ultimately lead to better performance," he explains.
Moving Forward
To address the confusion surrounding grade conversions, some institutions are exploring standardized grading scales. This would create more consistency and clarity for students and parents.
Students should review their course syllabi for grading specifics. They should also engage with their instructors to clarify any uncertainties about grading policies.
Ultimately, understanding the grading system is critical. It helps students to accurately assess their progress and identify areas for improvement.