Which Financial Statement Is Reported As Of A Specific Date
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-02-6a82acc4cf2d4434a77899c09d49e737.jpg)
Urgent clarification needed: Investors and financial professionals are grappling with a crucial distinction. Only the balance sheet reflects a company’s financial position *at a specific point in time*.
The confusion stems from the nature of financial reporting, where different statements capture performance over periods versus snapshots of assets, liabilities, and equity. This misunderstanding could lead to misinterpretations of a company’s financial health, directly impacting investment decisions.
The Balance Sheet: A Financial Snapshot
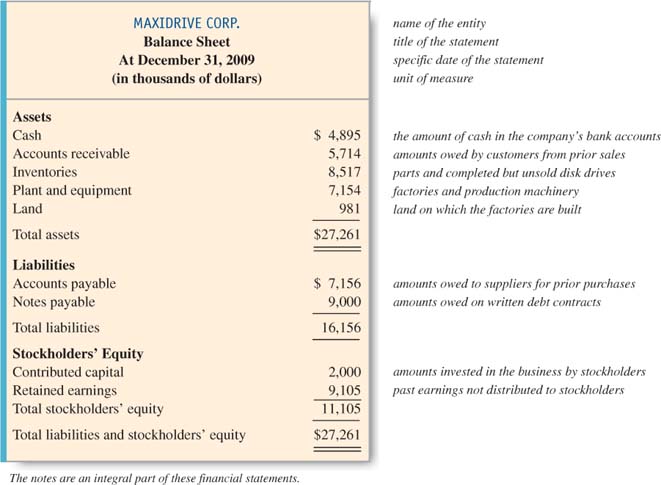
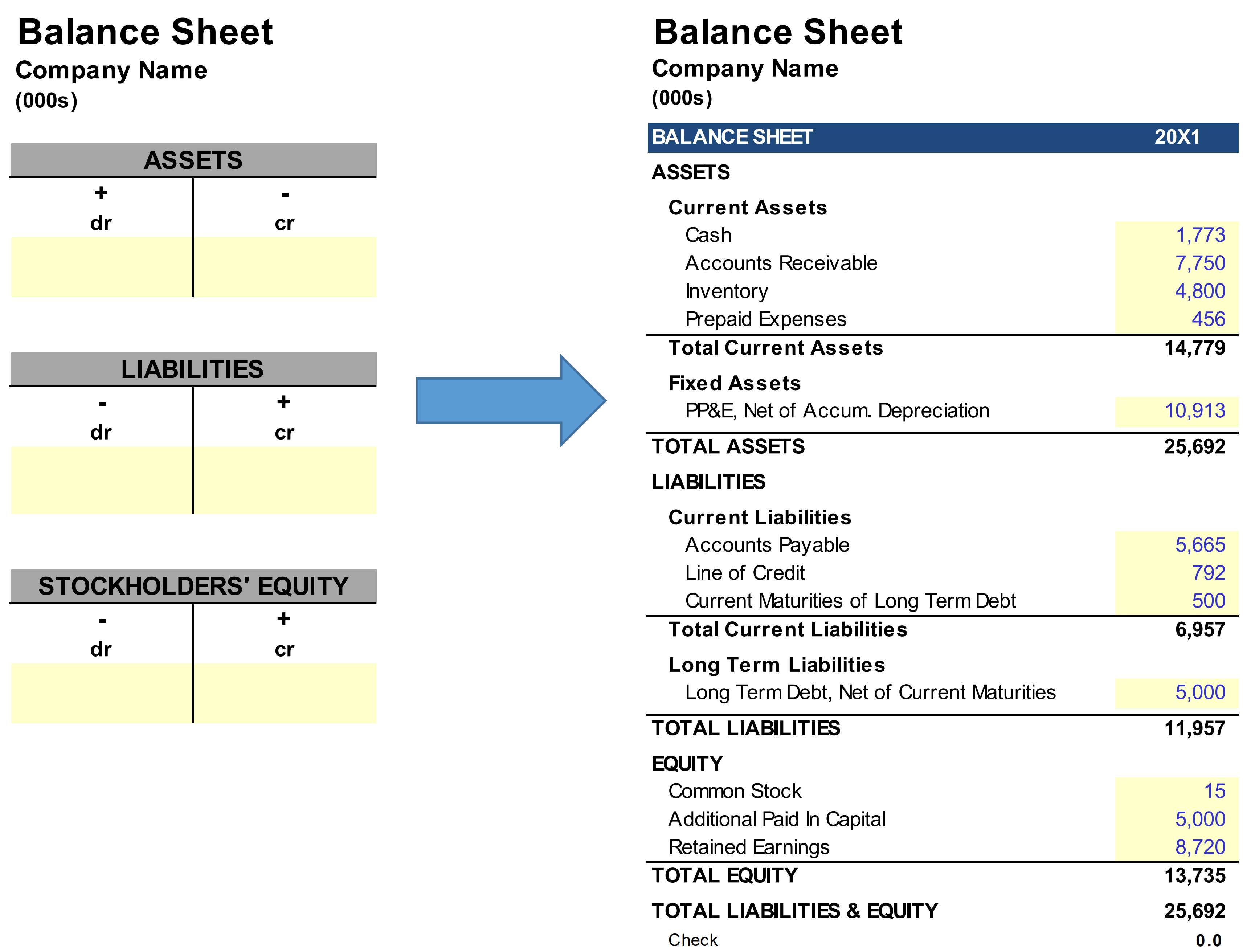
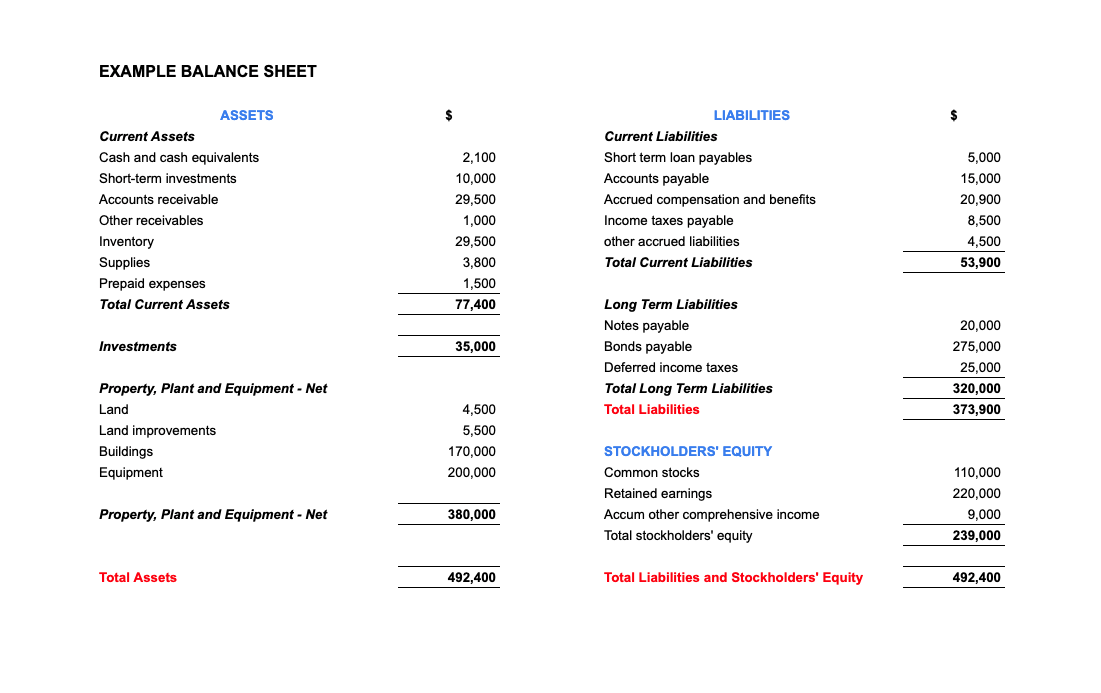
The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, adheres to the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
This equation is *always* in balance, representing a company’s resources (assets), obligations (liabilities), and the owners’ stake (equity) at a particular date.
Unlike other financial statements, the balance sheet provides a static view, like a photograph, showing the immediate financial standing of the entity. The date the balance sheet is prepared is crucial information.
Key Components: Assets, Liabilities, and Equity
Assets represent what a company owns, including cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). These are resources the company can use to generate future revenue.
Liabilities are a company's obligations to others, such as accounts payable, salaries payable, and debt. They represent claims against the company’s assets.
Equity represents the owners’ stake in the company. It's the residual value of assets after deducting liabilities. This includes items like common stock and retained earnings.
Other Financial Statements: Performance Over Time
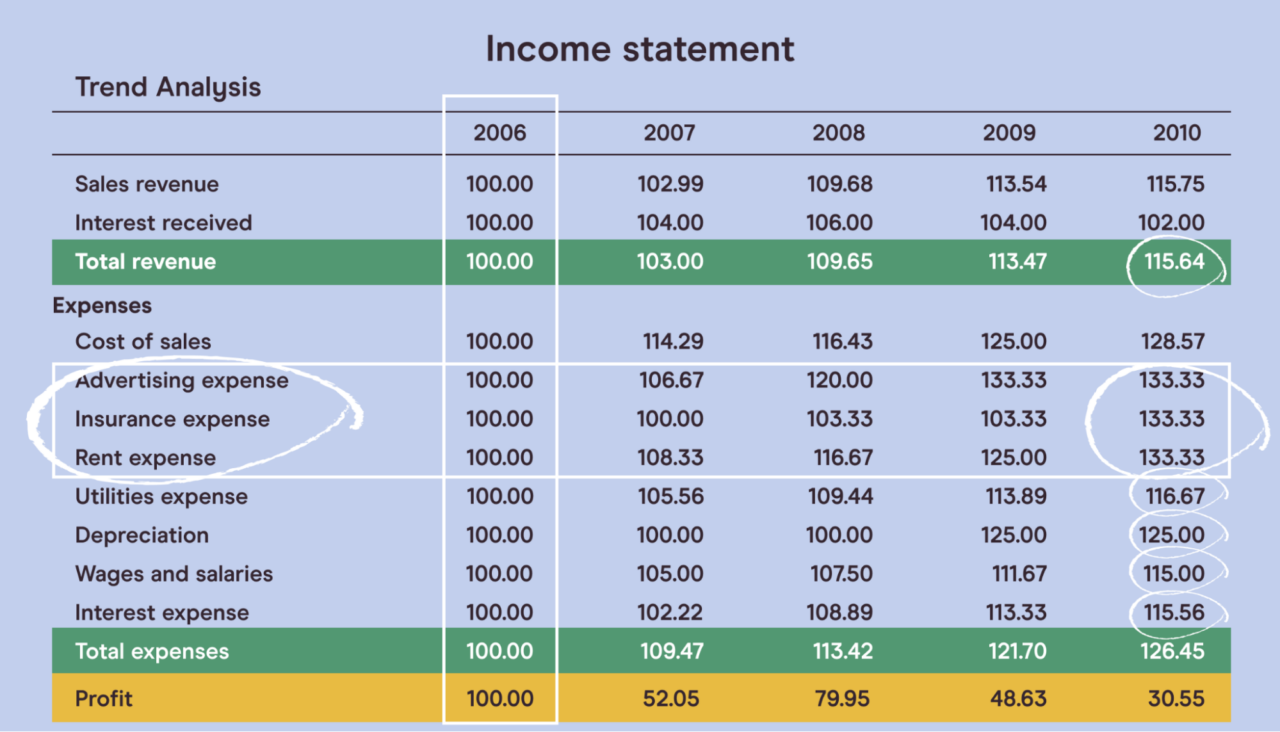
The income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of retained earnings report activities over a period of time, such as a quarter or a year.
These statements detail the flow of money in and out of a company, measuring profitability and cash generation, but do not offer a single-date snapshot of financial position.
Income Statement
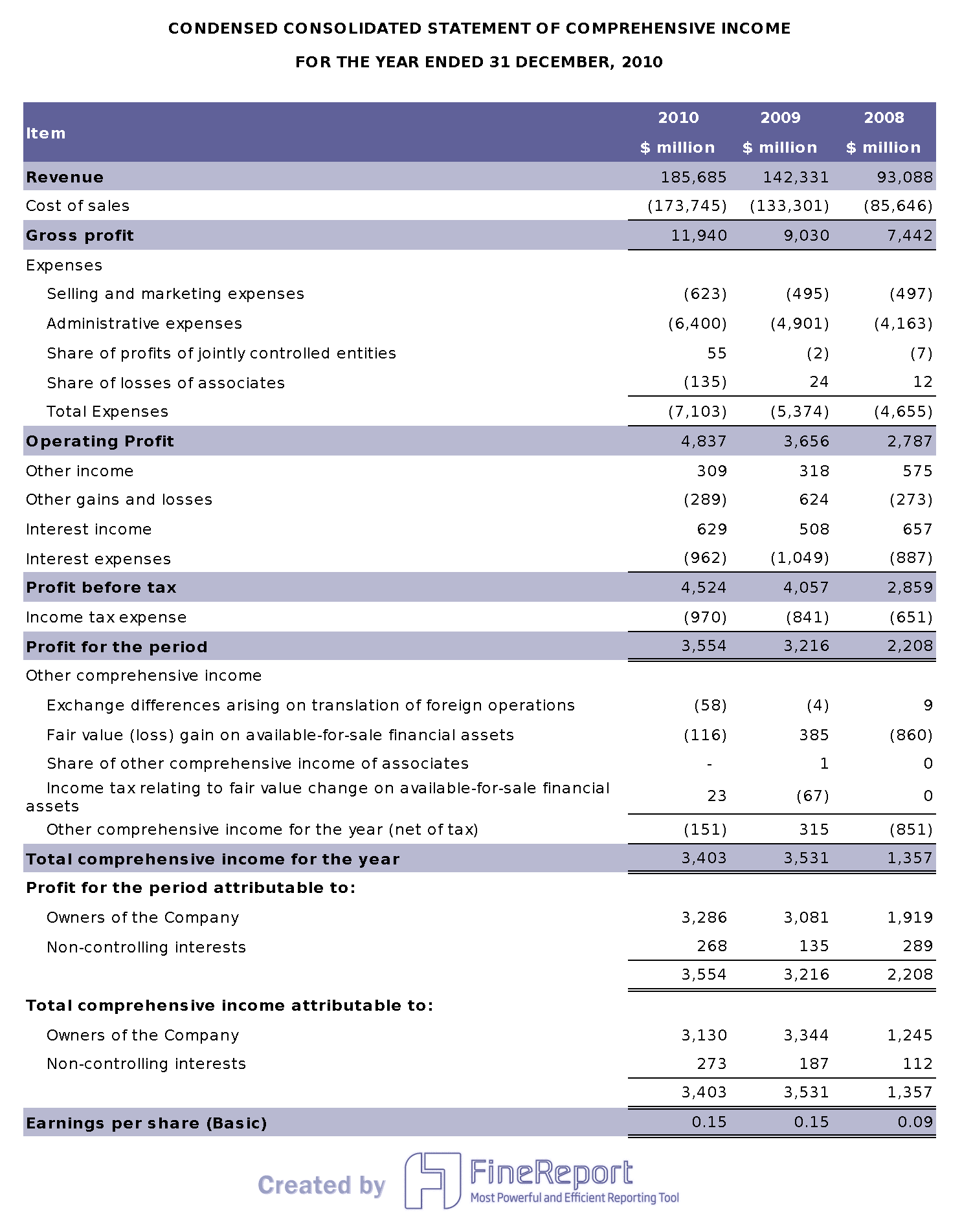
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, reports a company's financial performance over a period, showing revenues, expenses, and net income.
It shows how profitable a company has been over a period of time by subtracting expenses from revenues.
The information is captured between two dates, typically the start and end of a fiscal quarter or year.
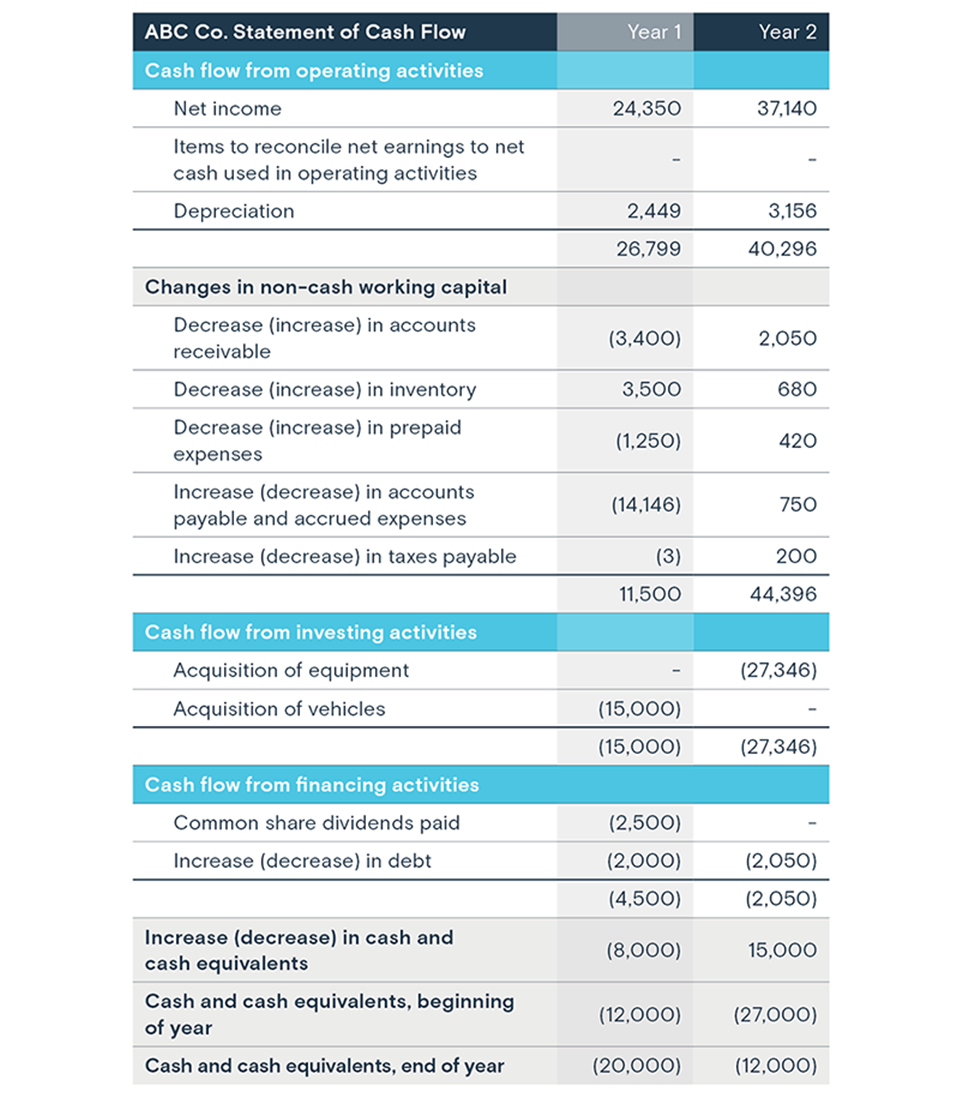
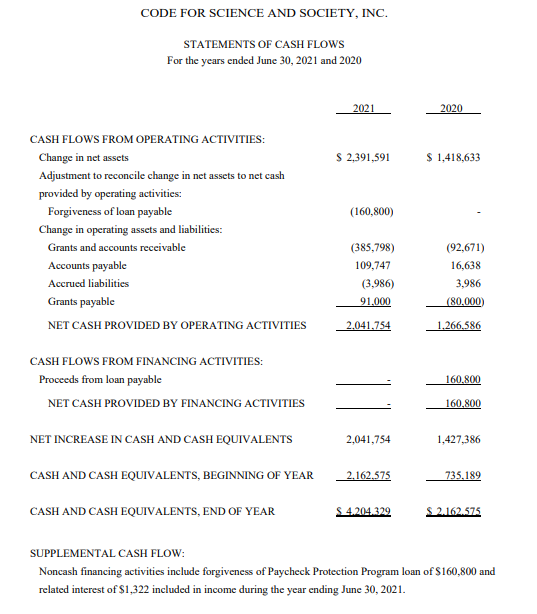
Statement of Cash Flows
The statement of cash flows tracks the movement of cash both into and out of a company during a period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities.
This statement explains the change in cash balance between the beginning and ending of the period.
This is also viewed over a period of time and is not a single static date.
Statement of Retained Earnings
The statement of retained earnings shows the changes in a company's retained earnings account over a period.
It outlines how much of the company's net income was retained for reinvestment versus distributed to shareholders as dividends.
Like the other two, this represents performance between a period of time, beginning and ending dates.
Consequences of Misunderstanding
Confusing the balance sheet with other financial statements can lead to incorrect interpretations of a company’s solvency and liquidity.
Investors may overestimate or underestimate a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations, impacting investment decisions. A misunderstanding can be costly.
Loan officers might incorrectly assess a company's creditworthiness, leading to poor lending decisions.
Who's Affected?
This clarification impacts a wide range of stakeholders: investors, creditors, analysts, and company management, *all must understand this key difference*.
Proper understanding is crucial for effective financial analysis and decision-making.
Misunderstanding could also affect students preparing for accounting and finance careers.
Next Steps
Financial professionals are urged to reinforce the importance of distinguishing between period-based and point-in-time financial statements.
Educational resources should clearly emphasize this difference, especially for students and new analysts.
Expect further clarification from regulatory bodies like the SEC regarding financial statement presentation and interpretation to further clarify the importance of the information presented on them.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-04-26at10.39.54AM-4a117e7e494c422ca6480746c97612a8.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-03-aac8341b98da4fd3a4f13ed3ee7fa053.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-04-26at10.45.59AM-aab9d8741c8f4ee1aff95f057ca2ab3a.png)