What Happens To A Stock When A Company Is Acquired

The news breaks: a major corporation announces the acquisition of a smaller company. For investors holding stock in the acquired entity, a mix of excitement and uncertainty immediately sets in. The value of their investment, and the future of their portfolio, hang in the balance.
Understanding what happens to a stock during an acquisition is crucial for investors. It's more than just a ticker symbol changing; it's a complex process with various potential outcomes affecting shareholder value, future investment strategies, and overall market dynamics. This article will delve into the intricacies of acquisitions, exploring the common scenarios shareholders face, the factors influencing the final outcome, and potential strategies for navigating this significant corporate event. We will also touch on perspectives from both the acquiring and acquired companies.
The Acquisition Process: A Stockholder's Perspective
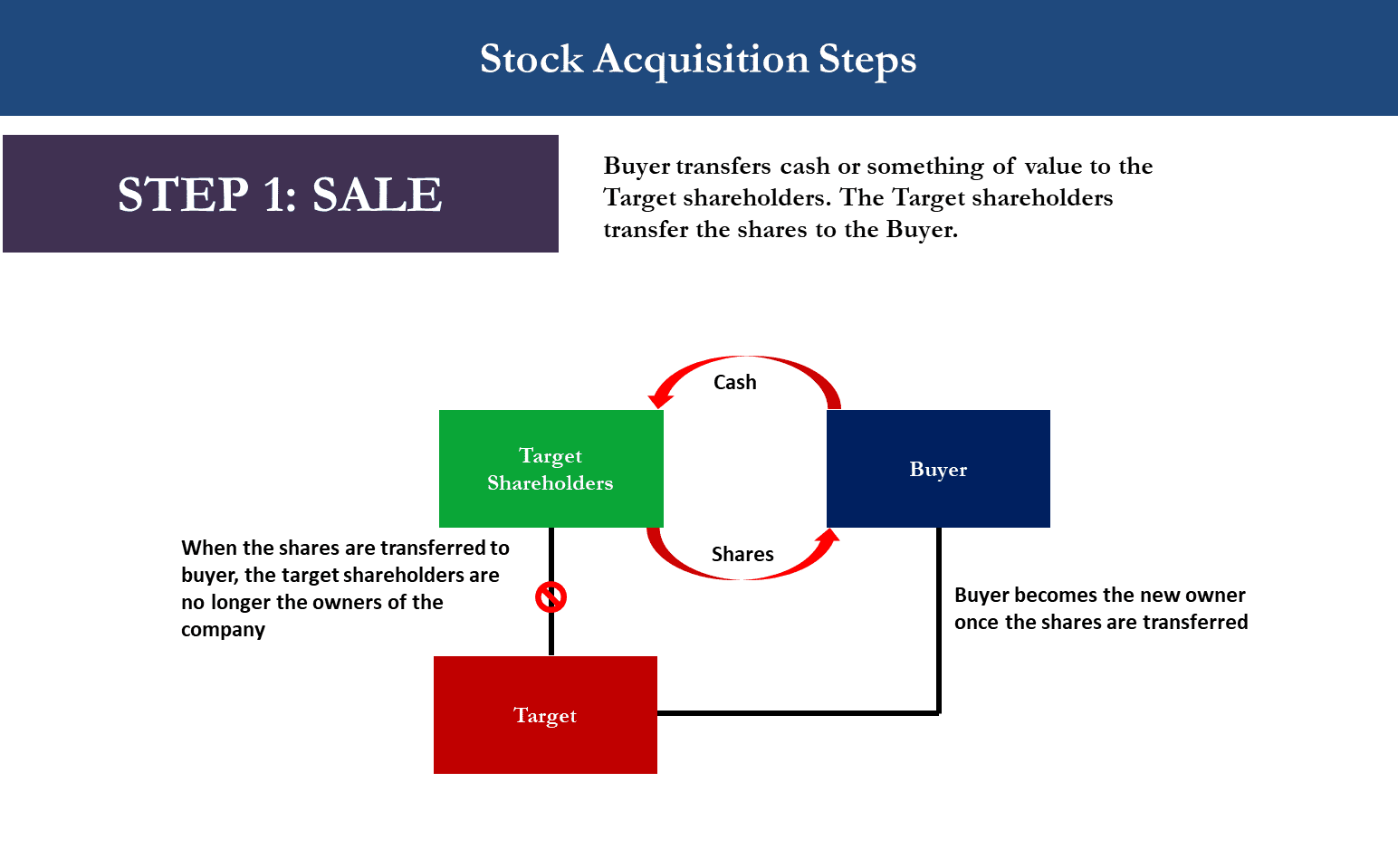
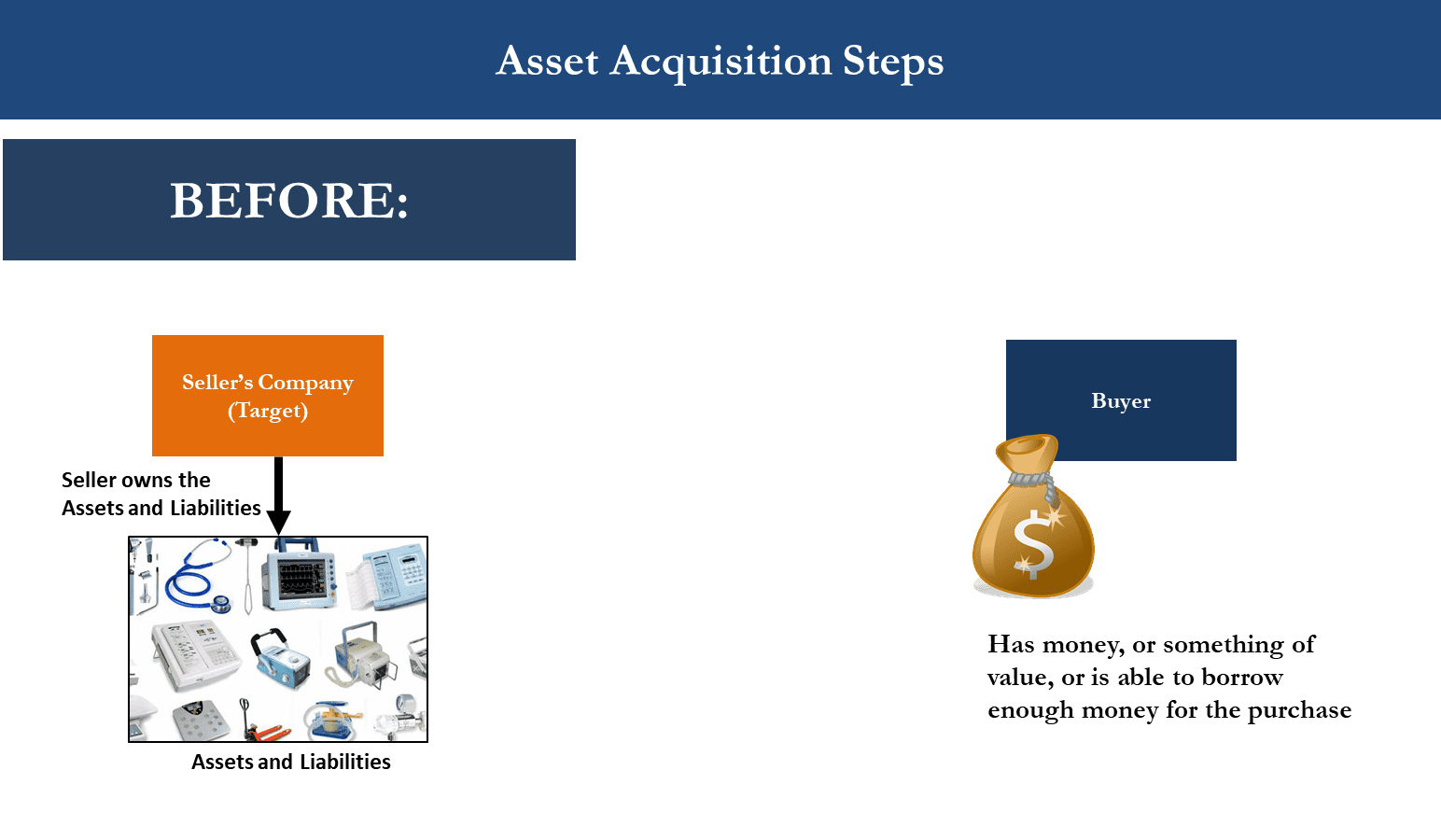
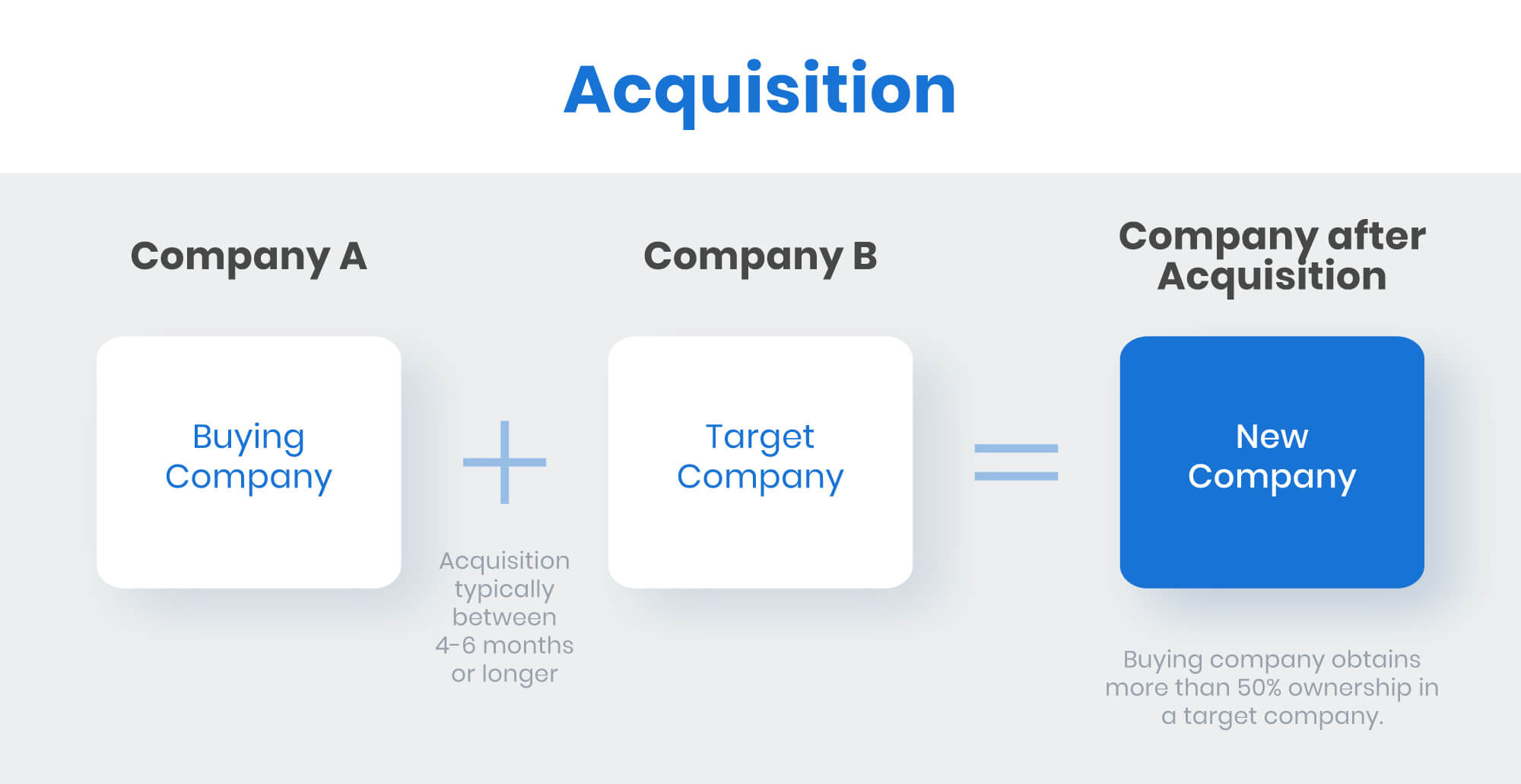
When a company is acquired, its stock typically ceases to exist as an independent entity. The acquiring company essentially purchases the assets and liabilities of the target company, including its outstanding shares.
Cash Offer
In a cash offer, the acquiring company offers to buy each share of the target company's stock for a specific price. This price is usually, but not always, higher than the market value of the stock before the announcement of the acquisition, representing a premium for shareholders.
Shareholders who accept the offer receive cash for their shares and relinquish their ownership in the company. Once the acquiring company secures enough shares (often a majority), the remaining shareholders are typically forced to sell their shares at the agreed-upon price, a process known as a "squeeze-out."
Stock Swap
A stock swap, or stock-for-stock deal, involves the acquiring company offering its own shares in exchange for the target company's shares. The exchange ratio is determined based on factors such as the relative valuation of the two companies.
Target company shareholders who accept the offer receive shares of the acquiring company, effectively becoming shareholders in the larger, combined entity. This allows shareholders to participate in the potential future growth of the merged organization, but also exposes them to the risks associated with the acquiring company's stock.
Hybrid Approach
Some acquisitions involve a combination of cash and stock. This allows the acquiring company to offer flexibility to the target company's shareholders.
Shareholders might be able to choose between receiving cash, stock, or a mix of both, subject to certain limitations. This hybrid approach can be attractive to shareholders with different investment objectives and risk tolerances.
Factors Influencing the Outcome
The ultimate fate of a stock during an acquisition depends on a variety of factors. These include the terms of the acquisition agreement, regulatory approvals, and shareholder votes.
Regulatory bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US, and equivalent agencies in other countries, scrutinize acquisitions to ensure they don't violate antitrust laws. If regulators block the acquisition, the deal may be terminated, and the target company's stock price could plummet.
Shareholder approval is often required, especially for stock swaps. If shareholders reject the acquisition, the deal could fall through, leading to uncertainty and potential losses for investors in the target company.
The market conditions at the time of the acquisition also play a significant role. A change in economic outlook or investor sentiment could affect the perceived value of both the acquiring and target companies, potentially impacting the final terms of the deal.
Perspectives from Both Sides
From the acquiring company's perspective, the acquisition is a strategic move aimed at expanding market share, acquiring new technologies, or achieving cost synergies. The goal is to create long-term value for its shareholders.
However, acquisitions also carry risks, such as overpaying for the target company, failing to integrate the two businesses effectively, or encountering unforeseen liabilities. A poorly executed acquisition can damage the acquiring company's stock price and reputation.
For the target company, an acquisition can provide access to greater resources, a larger customer base, and enhanced opportunities for growth. It can also provide an exit strategy for founders and early investors.
However, it can also lead to job losses, changes in corporate culture, and a loss of independence. The target company's management team may also be replaced or significantly restructured.
Navigating the Acquisition Landscape
Investors holding stock in a company targeted for acquisition should carefully consider their options. They should review the terms of the acquisition agreement, seek professional advice, and assess their own investment goals and risk tolerance.
It's crucial to understand the potential tax implications of the acquisition, particularly if it involves a cash payment. Investors may need to pay capital gains taxes on the profits from the sale of their shares.
Diversification is also a key strategy for mitigating risk. Holding a diversified portfolio can help reduce the impact of any single acquisition on an investor's overall returns.
Monitoring news and developments related to the acquisition is critical. Staying informed about regulatory approvals, shareholder votes, and any potential changes to the deal terms can help investors make informed decisions.
Looking Ahead
Acquisitions will continue to be a common feature of the business landscape. As industries evolve and companies seek to gain a competitive edge, mergers and acquisitions are likely to remain a popular strategy.
For investors, understanding the dynamics of acquisitions is essential for managing their portfolios and maximizing their returns. By carefully analyzing the terms of the deal, assessing the risks and opportunities, and seeking professional advice, investors can navigate the acquisition landscape with greater confidence.
Ultimately, the impact of an acquisition on a stock depends on a complex interplay of factors. Informed investors who understand these dynamics are better positioned to protect their investments and capitalize on opportunities that arise during this transformative corporate event. They must always keep their focus on doing their own research and remain vigilant about the companies they invest in.