What Happens When You Put An App In Deep Sleep
The notification popped up on Sarah's phone, a gentle nudge amidst the digital clamor of her day. "Putting Facebook to sleep to save battery," it read. She hadn't actively used the app in days, maybe weeks, and the phone, ever vigilant, was taking matters into its own hands. A tiny question formed in her mind: What *actually* happens when an app goes into this deep digital slumber?
That question, pondered by Sarah and countless others, gets to the heart of a crucial aspect of modern smartphone management: App deep sleep. This feature, increasingly common in both Android and iOS operating systems, represents a sophisticated method of optimizing battery life and system performance. Understanding its mechanics and consequences provides users with greater control over their digital environment.
The Silent Energy Drain: A Background
Smartphones are power-hungry devices. Even when they appear idle, many apps continue to operate in the background, consuming valuable battery life and system resources.
This background activity can include checking for updates, syncing data, sending notifications, and even tracking location. While some of these processes are essential, others are less critical and contribute to a gradual, often unnoticed, drain on battery power.
Early attempts to manage battery life involved manual closing of apps or relying on rudimentary task managers. However, these methods were often ineffective and required constant user intervention. The introduction of app deep sleep marked a significant step forward in automated power management.
The Deep Sleep Process: A Closer Look
When an app is put into deep sleep, the operating system essentially restricts its ability to run in the background. This restriction encompasses several key areas.
First, the app is prevented from initiating network activity. This means it can't connect to the internet to download updates, sync data, or send information.
Second, the app's ability to run scheduled tasks or background services is severely limited. These tasks, often invisible to the user, can consume significant processing power and battery life.
Third, the app is typically prevented from sending push notifications, unless these notifications are deemed high-priority or essential (e.g., critical security alerts).
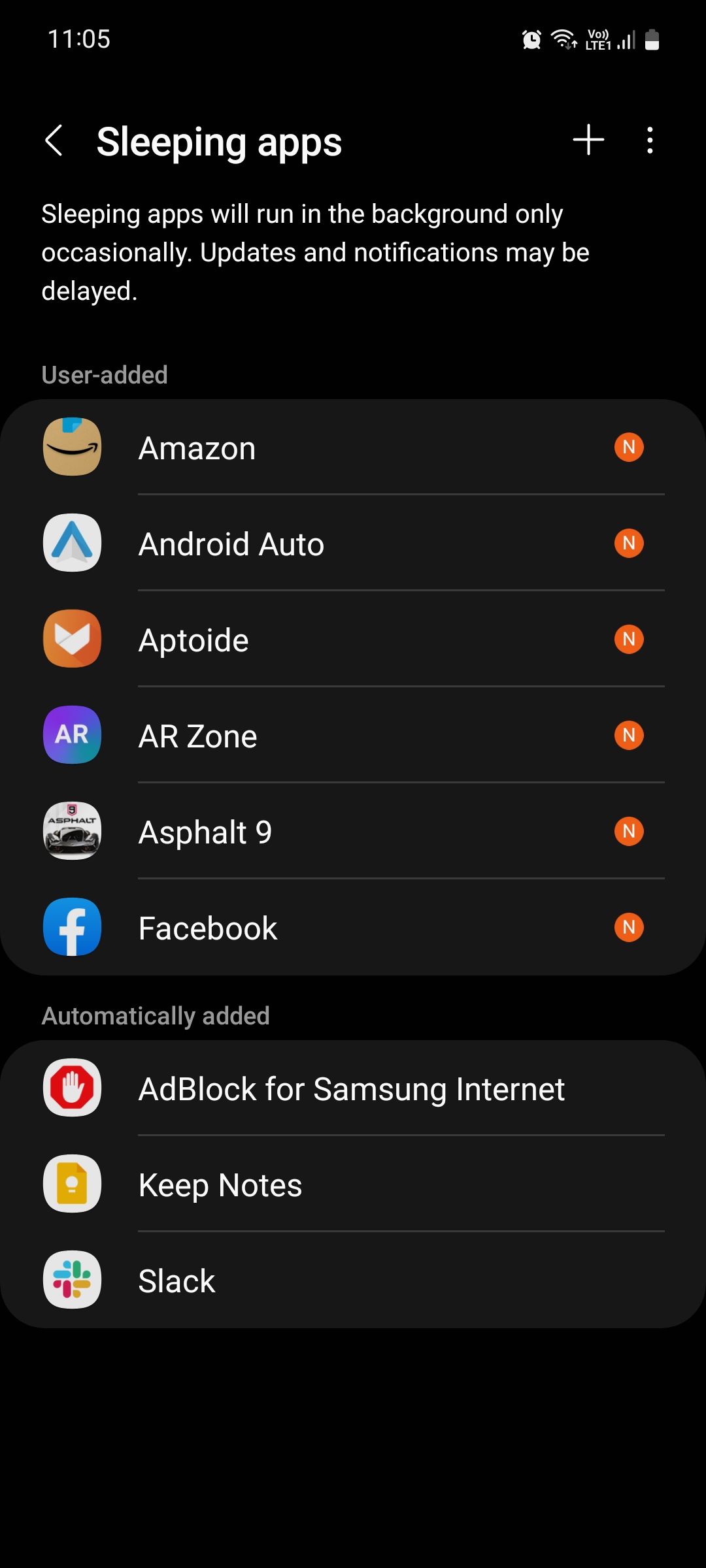
Importantly, deep sleep doesn't completely disable the app. It remains installed on the device and can be launched and used normally by the user. Only when the app is not actively used for an extended period does it enter this state of dormancy.
The Benefits of Deep Sleep: Battery and Beyond
The primary benefit of app deep sleep is, unsurprisingly, improved battery life. By preventing unnecessary background activity, the feature significantly reduces the drain on the battery, allowing the phone to last longer between charges.
This is particularly beneficial for users who have many apps installed or who use their phones extensively throughout the day. Samsung, in its official documentation on their One UI (Android based OS), highlights the intelligent battery management as a key feature, attributing it to improved performance and longer battery lifespan.
Beyond battery life, deep sleep can also improve overall system performance. By reducing the number of apps running in the background, the phone has more resources available for actively used applications. This can lead to faster app loading times, smoother multitasking, and a more responsive user experience.
According to tests done by various tech reviewers, applying deep sleep on rarely used apps can improve RAM availability by up to 15%, thus, reducing overall system load and improving responsiveness.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While app deep sleep offers numerous advantages, it's important to be aware of potential drawbacks. One common concern is the delayed delivery of notifications. If an app is in deep sleep, it may not be able to send notifications until it is actively launched by the user. This can be problematic for apps that rely on timely notifications, such as messaging apps or news aggregators.
Another potential issue is the disruption of background processes that users may find important. For example, a fitness tracking app might not be able to accurately record steps or activity data if it is in deep sleep. Similarly, a cloud storage app might not be able to automatically sync files in the background.
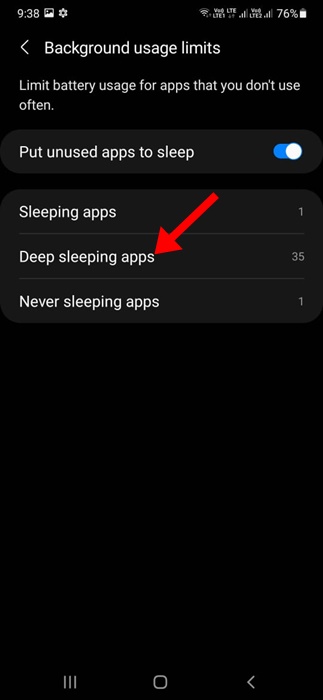
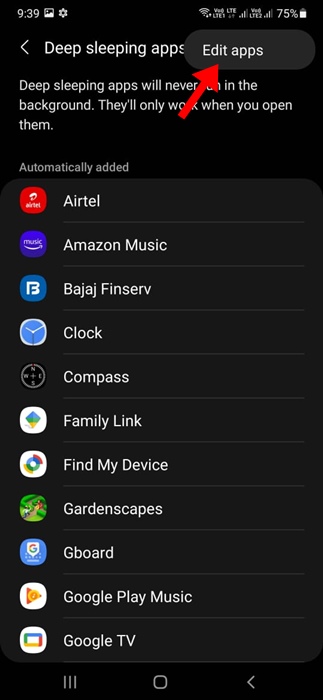
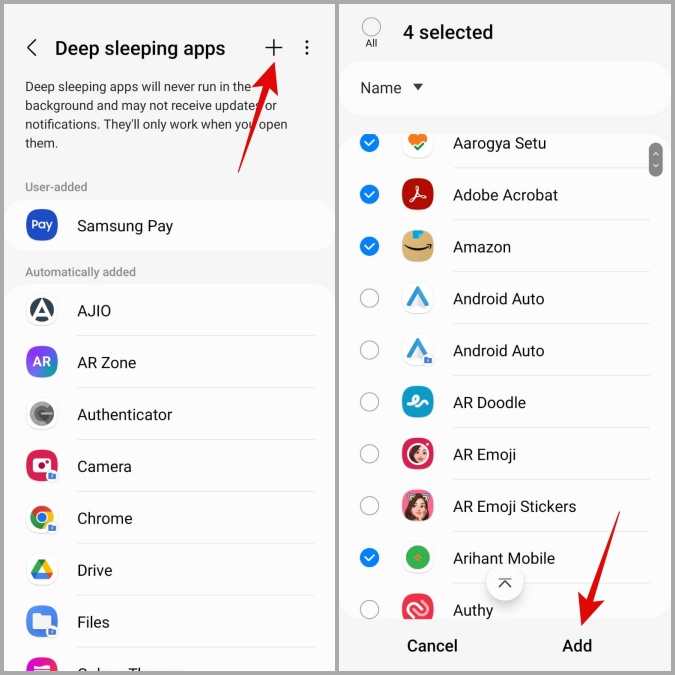
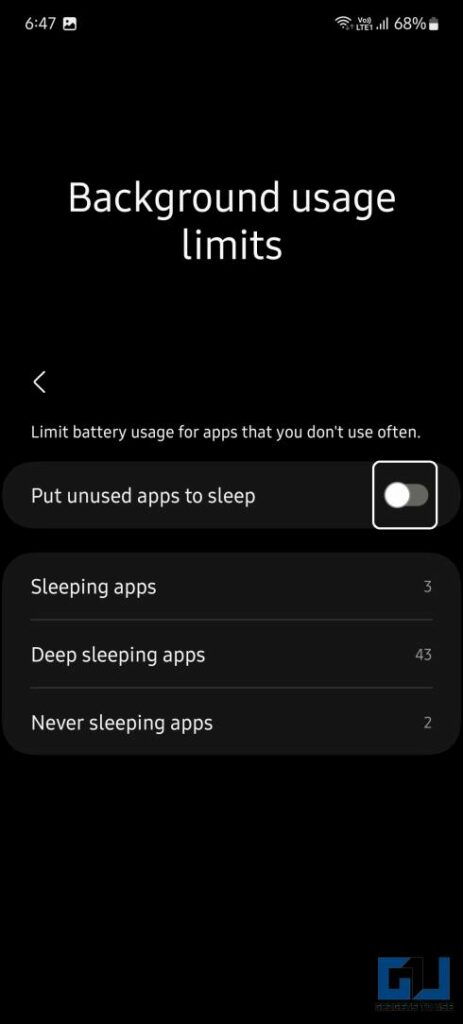
To mitigate these issues, most operating systems allow users to customize deep sleep settings. Users can typically exclude specific apps from deep sleep, ensuring that they continue to function normally in the background. They can also adjust the duration of inactivity required before an app enters deep sleep.
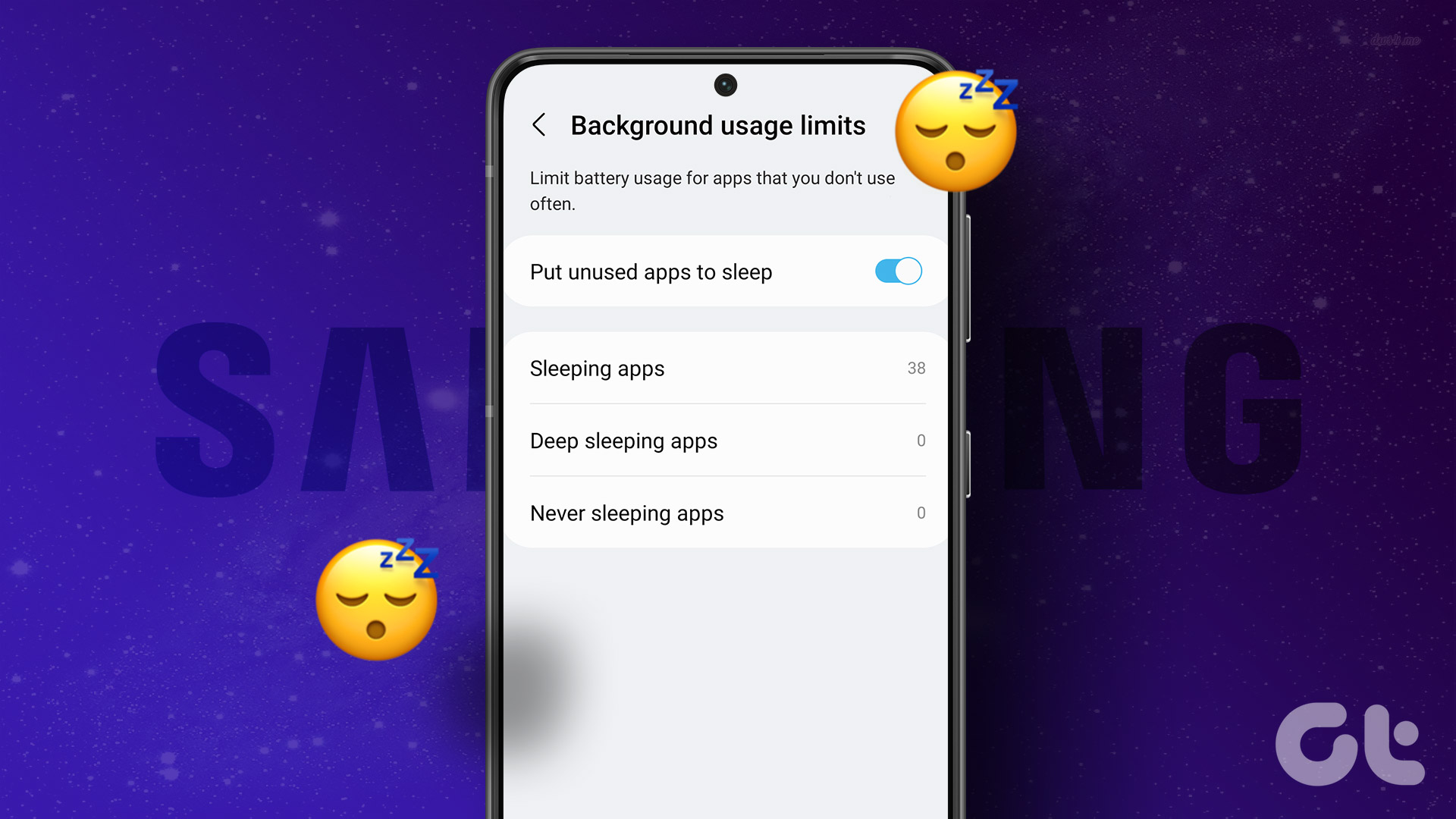
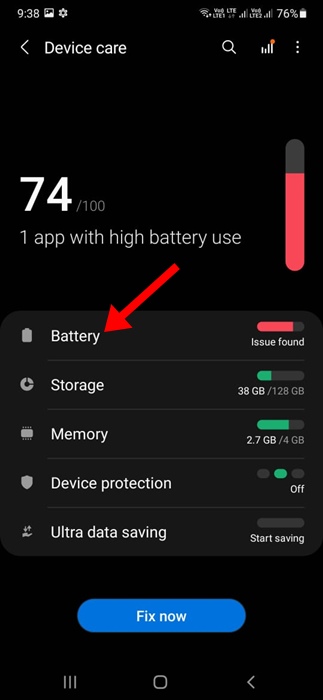
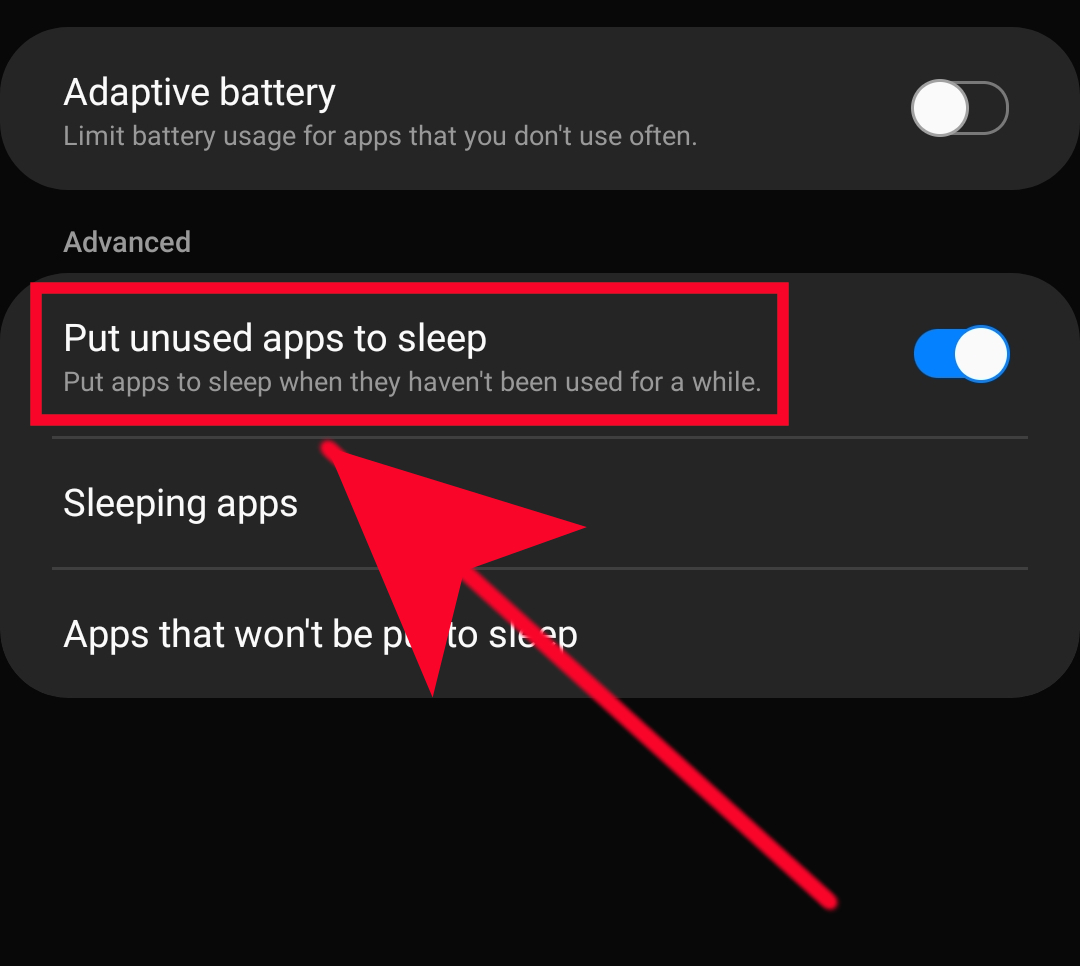
How to Manage Deep Sleep Settings
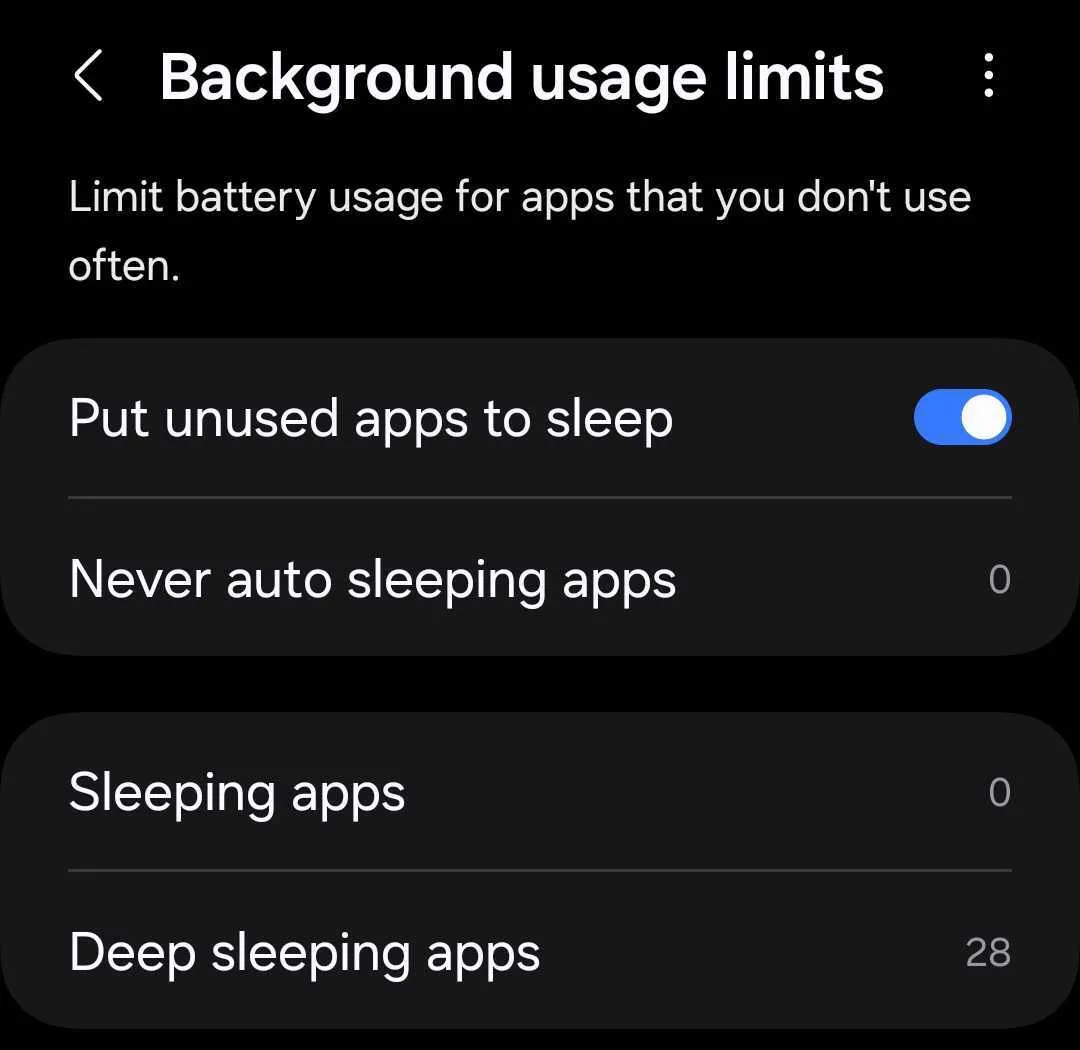
Managing deep sleep settings is generally straightforward. On Android devices, the feature is often found within the battery settings or device care section. Users can typically view a list of apps that are currently in deep sleep and manually add or remove apps from the list.
Similarly, on iOS devices, the "Background App Refresh" setting allows users to control which apps are allowed to run in the background. While iOS doesn't explicitly use the term "deep sleep," disabling background app refresh effectively achieves a similar result. Apple's optimization strategies automatically suspend apps not in active use, conserving resources. Independent testing shows a comparable energy saving when compared to Android's deep sleep feature.
It's recommended to review these settings periodically and adjust them based on individual usage patterns and preferences. Apps that are rarely used and don't require timely notifications can be safely put into deep sleep. Apps that are essential for communication, productivity, or other important tasks should be excluded.
The Future of Power Management
App deep sleep represents a significant advancement in smartphone power management, but it's likely just one step in an ongoing evolution. As devices become more powerful and feature-rich, the need for intelligent power optimization will only increase.
Future iterations of app deep sleep may incorporate more sophisticated algorithms that can dynamically adjust app behavior based on usage patterns and context. For example, an app might be allowed to run in the background during certain hours of the day (e.g., during the workday) but be put into deep sleep during other times (e.g., overnight).
Additionally, artificial intelligence and machine learning could play a greater role in identifying and optimizing power-hungry apps. These technologies could analyze app behavior to identify inefficiencies and suggest ways to reduce power consumption.
"The goal is to create a seamless and transparent user experience where power management happens automatically in the background, without requiring constant user intervention," said a senior software engineer at Google, speaking on the condition of anonymity. This vision suggests a future where smartphones are even more intelligent and efficient in managing their resources.
A Wake-Up Call for Digital Habits
Ultimately, the story of app deep sleep isn't just about technology; it's also about our relationship with our devices. It serves as a gentle reminder that we are in control of our digital environment and that we have the power to make choices that improve our battery life, system performance, and overall well-being.
By understanding how app deep sleep works and taking the time to manage our app settings, we can take greater ownership of our digital habits. This, in turn, can lead to a more mindful and productive relationship with our smartphones.
So, the next time you see that notification about putting an app to sleep, don't just dismiss it. Take a moment to consider the implications and make a conscious decision about whether that app truly needs to be running in the background. You might be surprised at the positive impact it has on your phone's performance and your own digital well-being. Maybe Sarah will start using it more often!