What Is Considered A Commercial Vehicle In California
Confusion reigns supreme as many California drivers grapple with understanding what exactly constitutes a commercial vehicle. Misclassification can lead to hefty fines, license suspensions, and even vehicle impoundment.
This article breaks down the complex definition of a commercial vehicle in California, clarifying the key factors that determine its classification and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
Defining the Commercial Vehicle in California
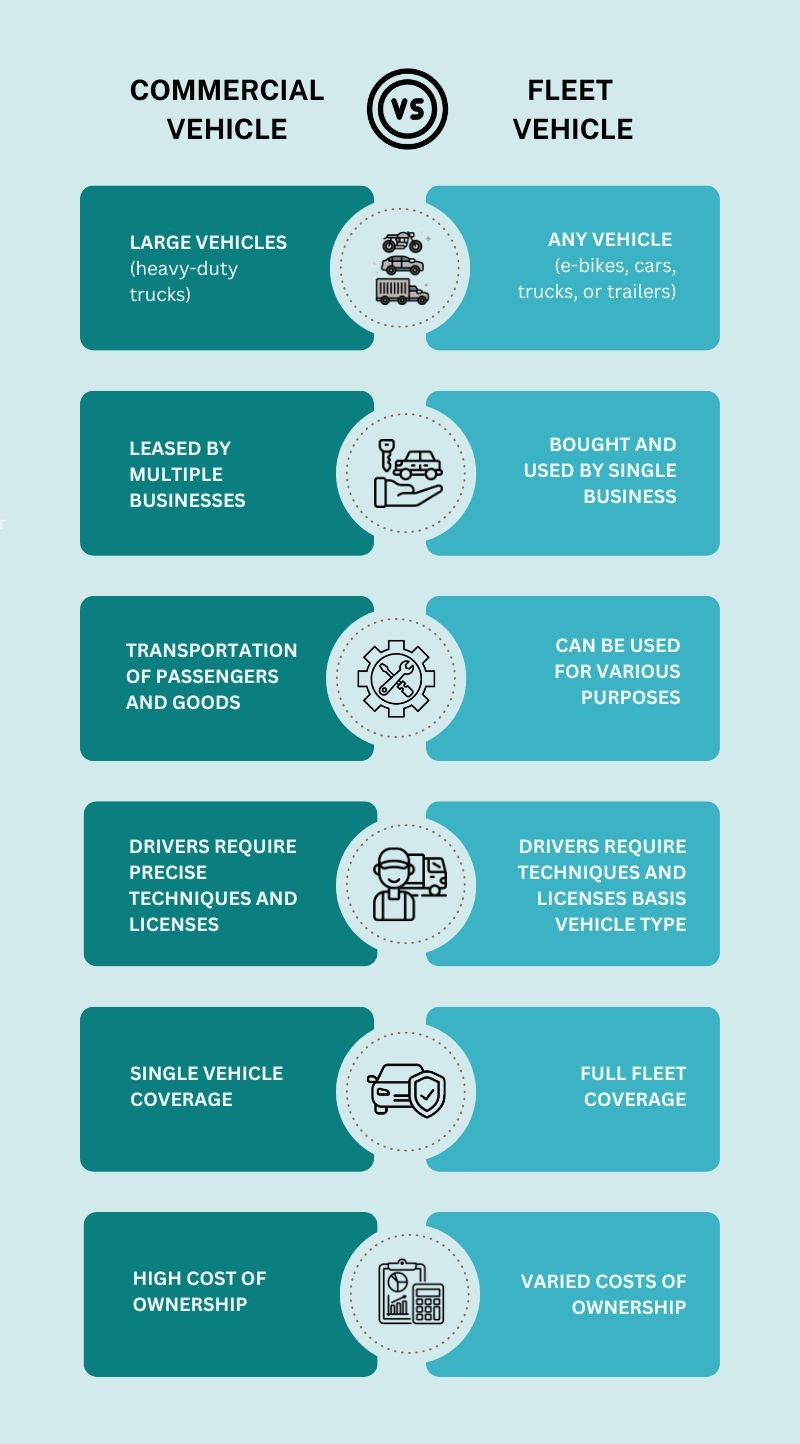
California Vehicle Code (CVC) Section 15210 defines a commercial vehicle broadly. It encompasses any vehicle used for the transportation of property, passengers, or for commercial purposes.
This definition extends beyond obvious examples like semi-trucks and buses. It includes vehicles of varying sizes and configurations.
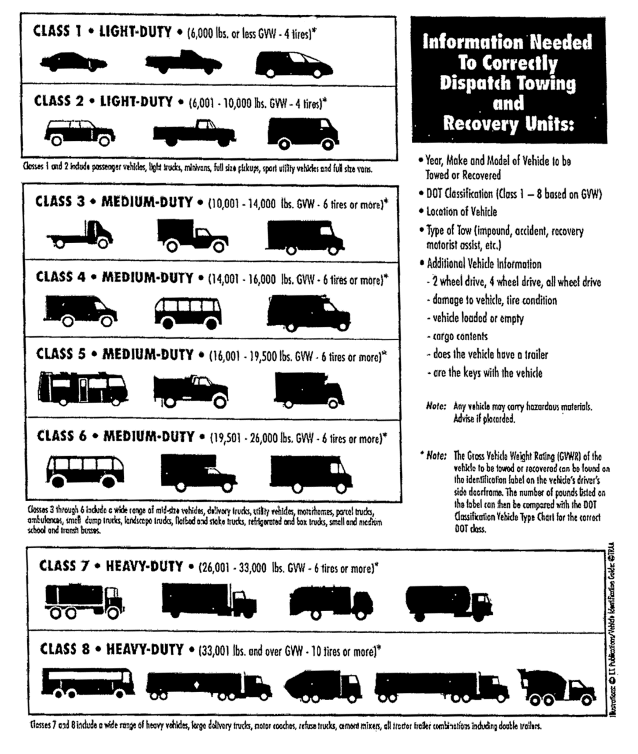
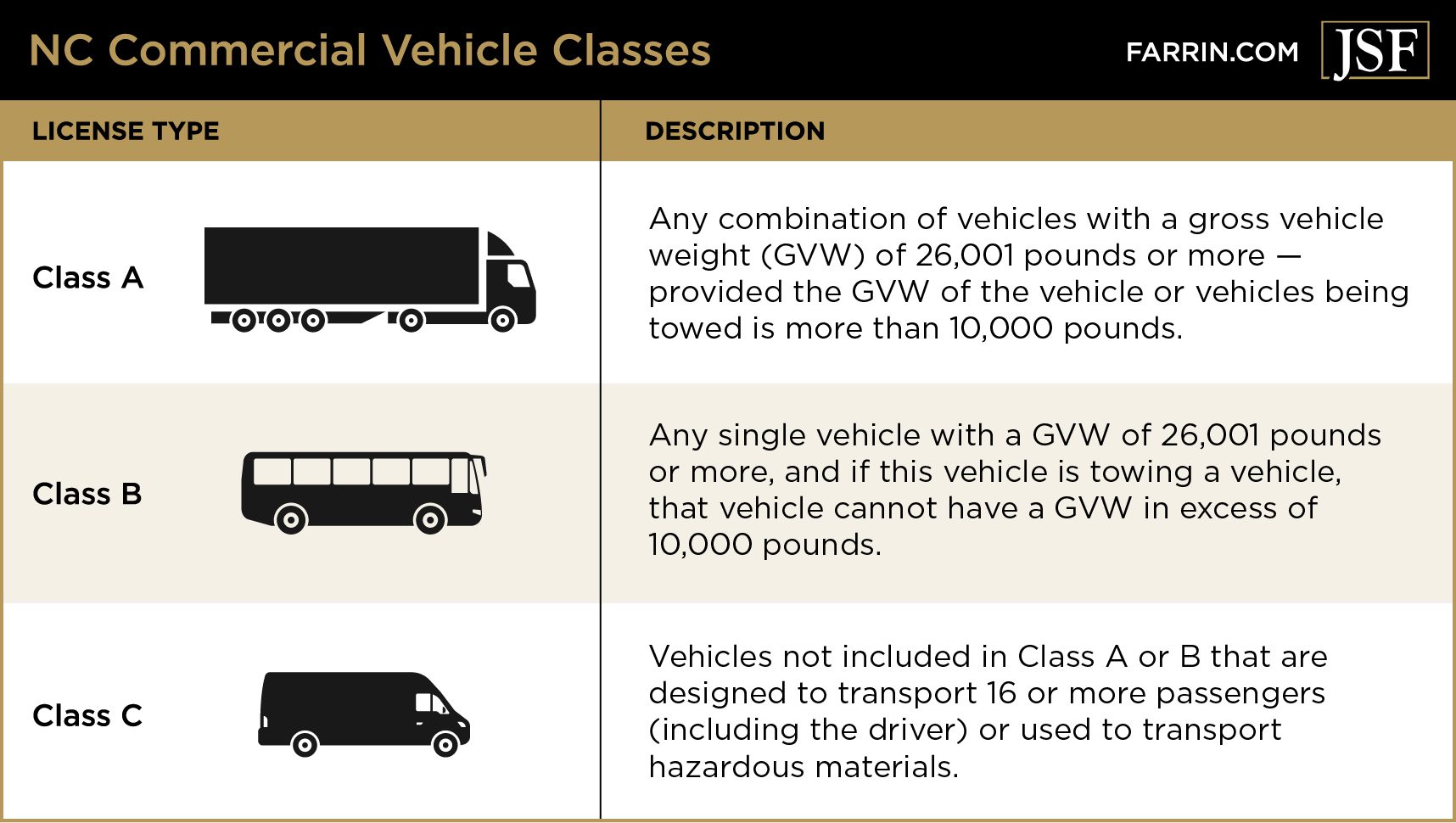
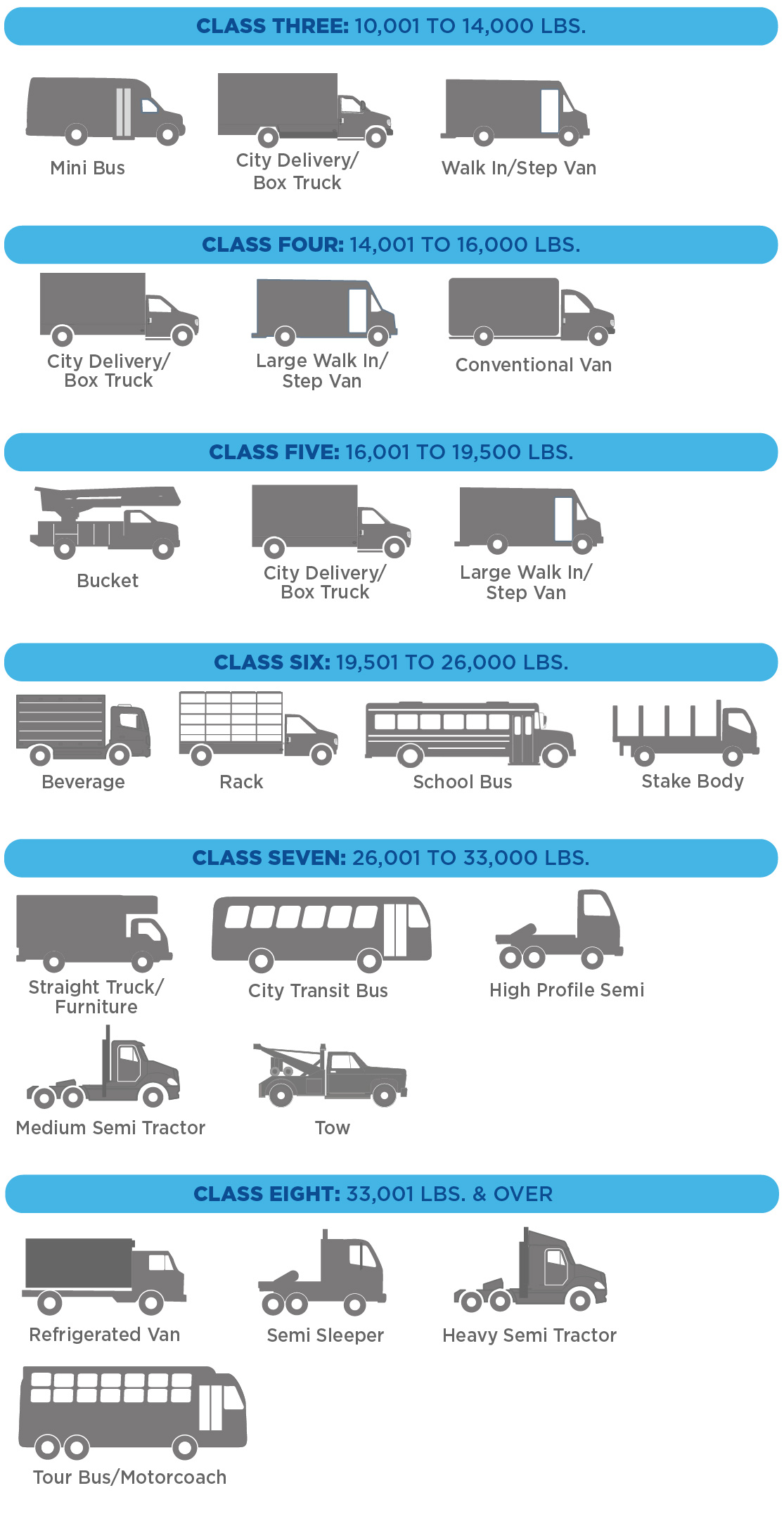
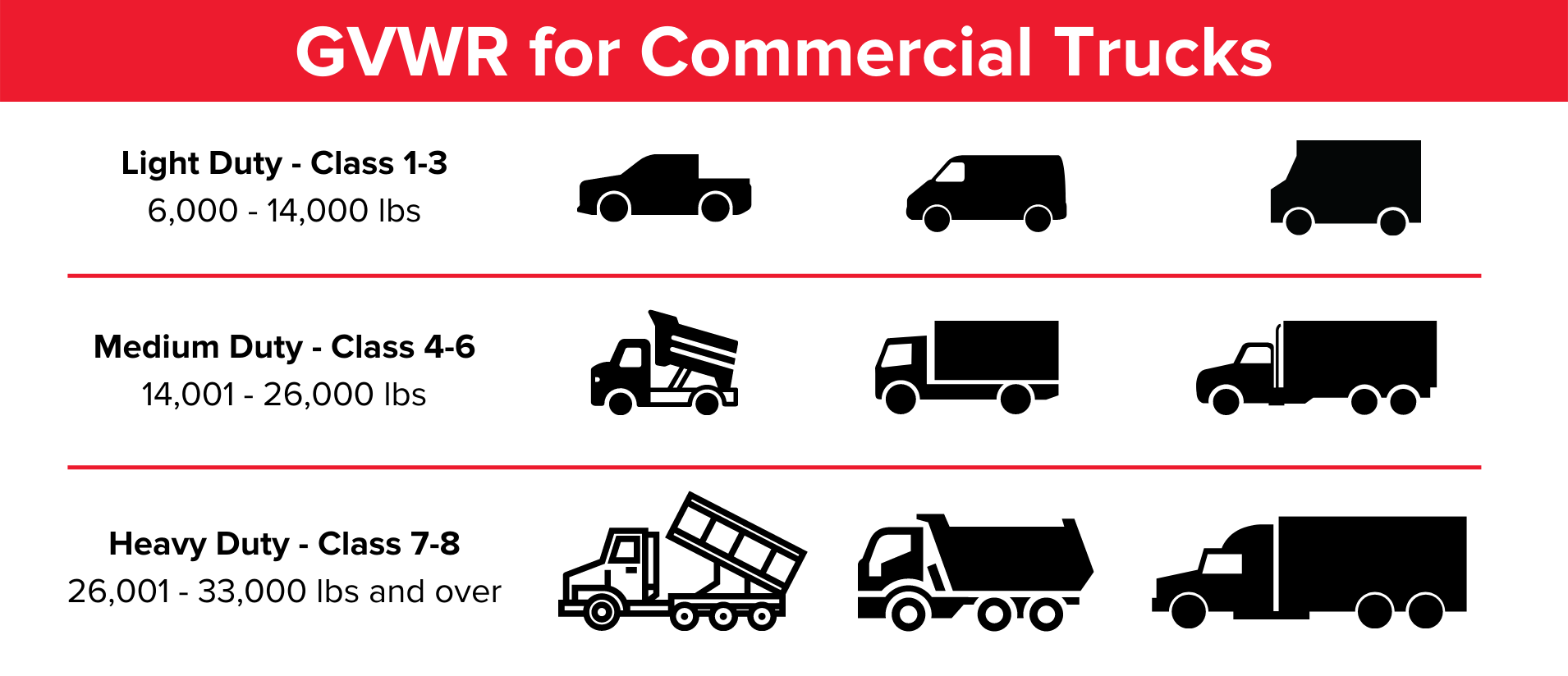
Weight Matters: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
One of the most critical factors is the vehicle's Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). This is the maximum weight the vehicle is designed to safely operate at, including the vehicle itself, passengers, and cargo.
A vehicle with a GVWR of 10,001 pounds or more is generally considered a commercial vehicle, regardless of its actual use. This triggers specific regulations.
According to the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV), this weight threshold necessitates compliance with stricter safety standards. This includes mandatory inspections and specific driver licensing requirements.
Commercial Use: Beyond Weight
Even if a vehicle has a GVWR below 10,001 pounds, it can still be classified as commercial. This happens if it is used for commercial purposes.
Commercial purposes include transporting goods or passengers for hire or profit. Examples include delivery vehicles, taxis, and ride-sharing services.
For example, a pickup truck used to transport tools and materials to a construction site for a paid project falls under this category. This applies even if the truck's GVWR is under the 10,001-pound threshold.
Passenger Transportation and Commercial Designation
Vehicles designed, used, or maintained to transport more than 10 passengers, including the driver, for compensation, are commercial vehicles. This applies regardless of GVWR.
This definition primarily targets shuttle services, tour buses, and other similar passenger transport operations. The key element is transporting passengers for compensation.
School buses, however, are subject to different regulations despite transporting passengers. This is because they operate under a separate set of rules and guidelines from the California Highway Patrol.
Hazardous Materials and Commercial Status
Any vehicle used to transport hazardous materials in quantities requiring placarding under federal regulations is automatically considered a commercial vehicle. This applies irrespective of the vehicle's GVWR or the nature of the business.
Transporting hazardous materials necessitates specialized training, endorsements on the driver's license, and adherence to stringent safety protocols. These are enforced by the California Department of Toxic Substances Control (DTSC).
Ignoring these regulations can result in severe penalties, including substantial fines and criminal charges.
Licensing and Compliance: What You Need to Know
Operating a commercial vehicle in California demands specific licensing requirements. This typically involves obtaining a Commercial Driver's License (CDL).
The type of CDL required depends on the GVWR of the vehicle, the type of cargo being transported, and the number of passengers.
Drivers must also comply with Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) regulations, including hours-of-service rules, drug and alcohol testing, and vehicle inspection requirements.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Operating a commercial vehicle without the proper license, permits, or insurance can lead to severe consequences. These include substantial fines, vehicle impoundment, and even criminal charges.
The California Highway Patrol (CHP) actively enforces commercial vehicle regulations. They conduct regular inspections and roadside checks to ensure compliance.
Furthermore, non-compliance can affect the driver's driving record. It can lead to license suspension or revocation.
Next Steps: Ensuring Compliance
If you operate a vehicle for commercial purposes, it is crucial to understand your obligations under California law. Consulting with the California DMV or a qualified legal professional is highly recommended.
Familiarize yourself with the relevant sections of the California Vehicle Code and FMCSA regulations. This proactive approach can save you from costly fines and legal troubles.
The California DMV offers resources and guidance on commercial vehicle regulations. Continuously monitor any changes or updates to the laws to maintain compliance.