What Is Needed To Determine A Facility's Cmi
Determining a healthcare facility's Case Mix Index (CMI) is crucial for understanding its patient complexity and resource utilization, impacting reimbursement, quality reporting, and strategic planning. But what exactly goes into calculating this important metric?
The Case Mix Index (CMI) is a relative value assigned to a diagnosis-related group (DRG) reflecting the average resources used to treat patients in that DRG. Facilities with higher CMI values generally treat more complex cases, requiring more resources.
Understanding the Core Components of CMI Calculation
Calculating a facility's CMI requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating patient data, coding accuracy, and a thorough understanding of reimbursement methodologies. Here's a breakdown of the key elements:
Accurate and Complete Coding
The foundation of any CMI calculation is precise and comprehensive medical coding. This involves assigning appropriate ICD-10 codes (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) to diagnoses, procedures, and other relevant patient information.
Coders must meticulously review medical records to capture all conditions and services that impact the DRG assignment. Incomplete or inaccurate coding can significantly skew the CMI.
DRG Assignment
Based on the coded data, each patient encounter is assigned a Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG). DRGs categorize patients with similar diagnoses, procedures, and resource consumption patterns.
Software, often integrated into electronic health record (EHR) systems, automates DRG assignment based on algorithms defined by Medicare and other payers. These algorithms are regularly updated to reflect changes in medical practice and coding guidelines.
Relative Weight Determination
Each DRG has an assigned relative weight, reflecting the average cost of treating patients within that DRG compared to the average cost of all Medicare patients. These relative weights are published annually by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
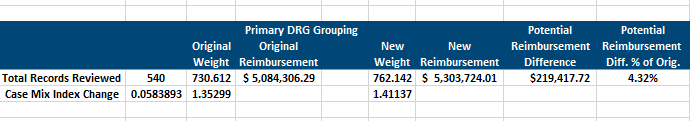
A DRG with a relative weight of 1.0 represents the average cost, while a DRG with a relative weight of 2.0 indicates that it costs twice as much to treat patients in that DRG compared to the average. These weights are crucial for the CMI calculation.
Calculating the Facility's CMI
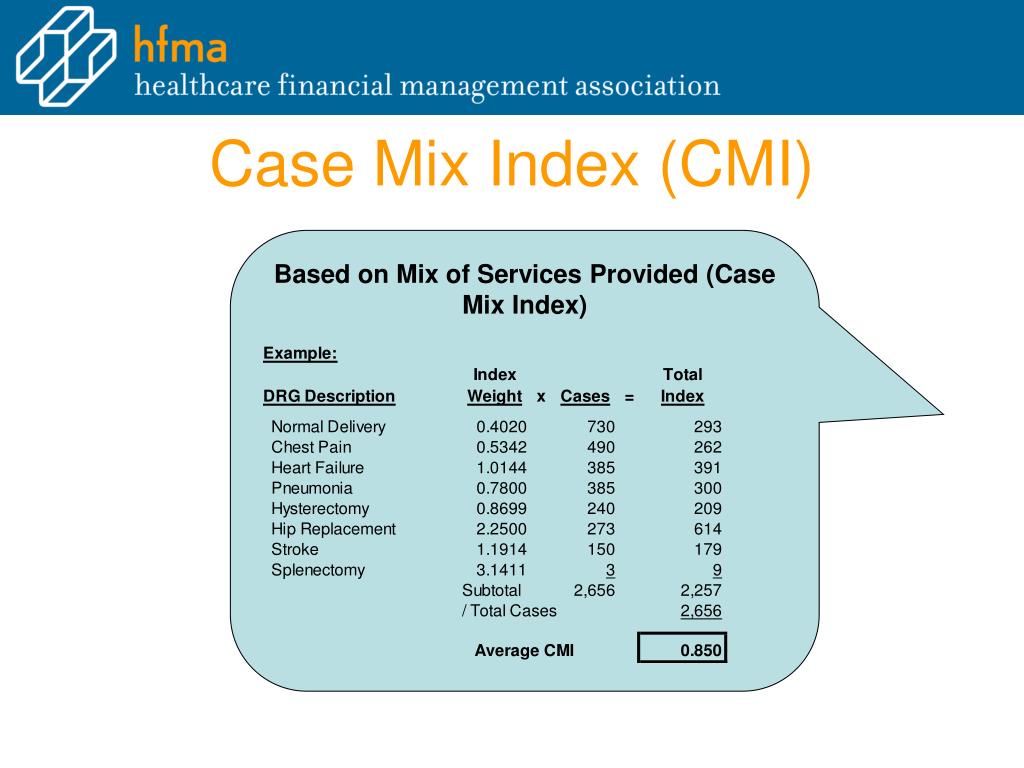
The facility's CMI is calculated by summing the relative weights of all Medicare discharges within a specific period (usually a year) and dividing by the total number of Medicare discharges.
The formula is: CMI = (Sum of DRG Relative Weights) / (Total Number of Discharges). This calculation provides a single number representing the average resource intensity of the facility's patient population.
Data Sources and Validation
The data required for CMI calculation originates from various sources within a healthcare facility. These include patient medical records, billing systems, and coding departments.
Rigorous data validation processes are essential to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information used in the calculation. This includes regular audits of coding practices and reconciliation of data between different systems.
Data integrity is vital for accurate CMI reporting and informed decision-making.
Significance and Implications of CMI
The CMI plays a significant role in hospital reimbursement under the Medicare Prospective Payment System (PPS). Higher CMI values generally translate to higher payments, reflecting the facility's treatment of more complex and resource-intensive cases.
However, CMI is not solely about reimbursement. It also serves as a benchmark for comparing a facility's performance against its peers.
Hospitals can use CMI data to identify areas for improvement in coding practices, resource allocation, and clinical efficiency.
Challenges and Future Directions
Maintaining an accurate CMI requires ongoing effort and vigilance. Coding changes, regulatory updates, and shifts in patient demographics can all impact the CMI.
Facilities must invest in training and education for coding staff to ensure compliance with the latest guidelines. Leveraging technology, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP), can help automate coding processes and improve accuracy.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the CMI will remain a critical metric for understanding patient complexity and resource utilization.
In conclusion, determining a facility's CMI is a complex process that relies on accurate coding, appropriate DRG assignment, and a thorough understanding of relative weights. The CMI's impact extends beyond reimbursement, influencing quality reporting, strategic planning, and the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery. By prioritizing data integrity and investing in robust coding practices, healthcare facilities can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their CMI, ultimately leading to better patient care and financial stability.