What Is The Business Cycle Definition

Imagine a serene lake, its surface rippling gently in a rhythmic dance. At times, the water rises, reflecting the clear sky with vibrant intensity. Then, it recedes, revealing the lakebed, calm and still. This ebb and flow, this constant motion, mirrors the very essence of the business cycle, the heartbeat of our economy.
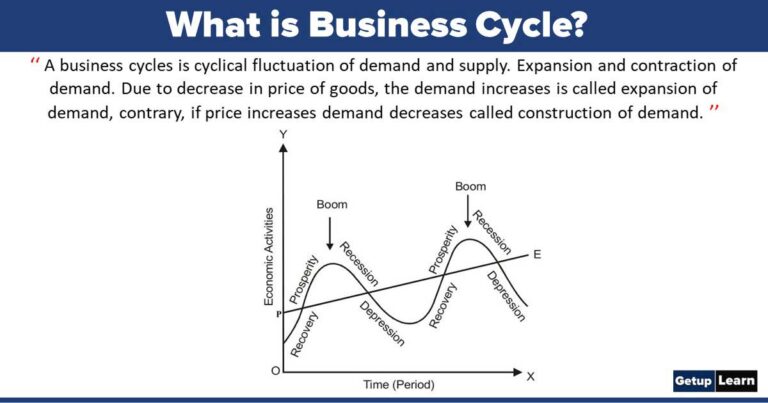
The business cycle, at its core, is the recurring pattern of expansion and contraction in economic activity that nations experience. Understanding this cycle is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike, as it helps them anticipate changes and make informed decisions.
Understanding the Business Cycle
The business cycle isn't a recent invention. It's been observed and studied for centuries. Early economists noticed that economies weren't static; they naturally went through periods of growth and decline.
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), a leading economic research organization, officially defines a recession as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months." Their pronouncements on the start and end dates of recessions are widely respected.
The Four Phases
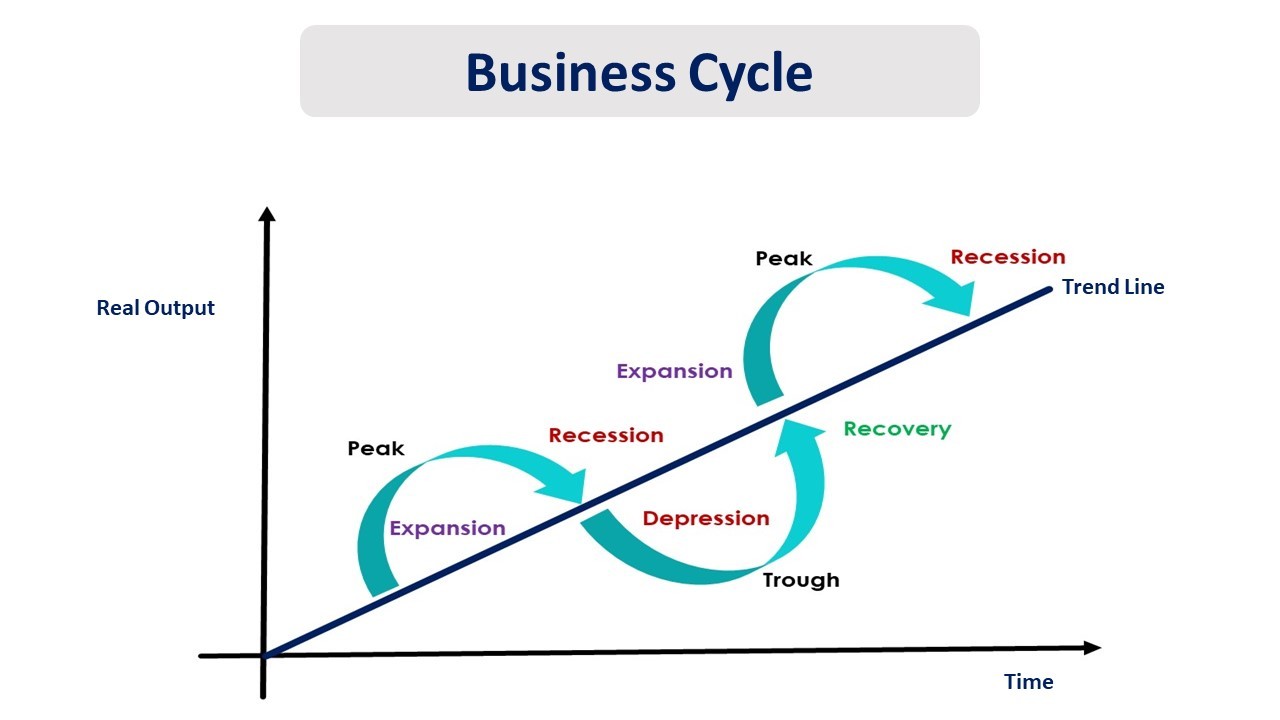
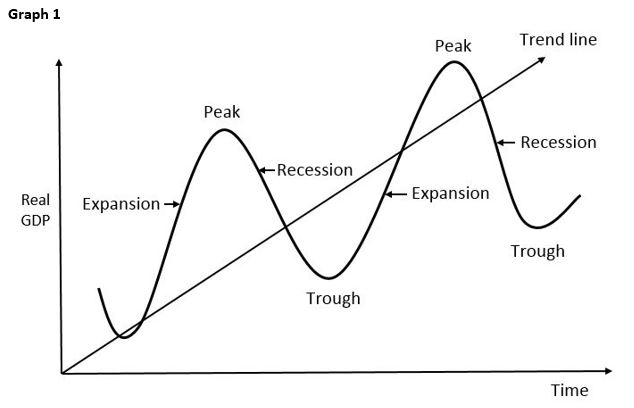
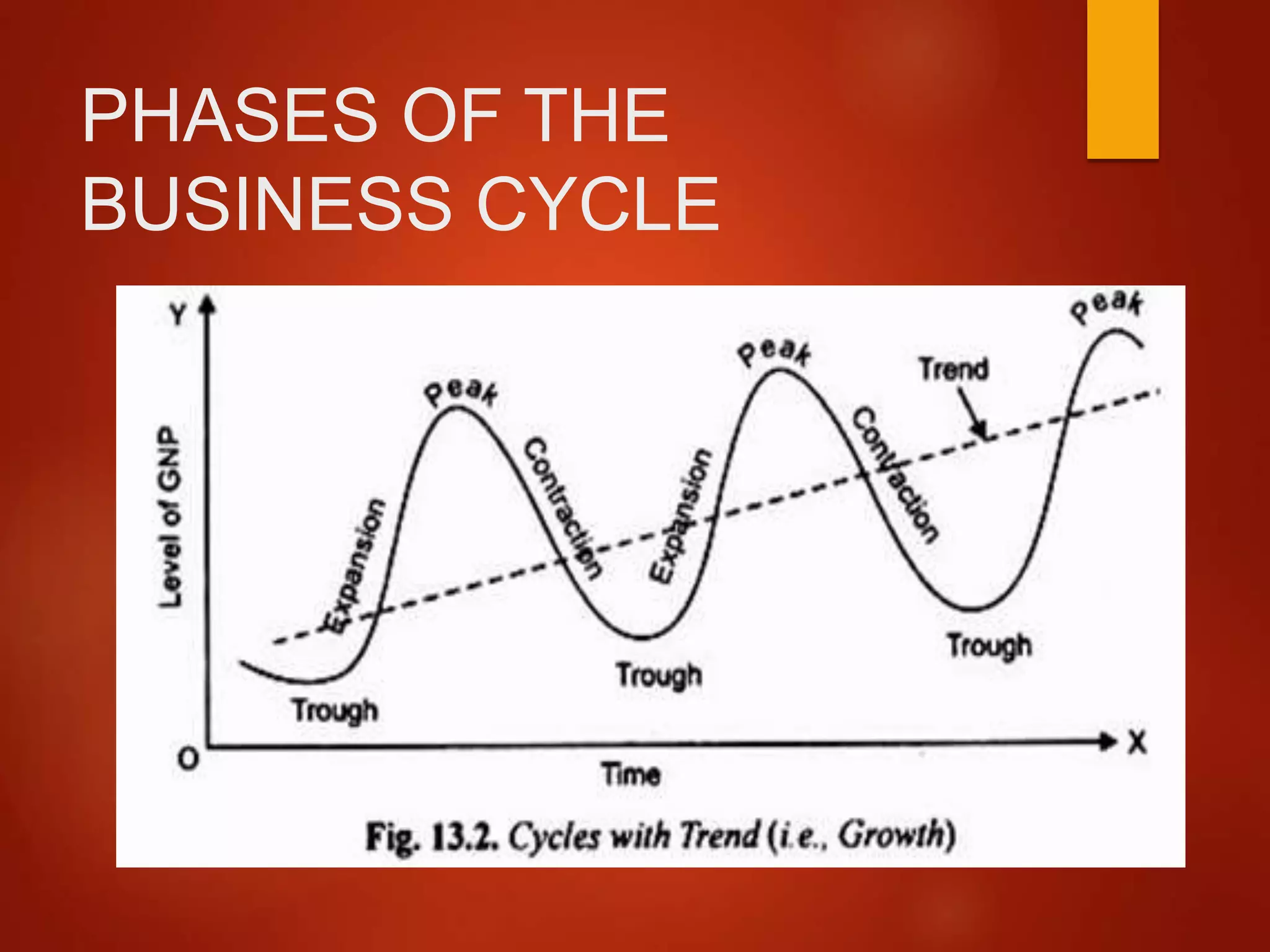
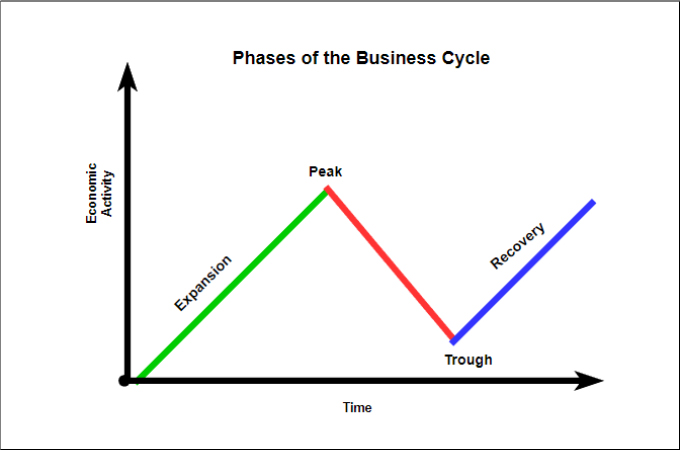
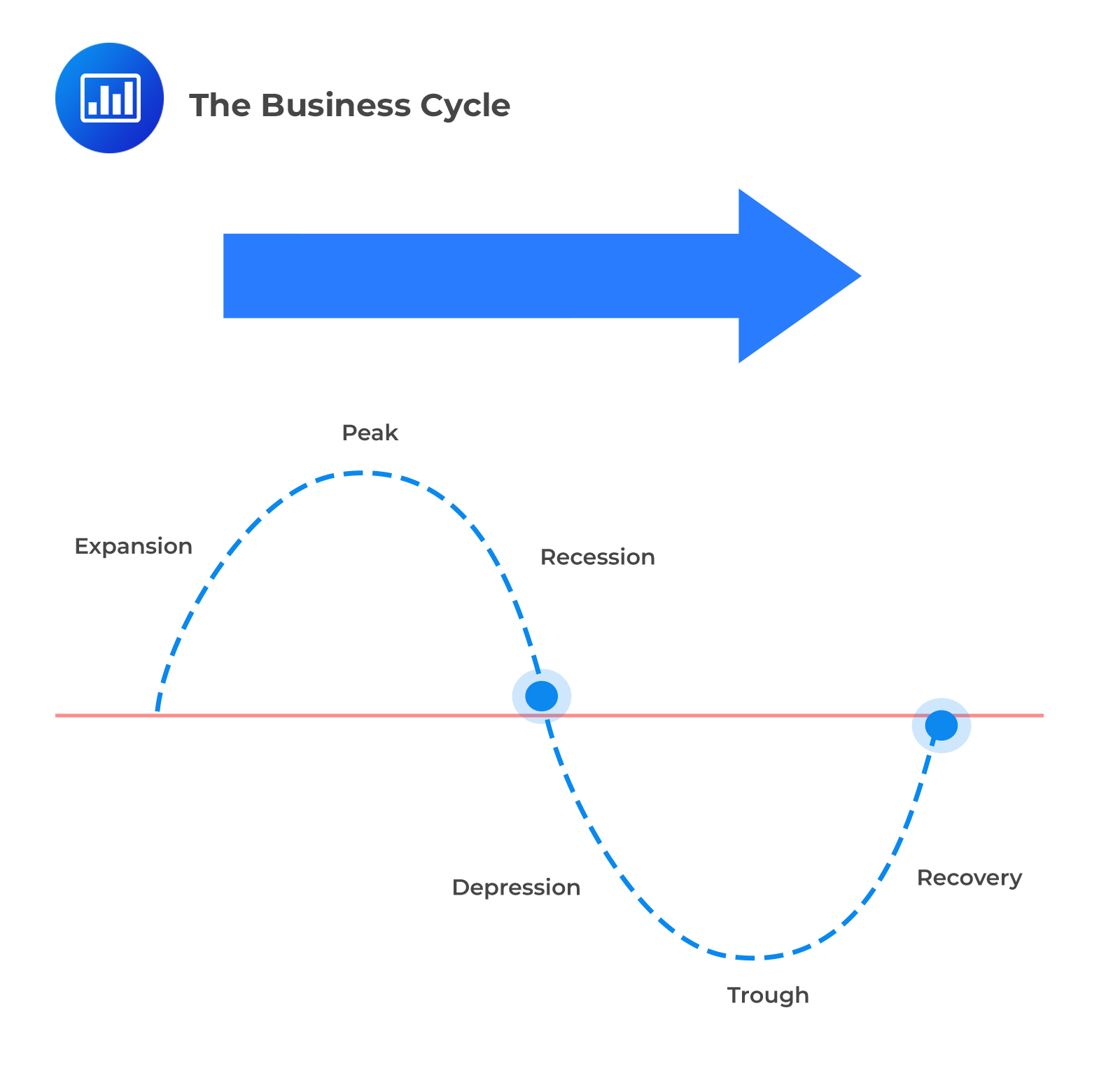
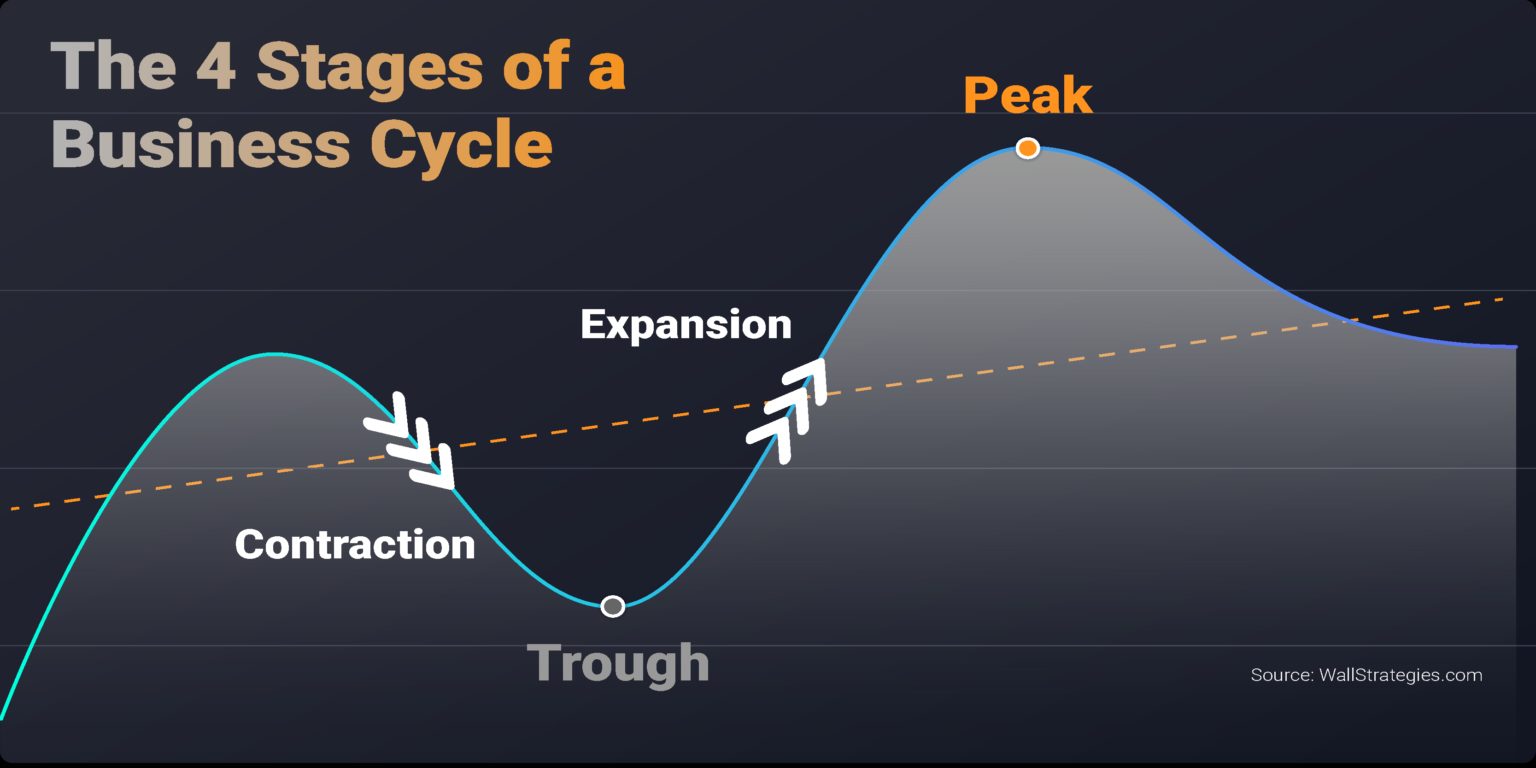
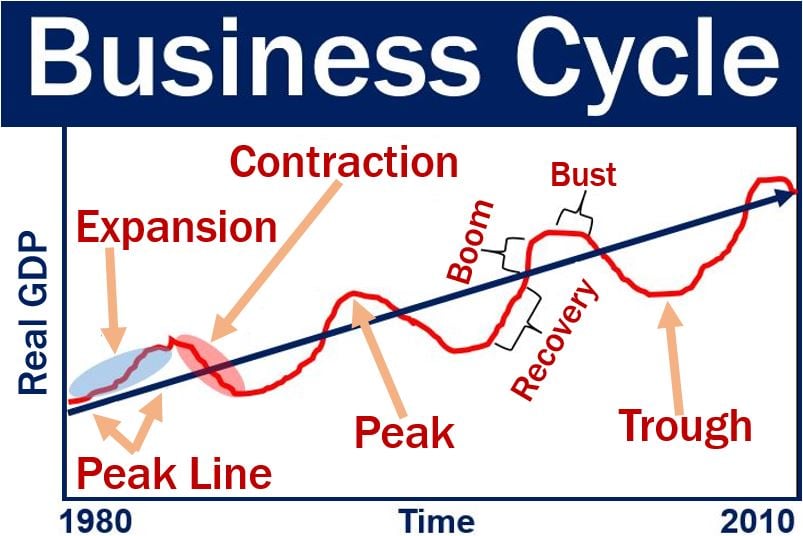
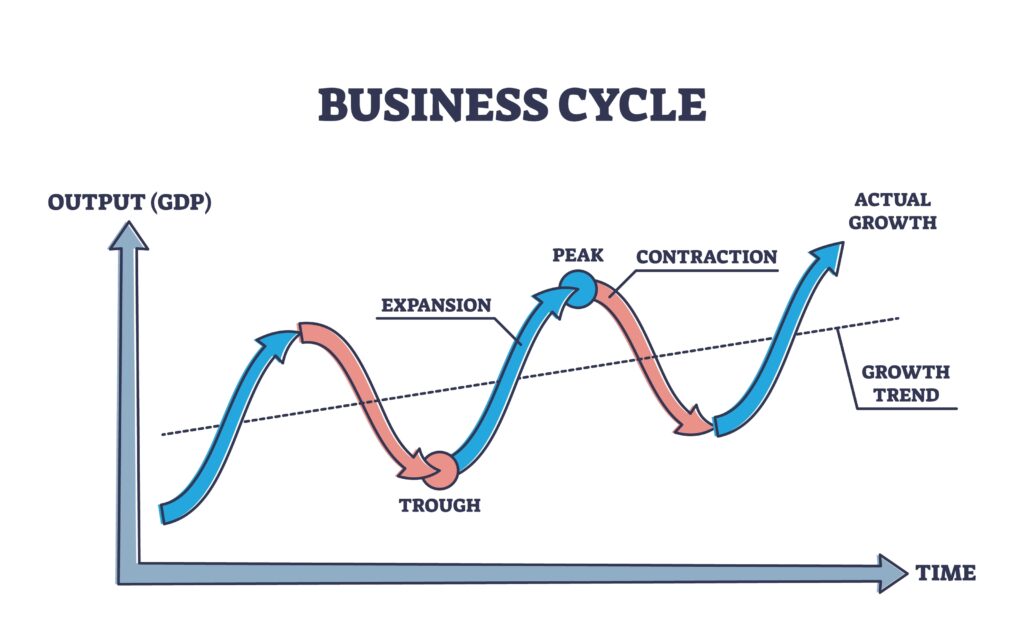
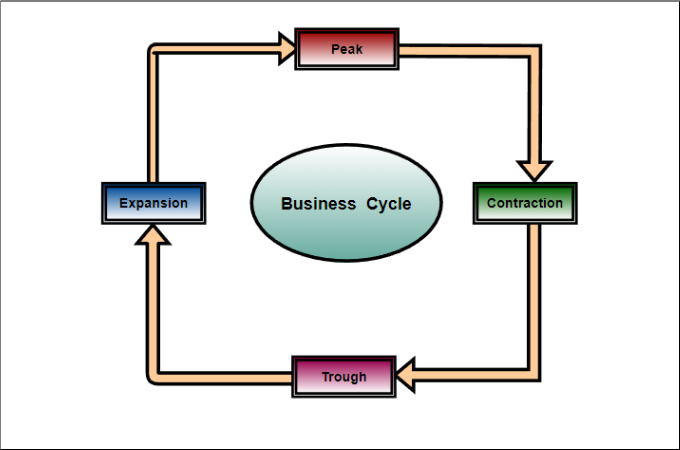
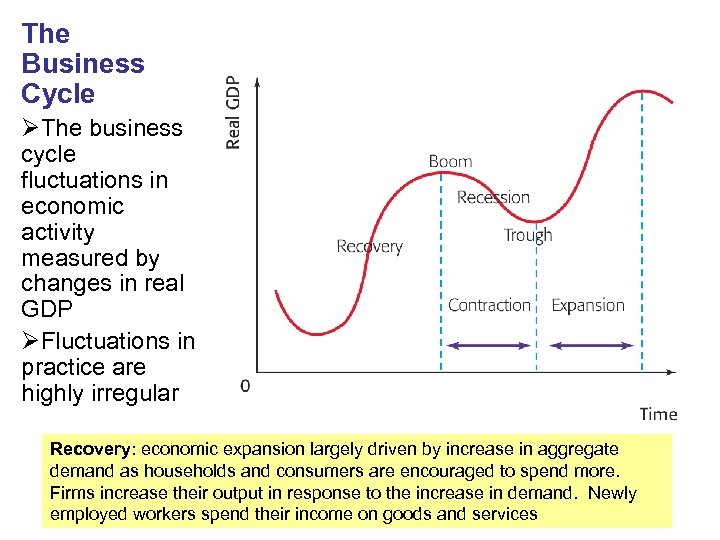
The business cycle typically consists of four distinct phases: expansion, peak, contraction (or recession), and trough. Let's explore each of these in more detail.
Expansion is a period of economic growth. During this phase, things are generally looking up: employment rises, consumer spending increases, and businesses invest more.
The peak represents the highest point of economic activity in the cycle. It's when the expansion reaches its limit, and the economy is running at full capacity.
A contraction, often referred to as a recession, is a period of economic decline. This is when unemployment rises, consumer spending decreases, and businesses cut back on investment.
The trough marks the lowest point of economic activity in the cycle. It's the point where the contraction bottoms out, and the economy is poised for a recovery.
Factors Influencing the Cycle
Numerous factors can influence the business cycle. These include changes in interest rates, government spending, consumer confidence, and global events.
Monetary policy, controlled by central banks like the Federal Reserve in the US, plays a significant role. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can try to stimulate or slow down economic activity.
Government fiscal policy, involving spending and taxation, also has a considerable impact. Increased government spending can boost demand, while tax cuts can stimulate investment.
"The business cycle is not a smooth, predictable process. It is subject to unexpected shocks and shifts in sentiment." - A leading economist
Consumer confidence is a crucial driver of economic activity. When people are optimistic about the future, they are more likely to spend money, fueling growth.
Global events, such as trade wars, pandemics, or geopolitical conflicts, can also significantly disrupt the business cycle. These events can create uncertainty and volatility in the global economy.
Significance and Implications
Understanding the business cycle is essential for making sound economic decisions. Businesses can use this knowledge to plan their investments, hiring, and pricing strategies.
Investors can use it to allocate their assets and manage risk. Policymakers rely on it to design effective economic policies that promote stability and growth.
By monitoring key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation, it is possible to gain insights into the current phase of the business cycle and anticipate future trends.
Navigating the business cycle requires adaptability and resilience. While the ups and downs are inevitable, understanding their dynamics allows individuals, businesses, and governments to make more informed choices and build a more stable and prosperous future.
.png)
/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phasesofthebusinesscycle-c7cb7a3ce6894e86a3e44d5b0fe4d5e2.jpg)
