What Is The Difference Between A Simple And Compound Leaf
Leaves, the fundamental solar panels of the plant kingdom, appear in a dazzling array of shapes and sizes. From the delicate needles of pine trees to the broad blades of banana plants, their diversity is a testament to evolution's ingenious solutions for capturing sunlight. But beneath this visual spectacle lies a critical distinction often overlooked: the difference between simple and compound leaves, a distinction that reveals much about a plant's evolutionary history and its adaptation to its environment.
Understanding the difference between simple and compound leaves is crucial for accurate plant identification and understanding plant physiology. This difference hinges on how the leaf blade is structured in relation to the leaf stem. While a simple leaf features a single, undivided blade, a compound leaf is composed of multiple leaflets attached to a central stalk. This article will delve into the defining characteristics of both types, explore their evolutionary significance, and highlight their importance in ecological studies.
Defining Simple Leaves
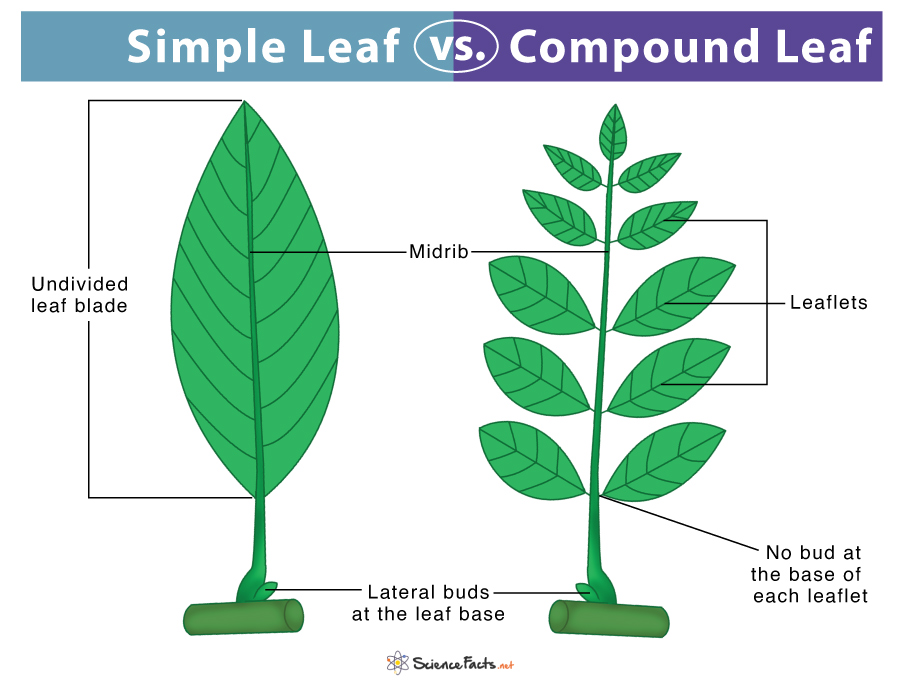
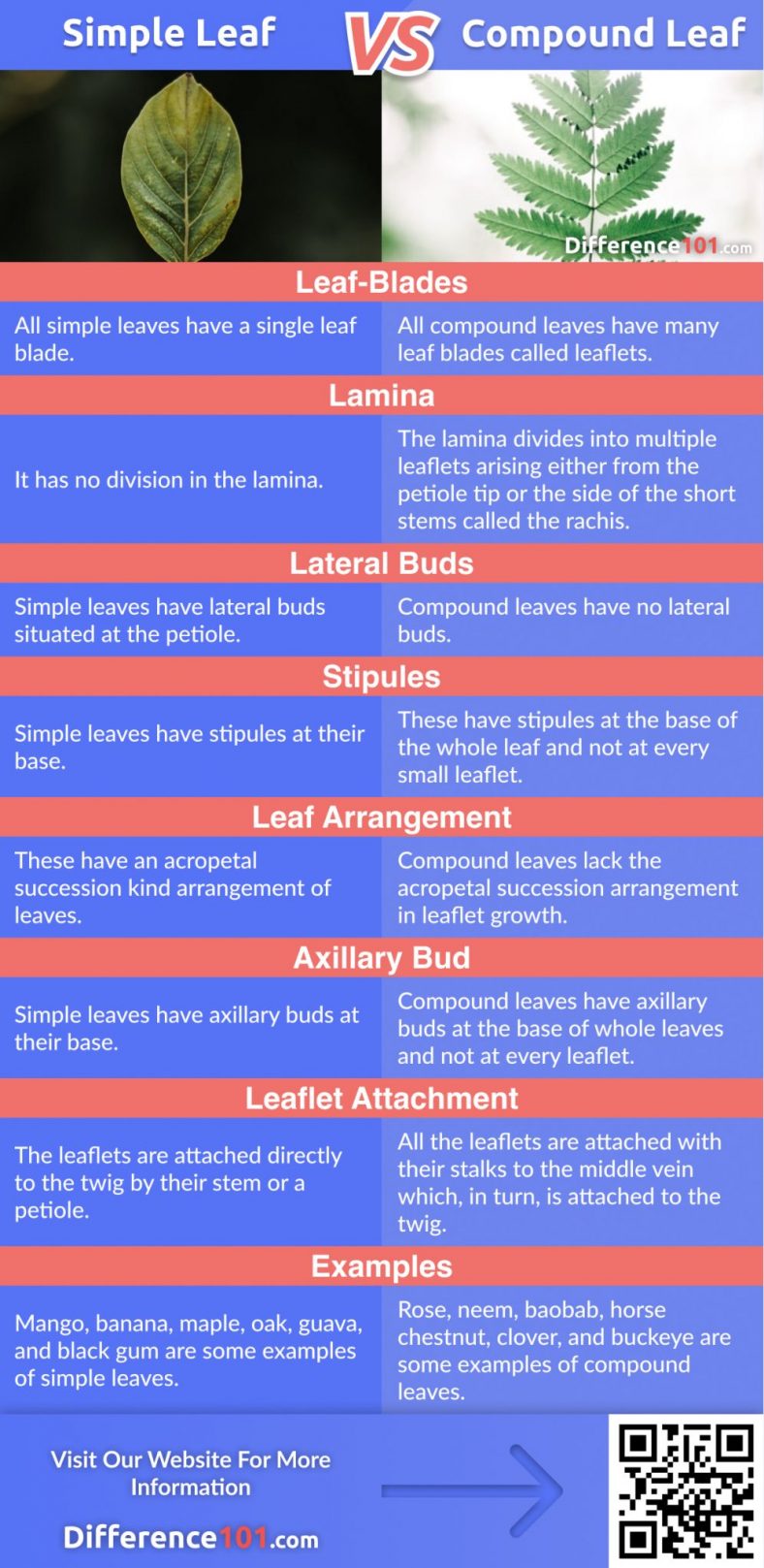
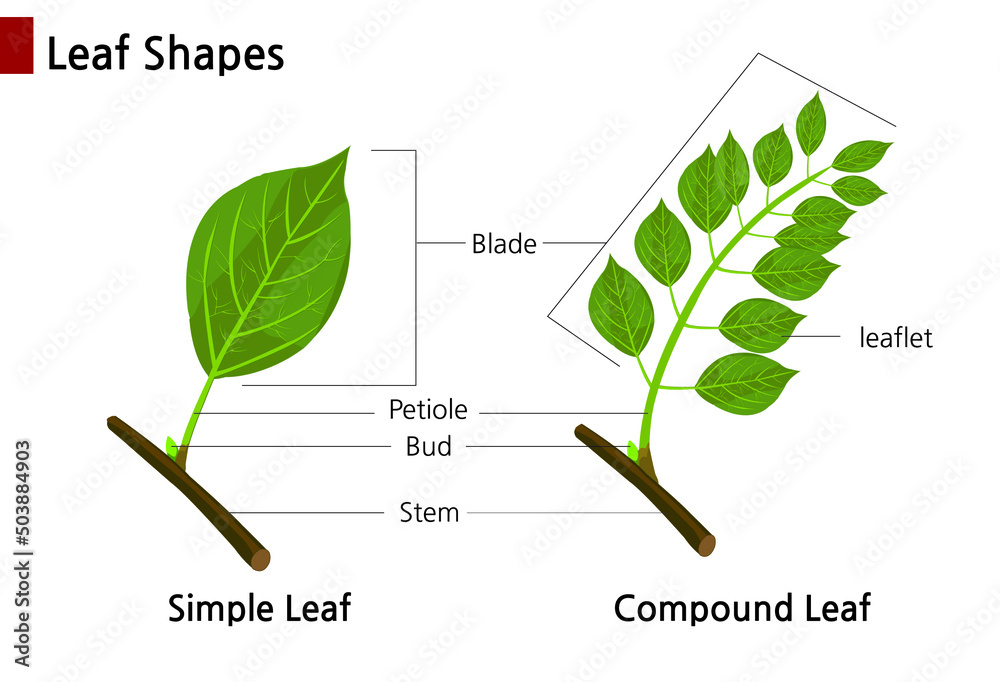
A simple leaf is characterized by a single, undivided blade. This blade, the main photosynthetic surface of the leaf, is attached to the stem by a petiole, also known as the leaf stalk.
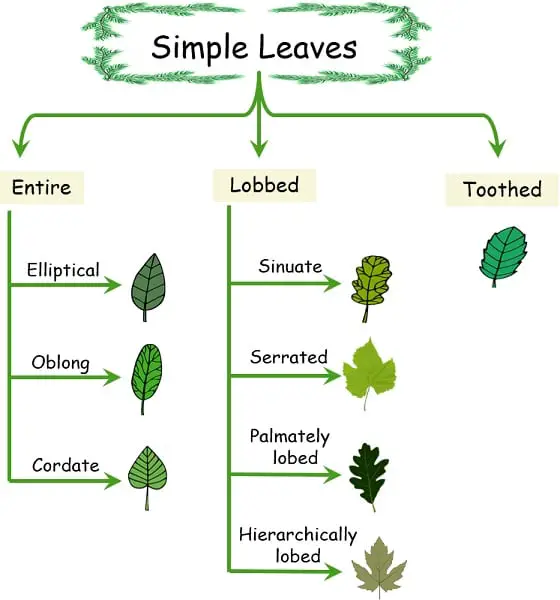
The edges of the blade can be smooth, toothed, lobed, or even deeply divided, but the key feature remains: a continuous leaf tissue without separation into distinct leaflets. Examples of plants with simple leaves include maple trees (Acer species), oak trees (Quercus species), and many fruit trees like apples (Malus domestica).
Unraveling Compound Leaves
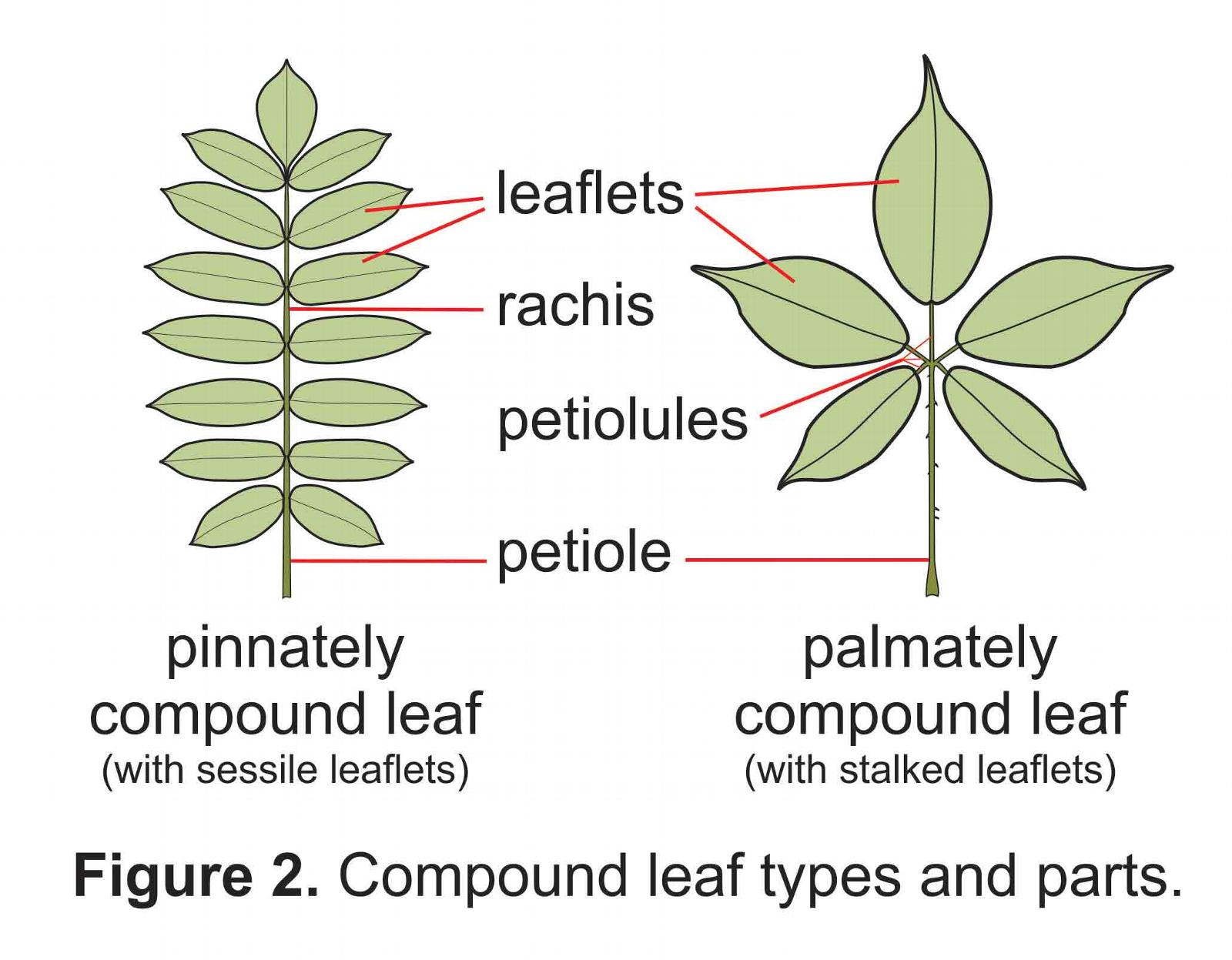
In contrast to simple leaves, compound leaves are composed of multiple leaflets, each resembling a small leaf itself. These leaflets are attached to a central stalk called the rachis, which extends from the petiole.
The entire structure, including the petiole, rachis, and leaflets, constitutes a single leaf. Think of a rose leaf or a walnut leaf; these are prime examples of compound leaves.
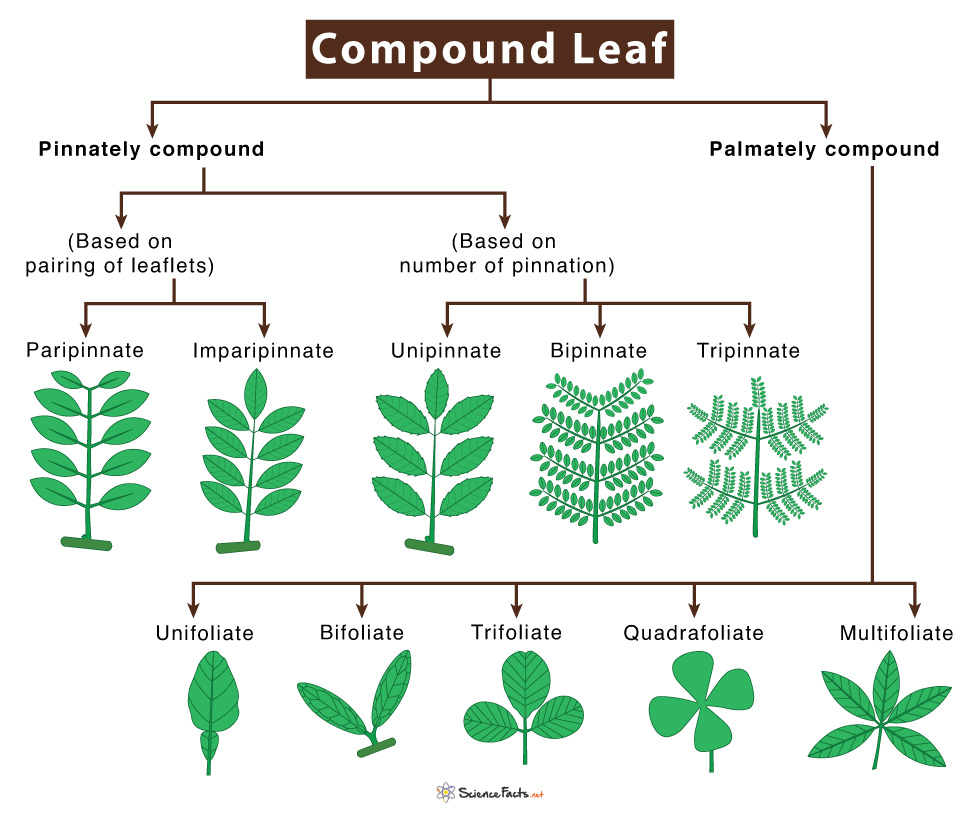
There are several types of compound leaves, including pinnately compound (leaflets arranged along both sides of the rachis), palmately compound (leaflets radiating from a central point), and bipinnately compound (leaflets divided into smaller leaflets).
Pinnately Compound Leaves
Pinnately compound leaves have leaflets arranged in pairs along the rachis, resembling a feather. Examples include ash trees (Fraxinus species) and black locust trees (Robinia pseudoacacia).
They can be further categorized as odd-pinnate (having a terminal leaflet) or even-pinnate (having a pair of leaflets at the end).
Palmately Compound Leaves
Palmately compound leaves have leaflets radiating outwards from a single point, similar to the fingers of a hand. Horse chestnut trees (Aesculus hippocastanum) and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) exhibit this type of leaf structure.
Bipinnately Compound Leaves
Bipinnately compound leaves are characterized by leaflets that are themselves divided into smaller leaflets, creating a more intricate and fern-like appearance. Examples include mimosa trees (Albizia julibrissin) and some species of acacia.
Key Distinguishing Features: Buds and Nodes
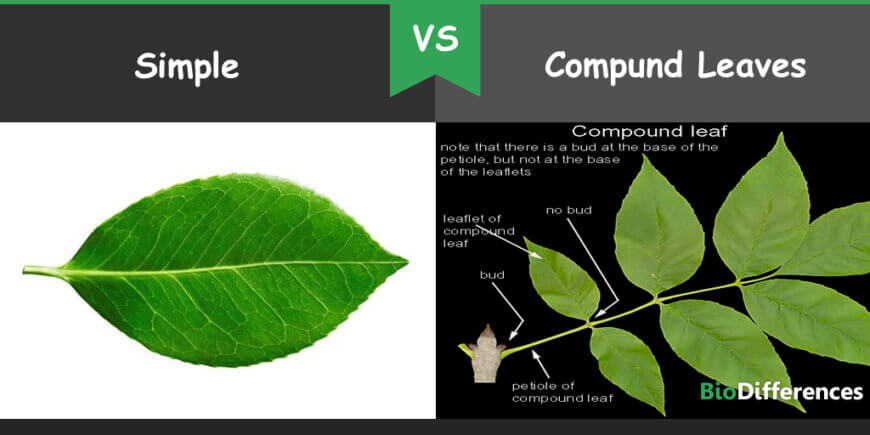
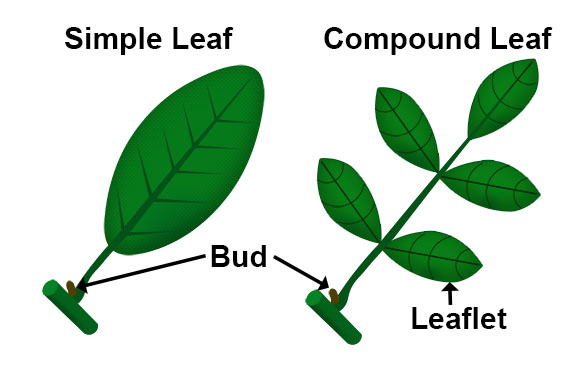
Perhaps the most critical distinguishing factor between a simple leaf and a leaflet of a compound leaf lies in the presence of buds. A leaf always has a bud at its base (where the petiole meets the stem), while leaflets never have buds at their base.
Similarly, leaves arise from nodes (points on the stem where leaves, buds, or branches emerge), while leaflets do not.
These seemingly subtle differences are fundamental for accurately identifying leaves and understanding plant morphology.
Evolutionary Significance
The evolution of simple and compound leaves reflects adaptation to diverse environmental conditions. The development of compound leaves is often seen as a response to factors like herbivory, drought, and extreme temperatures.
Compound leaves, with their smaller leaflets, may experience reduced water loss compared to large simple leaves, providing an advantage in arid environments. They may also be less susceptible to wind damage and insect herbivory because damage to one leaflet does not necessarily compromise the entire leaf.
According to a study published in the American Journal of Botany, the evolution of leaf compoundness has occurred independently in various plant lineages, suggesting its adaptive significance in a range of environments.
Ecological Implications
The type of leaf (simple or compound) can influence a plant's role in its ecosystem. Leaf litter composition, for example, can differ significantly between plants with simple and compound leaves.
The decomposition rate of leaf litter can affect nutrient cycling in the soil, impacting the overall health of the ecosystem. Furthermore, the structural complexity of compound leaves can provide habitat for insects and other small organisms, contributing to biodiversity.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found that plant communities with a mix of simple and compound-leaved species tend to have higher levels of invertebrate diversity compared to those dominated by a single leaf type.
Future Research Directions
While significant progress has been made in understanding the differences between simple and compound leaves, further research is needed to fully unravel the genetic and developmental mechanisms that control leaf morphology. Comparative genomic studies can shed light on the evolutionary pathways that led to the emergence of compound leaves in different plant lineages.
Investigating the physiological consequences of simple and compound leaf architectures in various environments can also provide valuable insights into plant adaptation. Understanding the ecological impacts of different leaf types is crucial for predicting how plant communities will respond to climate change and other environmental stressors.
By continuing to explore the intricacies of leaf morphology, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable diversity and resilience of the plant kingdom.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-difference-between-simple-and-compound-tree-leaves-4051112-final-f39de04e4de74d208aa5d35c68e7a8a6.png)