What Is The Elevation Of Michigan
Michigan, known for its Great Lakes coastline and diverse landscapes, presents a varied topography. Understanding its elevation is crucial for various fields, from environmental science to infrastructure planning and even recreational activities. The state's elevation isn't a single number, but a range that reflects its geological history and geographical features.
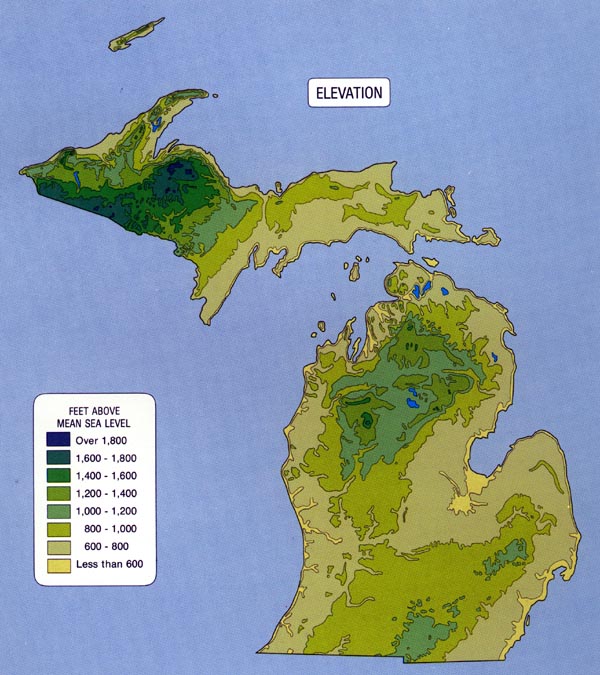
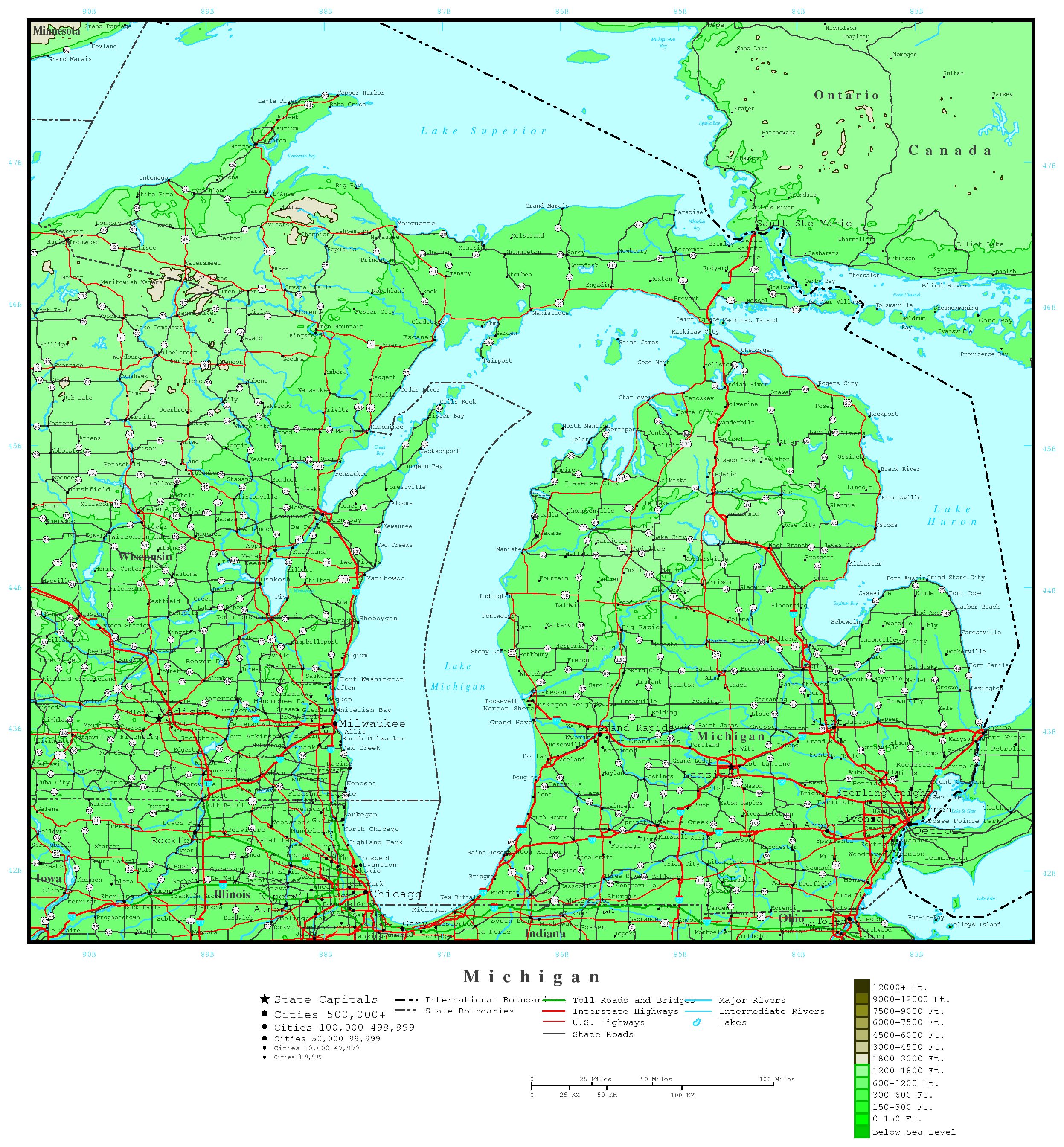
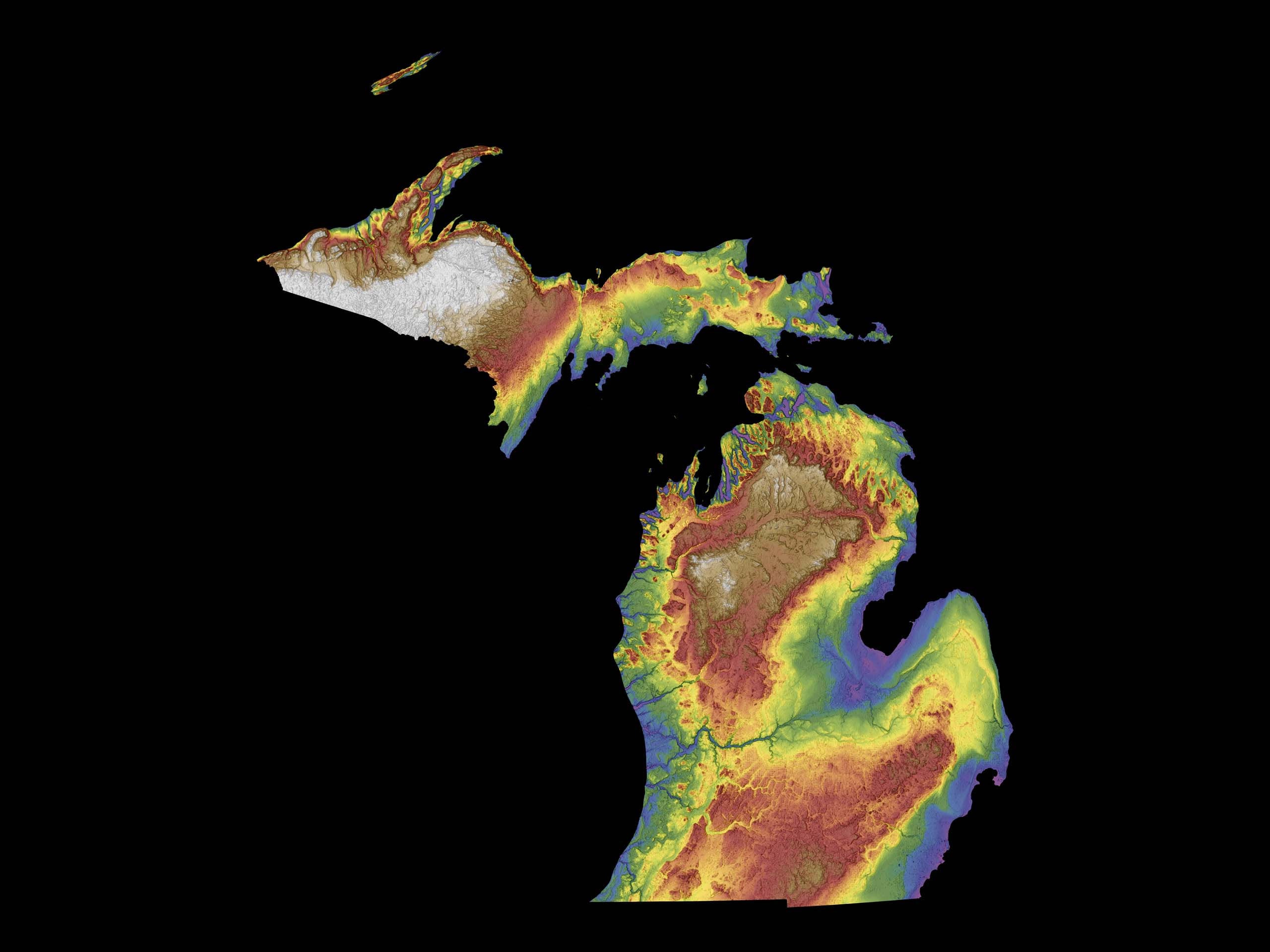
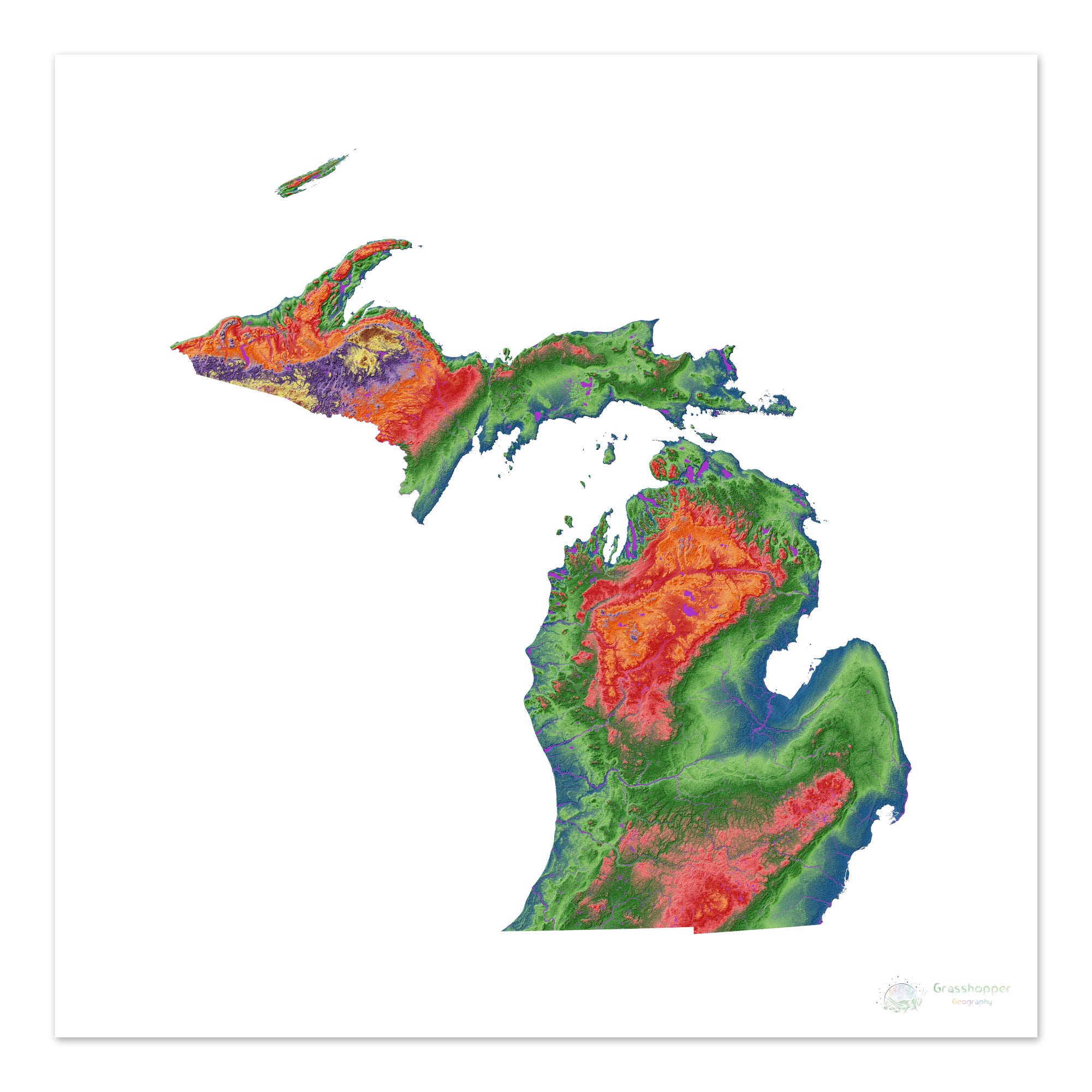
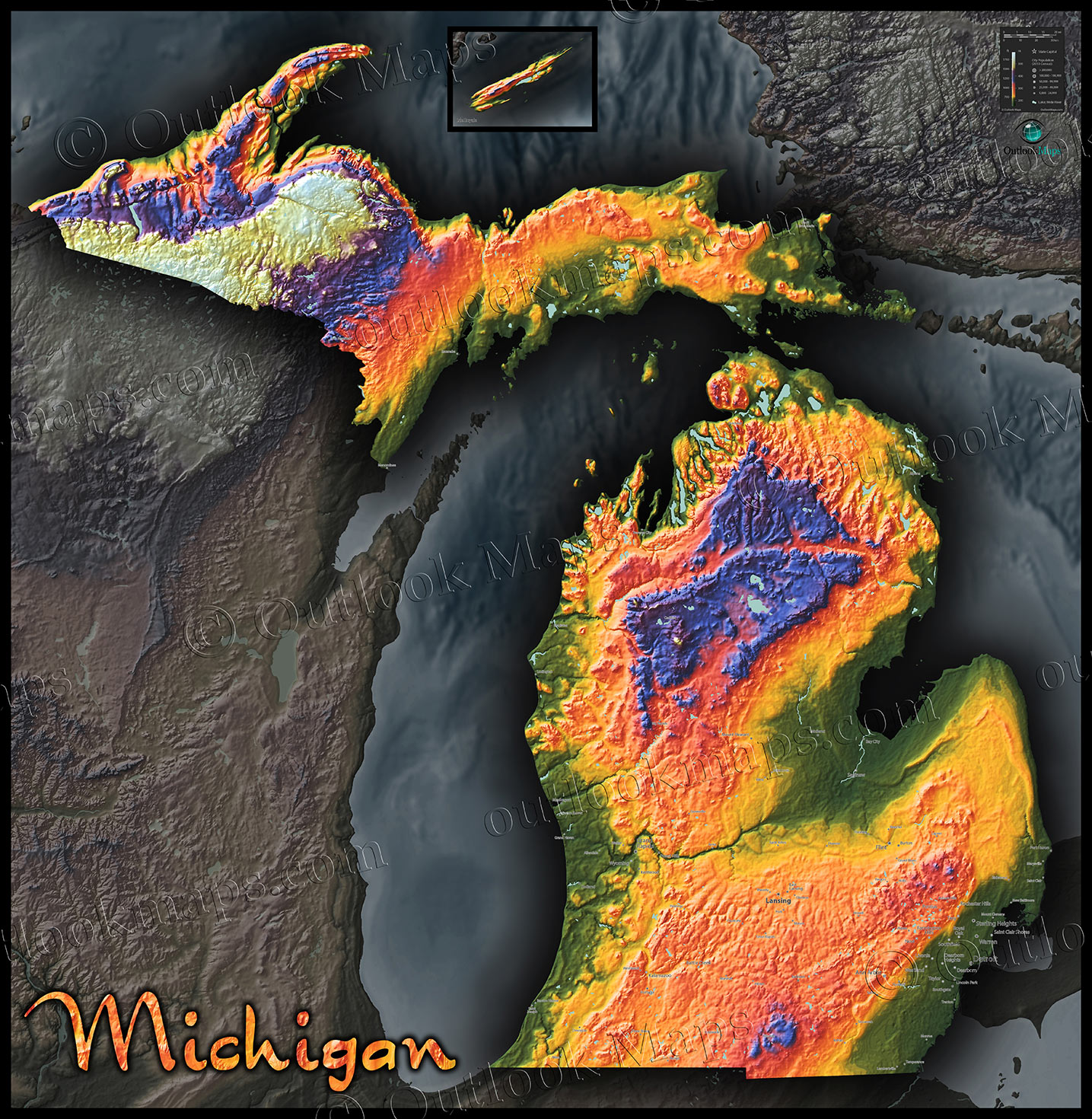
The elevation of Michigan ranges from 571 feet to 1,979 feet above sea level. This article will explore the key details of Michigan's elevation, including the highest and lowest points, its significance, and its impact on the state's environment and communities. The information is sourced from reputable organizations such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the Michigan Department of Natural Resources (MDNR).
Michigan's Elevation Extremes
Michigan's highest point is Mount Arvon, located in the Huron Mountains of the Upper Peninsula. It stands at 1,979 feet (603 meters) above sea level. Mount Arvon is a popular destination for hikers and outdoor enthusiasts, offering stunning views of the surrounding wilderness.
The lowest point is the surface of Lake Erie, which borders Michigan to the southeast. At its surface, Lake Erie sits at 571 feet (174 meters) above sea level. The Great Lakes, including Lake Erie, significantly influence Michigan's climate and economy.
Regional Elevation Variations
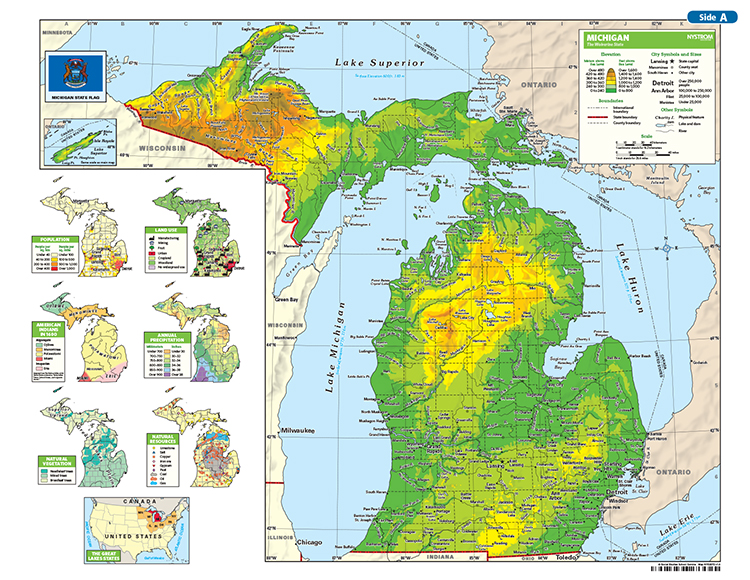
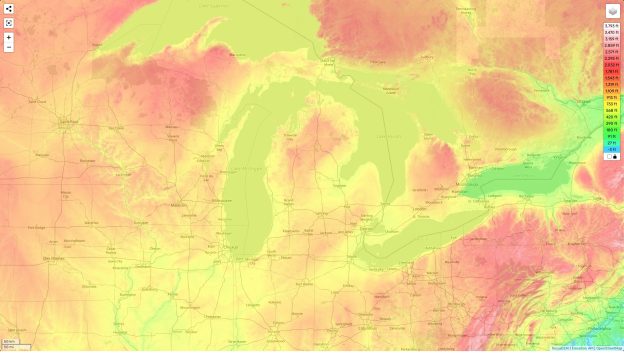
The Upper Peninsula (UP) generally has higher elevations compared to the Lower Peninsula. The Huron Mountains, located in the UP, are a rugged and hilly region characterized by ancient bedrock. This area contributes significantly to the state's overall elevation profile.
The Lower Peninsula is generally flatter, especially in the southeastern part of the state. However, there are still notable elevation changes, particularly along the "thumb" area and towards the northern regions. Rolling hills and glacial formations contribute to the diverse topography of the Lower Peninsula.
Data and Measurement
Elevation data is primarily collected and maintained by the USGS. They use various methods, including satellite imagery, aerial surveys, and ground-based measurements, to create detailed topographic maps. This data is crucial for accurate elevation assessments.
The MDNR also utilizes elevation data for resource management and conservation efforts. They use it for tasks such as flood risk assessment, habitat mapping, and infrastructure planning. Understanding elevation is essential for informed decision-making in environmental management.
Significance of Elevation
Elevation plays a significant role in Michigan's climate patterns. Higher elevations experience cooler temperatures and increased precipitation, often in the form of snow. This affects the growing seasons, ecosystems, and recreational opportunities in different regions.
Elevation also influences water drainage patterns. Higher elevations act as water divides, directing the flow of rivers and streams. Understanding these patterns is critical for managing water resources and preventing flooding.
"Elevation is a fundamental factor in understanding Michigan's environmental systems," says Dr. Emily Carter, a hydrologist at the University of Michigan. "It directly impacts everything from climate to biodiversity."
Impact on Infrastructure
Elevation is a crucial consideration in infrastructure development. Engineers must account for elevation changes when designing roads, bridges, and other structures. Proper planning ensures stability and longevity of infrastructure projects.
Elevation data is also used in telecommunications to optimize signal coverage. Cell towers are often placed on higher ground to maximize their range. Understanding the terrain helps companies provide reliable service.
Recreational Opportunities
Michigan's diverse elevations provide a wide range of recreational opportunities. Mount Arvon and other elevated areas attract hikers, climbers, and skiers. Lower elevations offer opportunities for boating, fishing, and swimming in the Great Lakes and inland waterways.
The state's topography also contributes to the popularity of activities such as mountain biking and off-roading. The varying terrain provides challenges and excitement for outdoor enthusiasts.
Potential Impacts
Changes in elevation, such as those caused by erosion or rising lake levels, can have significant impacts on communities. Erosion along coastlines can threaten homes and infrastructure. Rising lake levels can cause flooding and damage to property.
Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for implementing mitigation strategies. Coastal management plans and infrastructure improvements can help protect communities from the effects of changing elevations.
Furthermore, as climate change continues to affect weather patterns and sea levels, monitoring elevation changes becomes even more critical. Accurate data helps communities prepare for and adapt to future challenges.
In conclusion, the elevation of Michigan, ranging from 571 feet to 1,979 feet, is a defining characteristic of the state's geography. Its impact spans across various sectors, including environment, infrastructure, recreation, and community planning. The continuous monitoring and understanding of these elevations are vital for ensuring the sustainable development and resilience of Michigan.
![What Is The Elevation Of Michigan Elevation of Michigan [OC] [4000x5000] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/90x9t6ovvfc01.jpg)