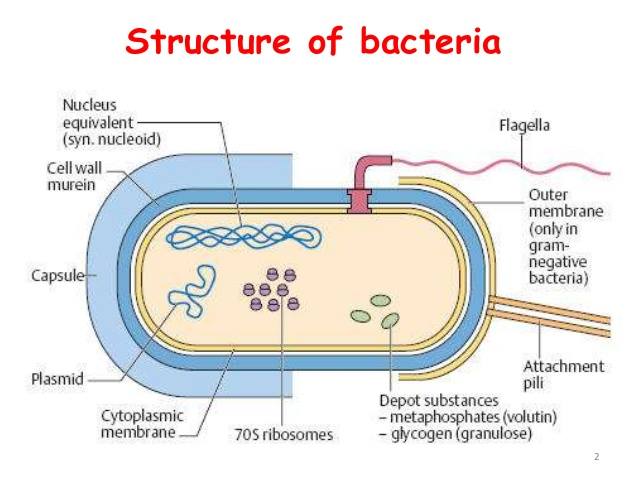
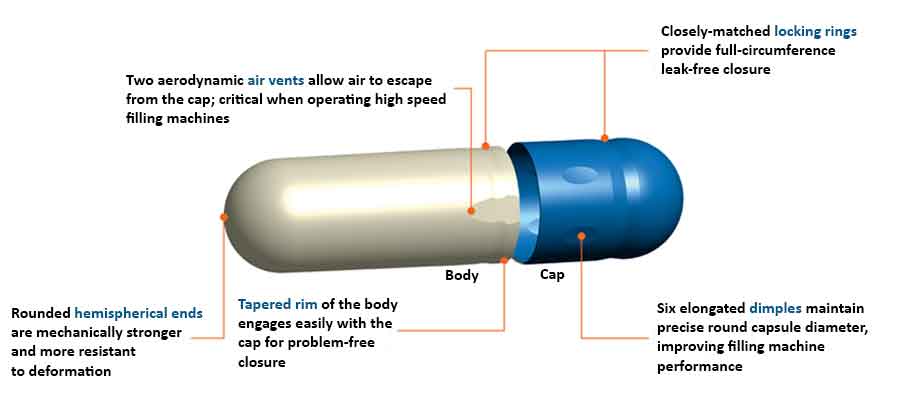
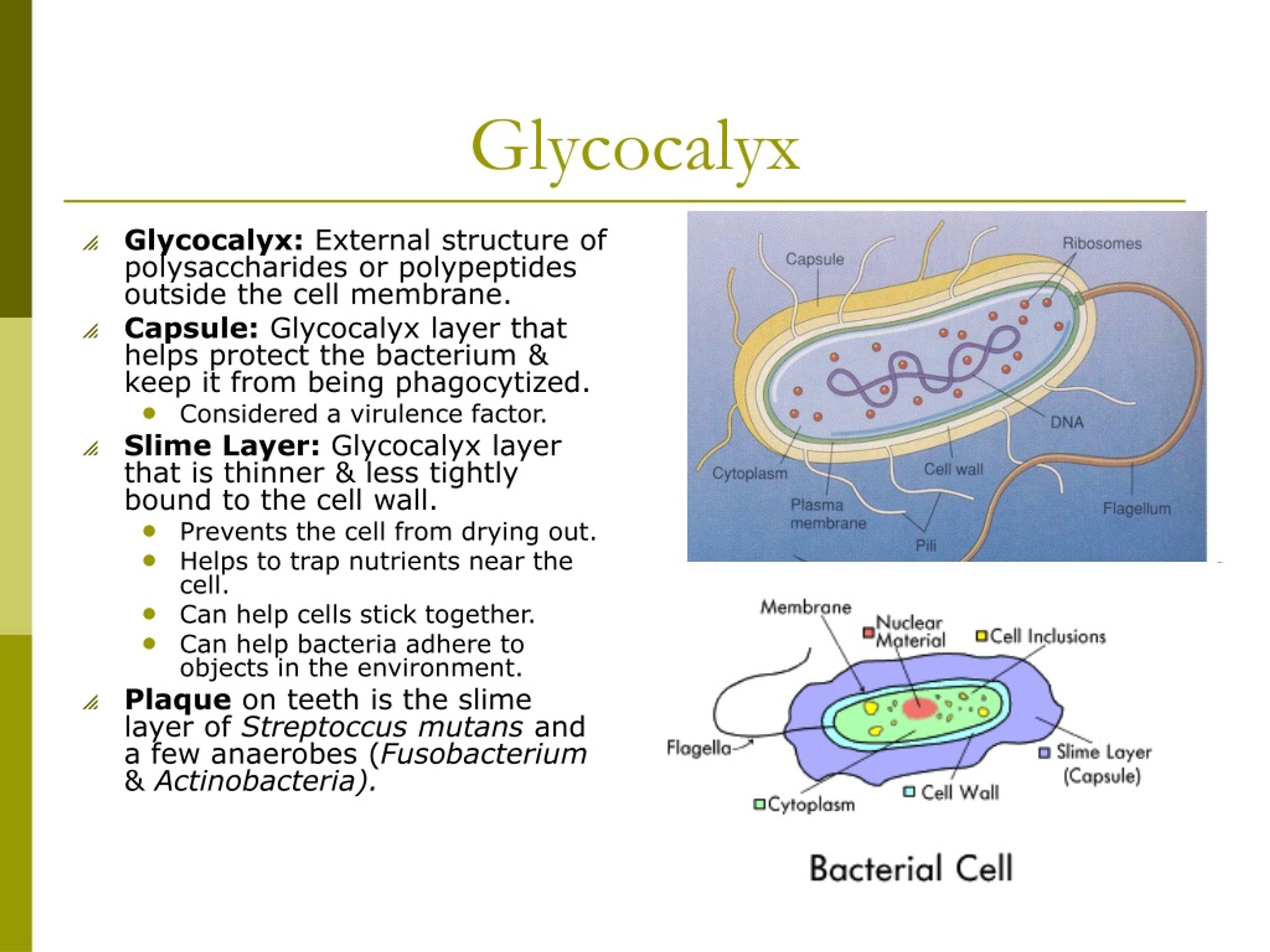
What Is The Function Of A Capsule

Imagine a world where every medicine tasted intensely bitter, where getting the right dose was a guessing game, and where protection from the environment was non-existent for delicate drug compounds. This wasn't so long ago. The humble capsule, often overlooked, has revolutionized how we take medication and supplements.
At its core, a capsule serves as a container, encasing medication or supplements for oral administration. It simplifies consumption, masks unpleasant tastes, ensures accurate dosages, and safeguards ingredients from degradation, making it an indispensable tool in modern healthcare and personal wellness.
The Genesis of Encapsulation
The story of the capsule begins with a need: a need to deliver medicine more effectively and palatable. Early attempts at medication often involved crude mixtures with inconsistent dosages and unappealing flavors. This made compliance difficult and sometimes even hindered the therapeutic effects.
While rudimentary forms of encapsulation existed earlier, the modern capsule, as we know it, took shape in the 19th century. Mothes and Dublanc, two French pharmacists, are credited with patenting the first two-piece hard gelatin capsule in 1834. This was a revolutionary innovation, allowing for precise dosing and improved taste masking.
Gelatin: The Original Encapsulation Material
For many years, gelatin reigned supreme as the primary material for capsule manufacturing. Gelatin, derived from collagen, offers several advantages. It's non-toxic, readily soluble in water, and easily molded into various shapes and sizes.
However, gelatin capsules have limitations. They can be susceptible to moisture and temperature variations, and they are derived from animal sources, which may be a concern for some individuals with dietary restrictions.
The Rise of Non-Gelatin Alternatives
In response to these limitations, the pharmaceutical industry began exploring alternative materials for capsule manufacturing. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), a plant-derived polymer, emerged as a leading contender.
HPMC capsules, also known as vegetarian or vegan capsules, offer several advantages over gelatin. They are less susceptible to moisture, more stable at higher temperatures, and suitable for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets. This significantly broadens their applicability.
Functions of a Capsule: Beyond Simple Encasing
The capsule's primary function is to encapsulate and deliver its contents, but its role extends far beyond that. It performs several crucial functions that contribute to the efficacy and user experience of medications and supplements.
Taste Masking and Improved Compliance
Many medications have a bitter or unpleasant taste, making them difficult to swallow and discouraging compliance. Capsules effectively mask these tastes, making it easier for individuals to take their medication as prescribed.
Improved compliance directly translates to better health outcomes. By removing the unpleasant taste experience, capsules encourage regular intake, leading to more consistent therapeutic effects.
Dosage Accuracy
Capsules allow for precise dosing of medication or supplements. The filling process, often automated, ensures that each capsule contains the exact amount of the active ingredient, eliminating the potential for errors associated with manual measurements.
This accuracy is particularly important for medications with a narrow therapeutic window. These medications require precise dosing to achieve the desired effect without causing adverse reactions.
Protection of Active Ingredients
Many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are sensitive to environmental factors such as light, moisture, and oxygen. Capsules provide a protective barrier against these factors, preventing degradation and maintaining the potency of the API.
This protection is crucial for ensuring that the medication remains effective throughout its shelf life. It also allows for the formulation of medications that would otherwise be unstable in tablet or liquid form.
Targeted Release Mechanisms
Modern capsule technology goes beyond simple immediate release. Capsules can be designed to release their contents at specific locations within the gastrointestinal tract, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
For example, enteric-coated capsules resist dissolving in the acidic environment of the stomach. They release their contents in the small intestine, which is beneficial for medications that are sensitive to stomach acid or that need to be absorbed in the small intestine for optimal effect.
Improved Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to the extent and rate at which the active ingredient in a medication is absorbed into the bloodstream. Capsules can enhance the bioavailability of certain drugs, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes.
This can be achieved through various formulation strategies, such as incorporating excipients that promote drug dissolution or using specialized capsule materials that enhance absorption.
The Capsule Landscape Today
Today, the capsule industry is a multi-billion dollar market, with a wide range of capsule types, sizes, and materials available. Technological advancements continue to drive innovation, leading to more sophisticated and targeted delivery systems.
Capsules are not limited to pharmaceuticals; they are widely used in the nutraceutical and dietary supplement industries. Vitamins, minerals, herbal extracts, and other health-enhancing substances are often encapsulated for ease of consumption and improved stability.
The Future of Capsule Technology
The future of capsule technology promises even more sophisticated and personalized drug delivery. Researchers are exploring novel materials, such as polymers that respond to specific stimuli within the body, and advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, to create custom capsules tailored to individual patient needs.
Imagine capsules that release medication only when and where it's needed, minimizing side effects and maximizing therapeutic benefit. This level of precision and personalization holds immense potential for revolutionizing healthcare.
"The humble capsule has played a significant role in advancing healthcare and improving patient outcomes. Its simple yet effective design has revolutionized drug delivery, and ongoing innovation promises even greater advancements in the future." - A Pharmaceutical Industry Expert
From its humble beginnings as a simple way to mask unpleasant tastes, the capsule has evolved into a sophisticated tool for drug delivery. It ensures accurate dosing, protects delicate ingredients, and even targets specific areas of the body.
As technology advances, the future of capsules is poised to revolutionize healthcare. It promises customized solutions tailored to individual needs, making medication more effective, convenient, and personalized than ever before.




+outside+the+cell+wall..jpg)