What Is The Value Of 3 In 630
Imagine a child, brow furrowed in concentration, carefully arranging colorful blocks. Each block, a symbol of a number, holds its own unique value depending on where it's placed. It's a simple game, yet it lays the foundation for understanding a fundamental concept in mathematics: place value.
At its core, the question "What is the value of 3 in 630?" delves into this principle. The digit 3 in the number 630 represents 3 tens, or 30. Understanding place value is not just an academic exercise; it’s a cornerstone of numeracy, essential for everything from managing finances to understanding scientific data.
The Foundation of Place Value
The concept of place value wasn't always universally understood. Ancient number systems, like Roman numerals, lacked a symbol for zero and didn't inherently assign a value based on position.
The development of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system, which includes the digits 0-9 and a place value system, revolutionized mathematics. Historians trace its origins back to ancient India, with significant contributions from Arab mathematicians who facilitated its spread across the globe. This system, now used worldwide, allows us to represent any number, no matter how large, using just ten symbols, thanks to the power of place value.
Understanding the Components of 630
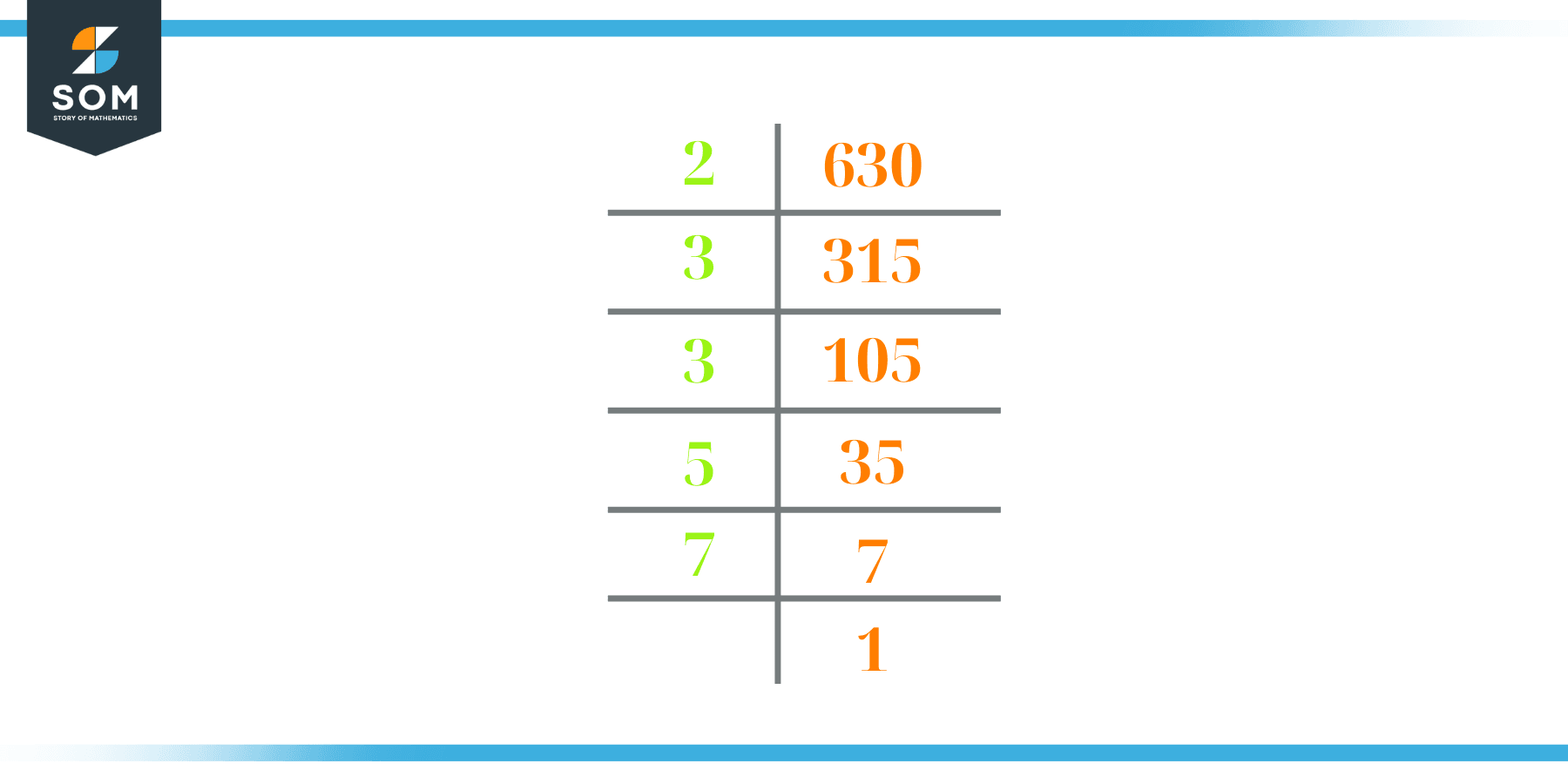
To truly grasp the value of the 3 in 630, let's break down the number itself. The number 630 is composed of three digits: 6, 3, and 0.
Each digit occupies a specific place: hundreds, tens, and ones. The 6 is in the hundreds place, representing 600. The 3 is in the tens place, representing 30. The 0 is in the ones place, representing zero.
Therefore, 630 can be expressed as (6 x 100) + (3 x 10) + (0 x 1). This breakdown clearly demonstrates the value of each digit based on its position.
Why Does Place Value Matter?
Understanding place value is fundamental to performing arithmetic operations. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division all rely on a solid grasp of how digits contribute to the overall value of a number based on their placement.
Consider adding 10 to 630. Without understanding place value, it would be difficult to correctly adjust the digits. With it, we know we’re adding one to the tens place, resulting in 640.
Beyond basic arithmetic, place value is crucial in more advanced mathematical concepts like decimals, fractions, and algebra. Its understanding allows us to manipulate and interpret numerical data with accuracy and confidence.
Real-World Applications
The importance of understanding place value extends far beyond the classroom. In personal finance, it's essential for budgeting, managing bank accounts, and understanding interest rates.
In healthcare, understanding dosages of medication often involves working with decimal places and varying scales, making place value knowledge critically important. Science relies heavily on place value too. Measurements, calculations, and understanding scales of magnitude in physics, chemistry, and biology all depend on the principle of place value.
According to the National Numeracy organization, a lack of numeracy skills, often rooted in a poor understanding of place value, can significantly impact an individual's life chances. Their research consistently demonstrates a correlation between strong numeracy skills and improved employment opportunities, financial stability, and overall well-being.
Common Misconceptions and How to Avoid Them
One common misconception is that the 3 in 630 simply represents "3". Children, in particular, might focus on the digit itself without considering its position within the number.
Another misconception involves confusing the place value of different digits. For example, someone might mistakenly think the 6 in 630 represents 60 instead of 600.
To avoid these misconceptions, educators often use visual aids like base-ten blocks to represent numbers. These blocks allow students to physically manipulate the units, tens, and hundreds, reinforcing the concept of place value in a tangible way. Games and interactive activities can also make learning place value more engaging and effective.
Teaching Place Value Effectively
Effective teaching of place value starts with concrete examples and gradually progresses to abstract concepts. Starting with manipulatives such as counters or blocks can help students visualize the quantities involved.
Using a place value chart is also very helpful. The chart visually shows the place and value of each digit within a number.
Regular practice with a variety of exercises is essential for solidifying understanding. These exercises can include writing numbers in expanded form (e.g., 630 = 600 + 30 + 0), comparing numbers based on place value, and solving word problems that require an understanding of place value.
The Enduring Relevance of Numeracy
In an increasingly data-driven world, numeracy skills are more important than ever. The ability to understand and interpret numerical information is essential for navigating daily life and participating fully in society.
Organizations like OECD (The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) emphasize the importance of investing in numeracy education to equip individuals with the skills they need to succeed in the 21st century. Their studies show a direct link between a country's numeracy levels and its economic competitiveness.
Understanding the value of the 3 in 630 might seem like a small thing, but it's a building block for so much more. It's a gateway to understanding the world around us and empowering ourselves to make informed decisions. From balancing a checkbook to interpreting scientific research, the principles of place value underpin our ability to engage with the world in a meaningful way.





![What Is The Value Of 3 In 630 SOLVED: 15.1] A charge What is the of+3 uc i 1 located 1 1 direction of](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/c42f63d3dd4c4c738ef1886236169d39.jpg)