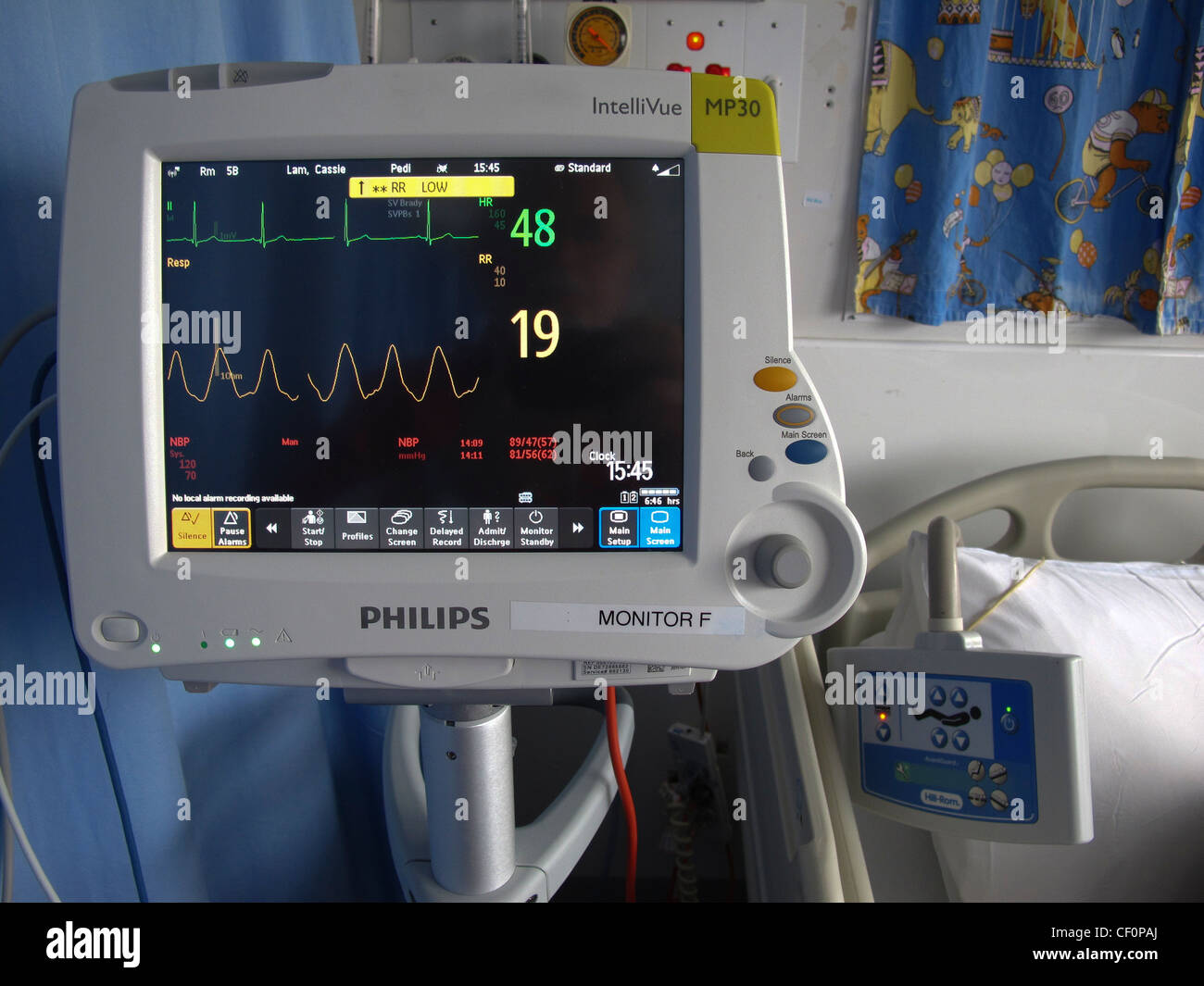
What Is The White Line On A Hospital Monitor

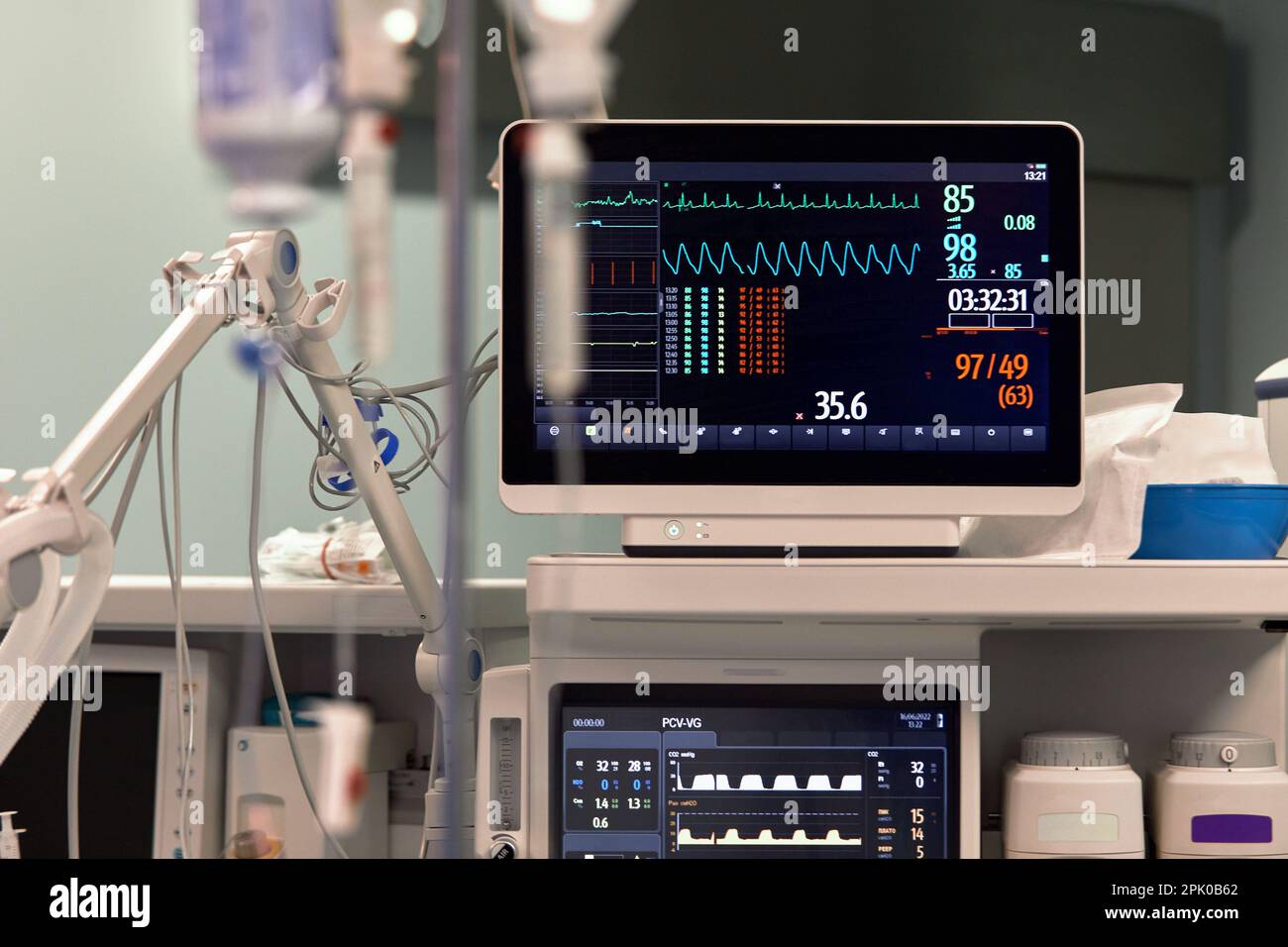
Hospitals are complex environments filled with sophisticated technology designed to monitor and support patient health. One common sight in these settings is the patient monitor, displaying a series of waveforms and numerical values. While many focus on the fluctuating lines representing heart rate or oxygen saturation, a seemingly simple feature often goes unnoticed: the white line.
Understanding the function of this white line is crucial for both medical professionals and those interested in comprehending the information presented on patient monitors. This article will delve into the purpose of the white line, its significance in interpreting patient data, and its role in clinical decision-making.
Deciphering the Monitor: The White Line's Role
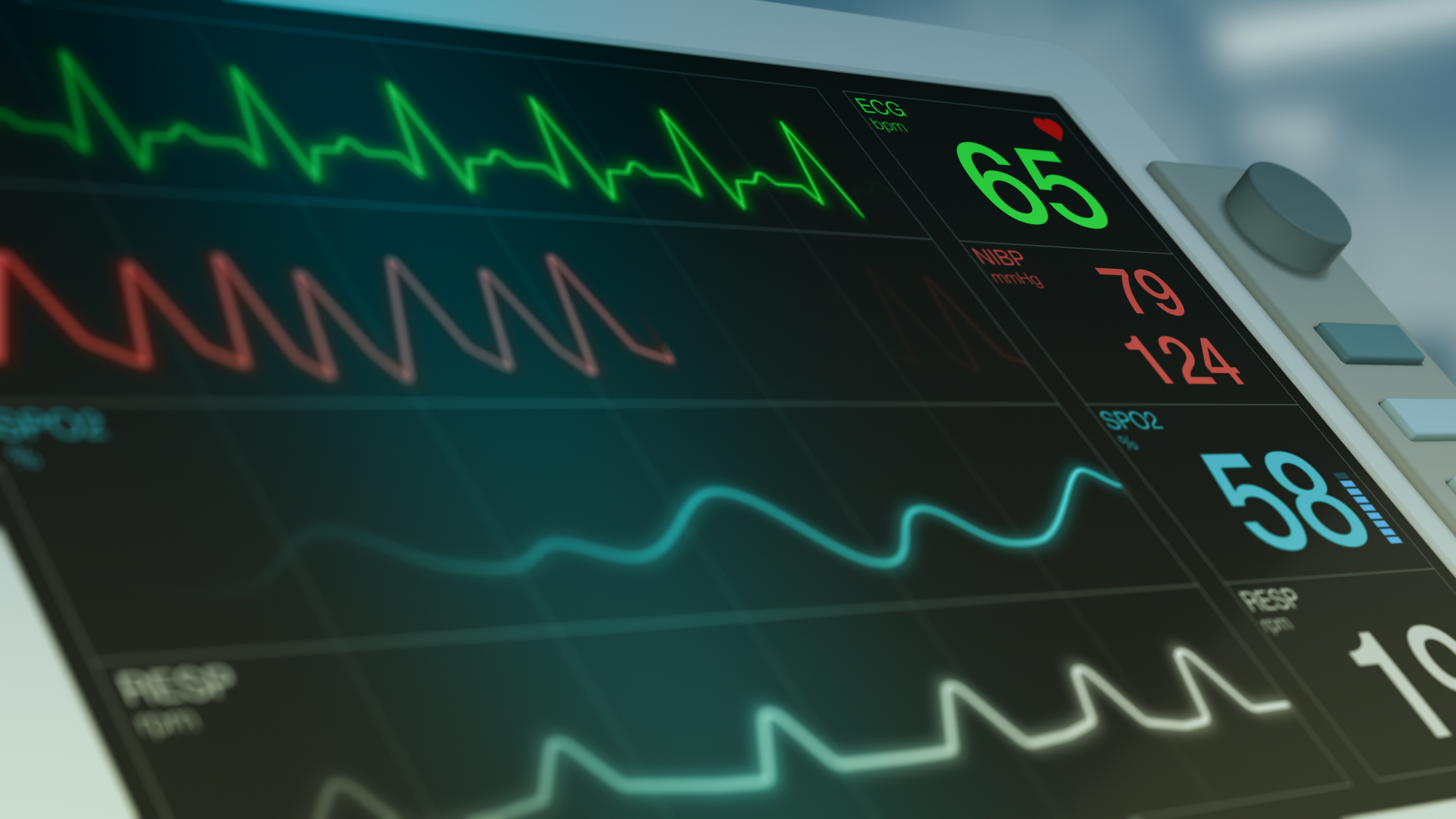
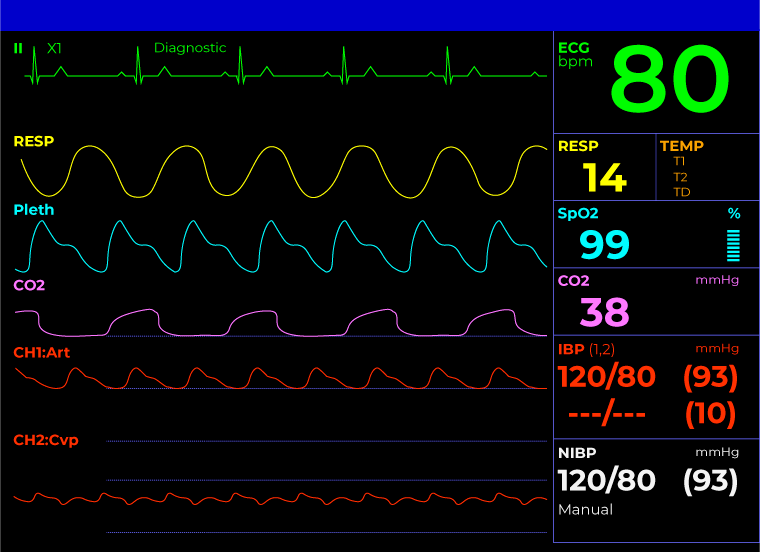
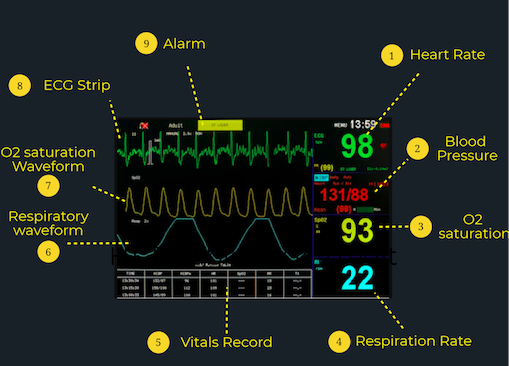
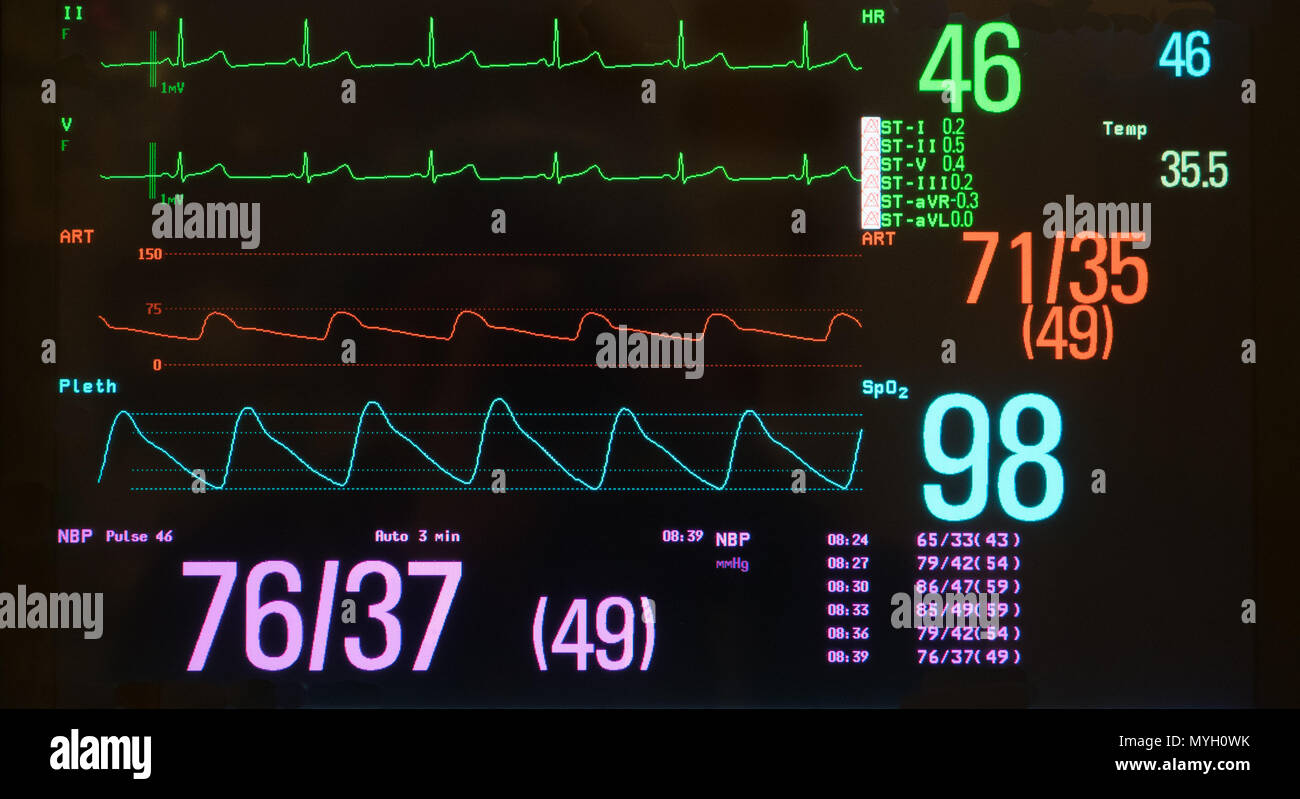
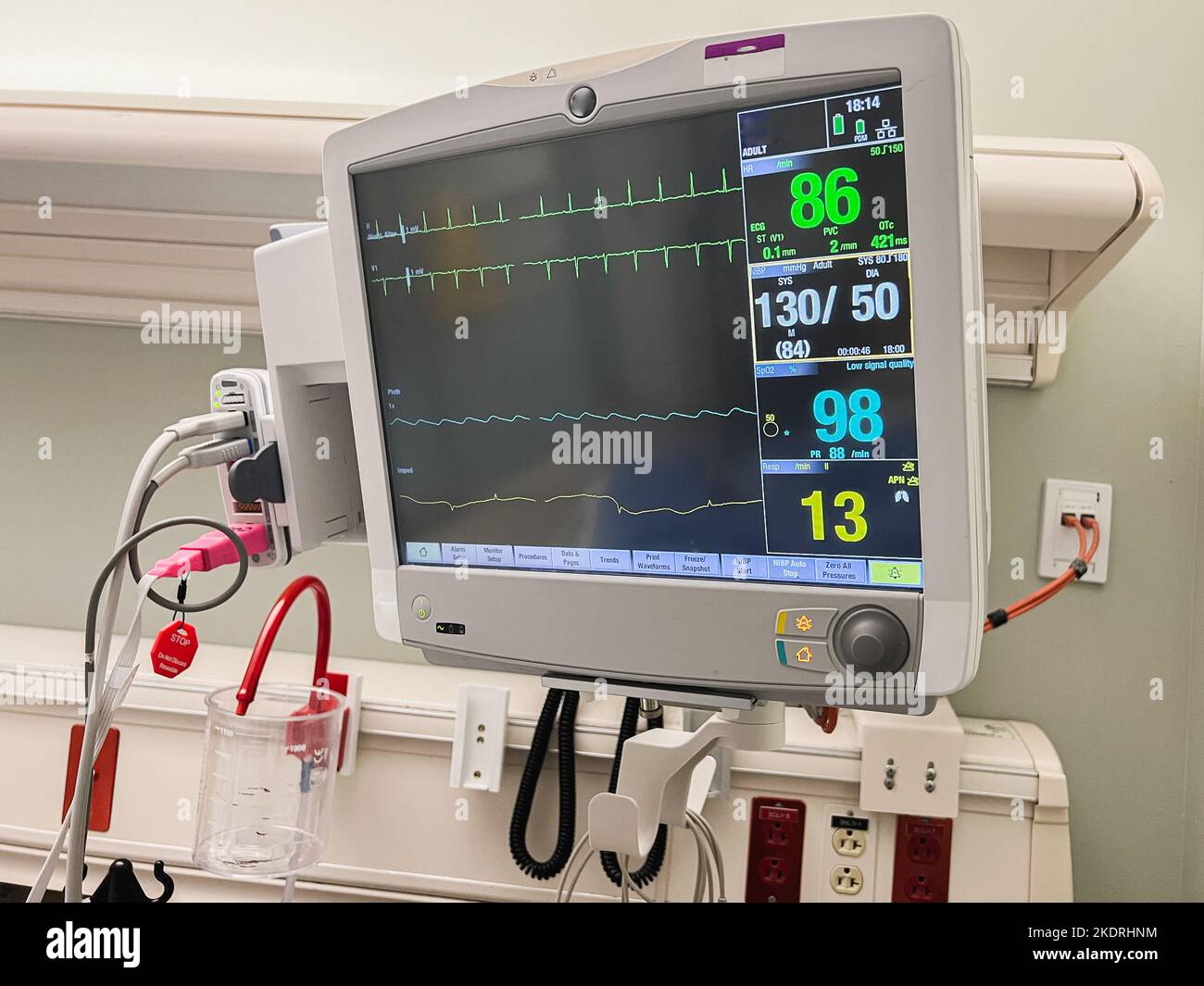
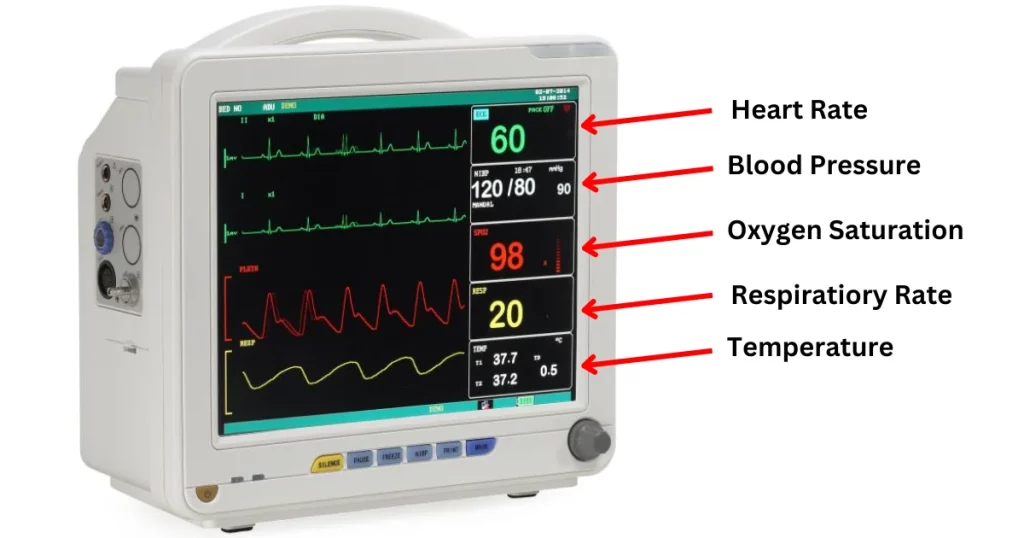
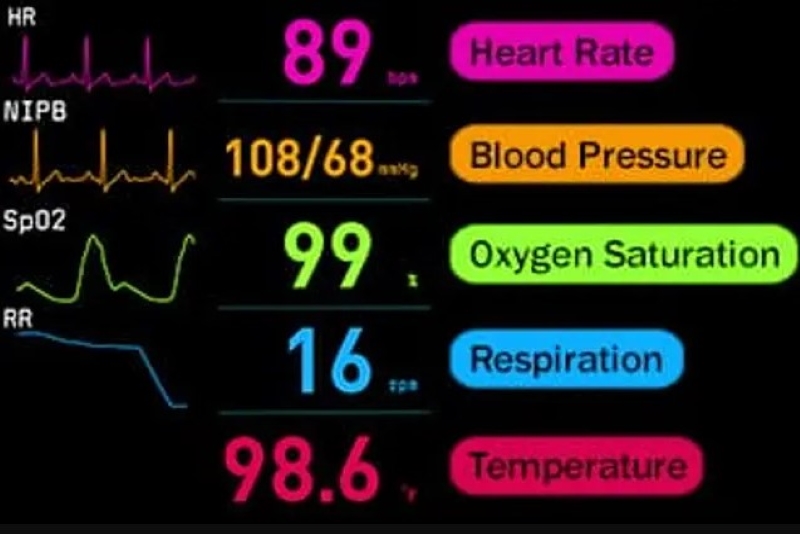
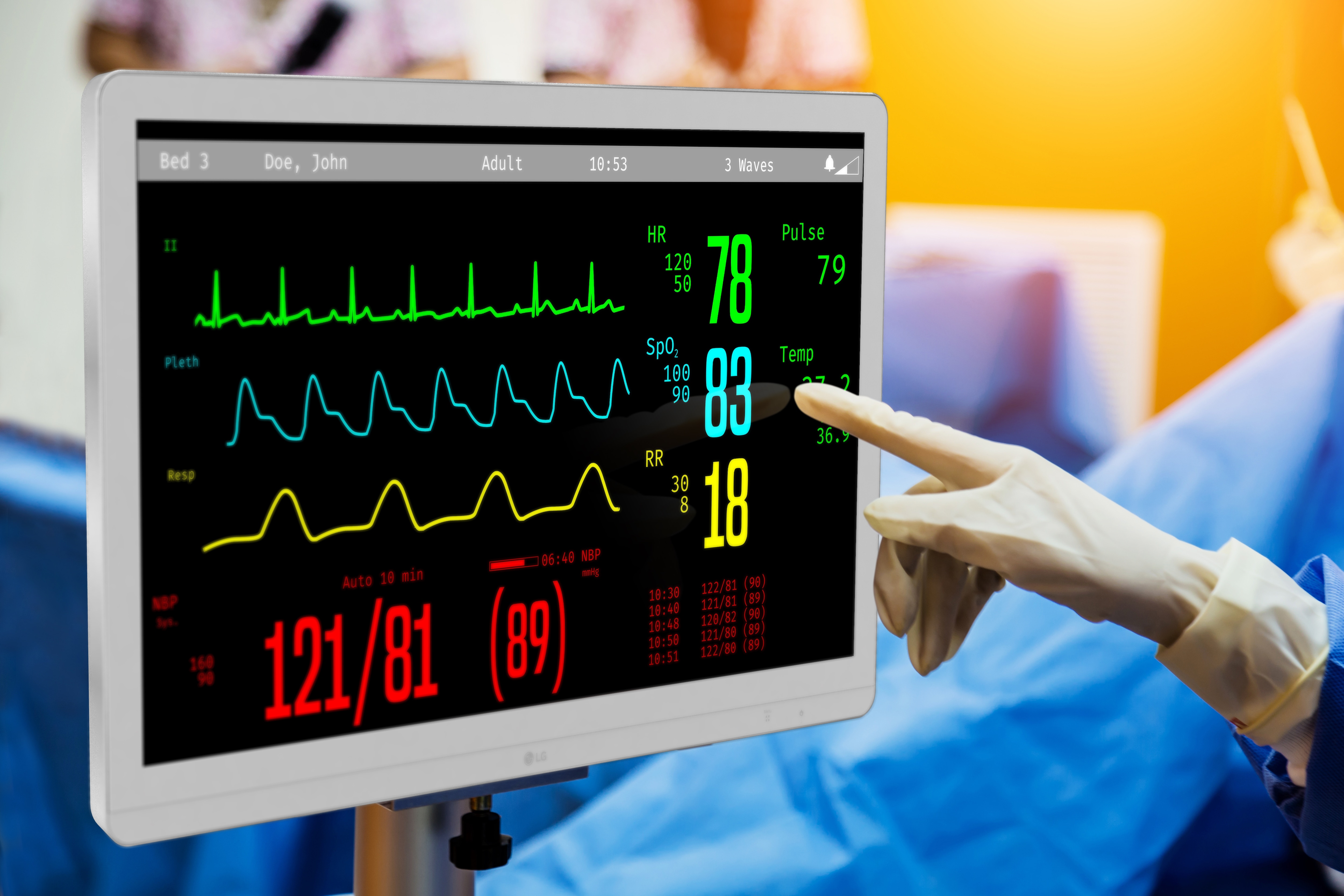
The white line on a hospital monitor serves as a baseline or reference point for other waveforms displayed on the screen. Its primary function is to provide a visual cue for interpreting the amplitude and changes in the signals representing vital signs such as electrocardiogram (ECG), respiration, and arterial blood pressure.
Think of it as the zero point on a graph. Without this baseline, it would be significantly more difficult to accurately assess the magnitude and direction of the physiological changes being monitored.
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) and the White Line
In the context of an ECG, the white line is particularly important. It represents the isoelectric line or baseline, the period when there is no electrical activity occurring in the heart between beats.
The various deflections above and below this line, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, represent different phases of the cardiac cycle. Changes in these deflections relative to the white line can indicate various cardiac abnormalities.
For example, an elevated ST segment, where the segment between the QRS complex and the T wave is significantly above the white line, is a key indicator of a possible myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Respiration Monitoring
The white line also plays a vital role in monitoring respiration. The respiratory waveform displays the rise and fall of chest movement during breathing.
The white line provides a reference for determining the depth and regularity of breaths. Shallow breathing, indicated by small deflections from the white line, might suggest respiratory distress, while deep breaths would show larger excursions.
Furthermore, irregular breathing patterns can be quickly identified by observing the inconsistent spacing and amplitude of the respiratory waveform relative to the white line.
Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring
For patients with invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring, the white line again serves as the baseline. The waveform displays the systolic and diastolic pressures, which are read as the peak and trough of the waveform relative to the white line.
A stable white line helps clinicians quickly assess the patient's blood pressure trends. Fluctuations in the position of the waveform relative to the white line can indicate changes in blood pressure requiring intervention.
Importance for Clinical Decision-Making
The white line, though seemingly simple, is a fundamental tool for medical professionals in making informed clinical decisions. By providing a stable reference point, it allows for accurate interpretation of physiological signals.
This accuracy is critical in diagnosing conditions, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and responding to critical events. Without a clear baseline, subtle but important changes in vital signs could be missed or misinterpreted.
Moreover, the white line contributes to the overall efficiency of patient monitoring. It enables medical staff to quickly assess a patient's condition at a glance, especially in high-pressure situations such as intensive care units or emergency departments.
Beyond the Basics: Calibration and Artifacts
It's important to note that the accuracy of the white line depends on proper monitor calibration. Routine checks and adjustments are essential to ensure the baseline is correctly positioned and that the displayed waveforms are a true representation of the patient's physiological state.
Furthermore, artifacts, or extraneous signals that can interfere with the waveforms, can also affect the position and stability of the white line. These artifacts can arise from patient movement, electrical interference, or faulty equipment.
Medical professionals must be trained to recognize and mitigate artifacts to ensure accurate monitoring and interpretation.
For patients, understanding that the medical team is carefully observing and analyzing the information displayed on the monitor, including the position of the waveforms relative to the white line, can provide a sense of reassurance.
The white line is not merely a graphical element, but a vital component in providing effective and safe patient care.
The Undervalued Element
While often overlooked, the white line on a hospital monitor represents a key element in the continuous surveillance of a patient's vital functions. Its role as a baseline is essential for accurately interpreting complex physiological data.
The understanding of this seemingly simple element is indispensable for healthcare professionals, and appreciating its significance can empower patients to be more informed and engaged in their own care.
The continued advancement of patient monitoring technology will undoubtedly refine and enhance the way we visualize and interpret vital signs, yet the fundamental principle of a stable baseline, represented by the white line, will likely remain a cornerstone of patient care.