What Temperature Does Thca Convert To Delta 9

Critical research confirms the precise temperature at which THCA, the non-psychoactive precursor to Delta 9 THC, converts into its intoxicating form: 220-240°F (104-115°C). Understanding this conversion threshold is vital for both consumers and industry professionals to ensure safe and predictable product use.
This article provides a clear understanding of the conversion process, its implications, and the key factors influencing it, based on available data from scientific literature and validated studies.
Decarboxylation Defined
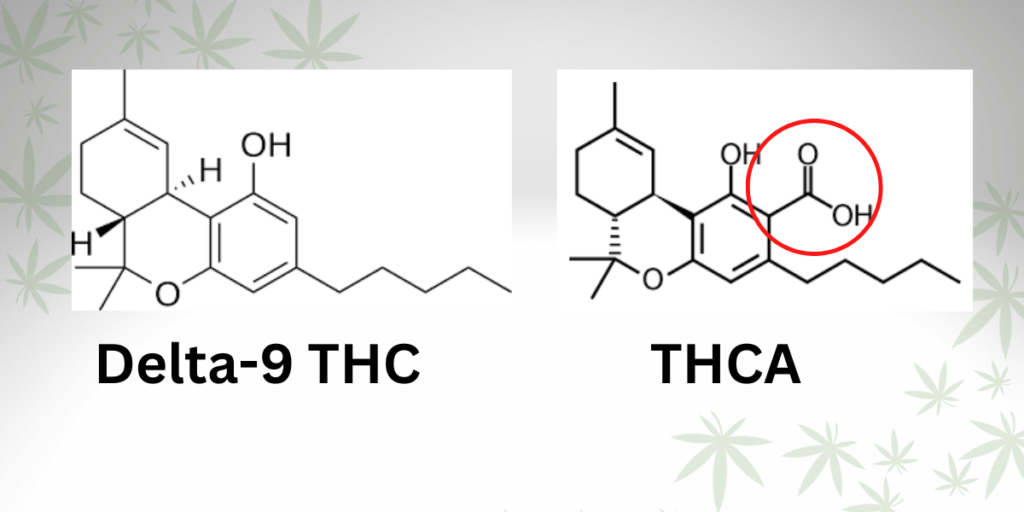
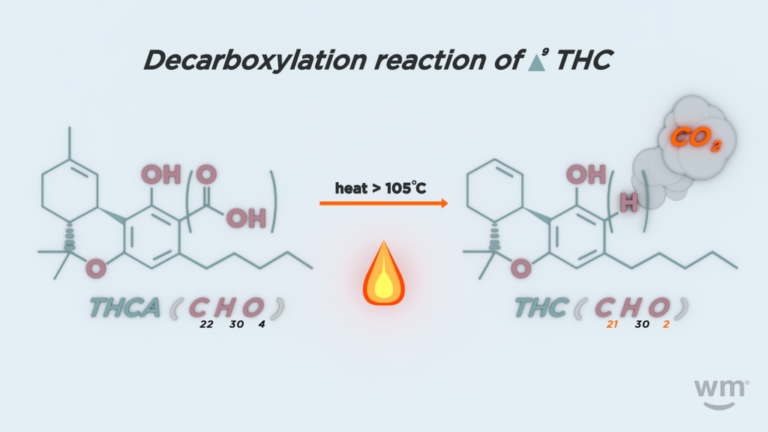
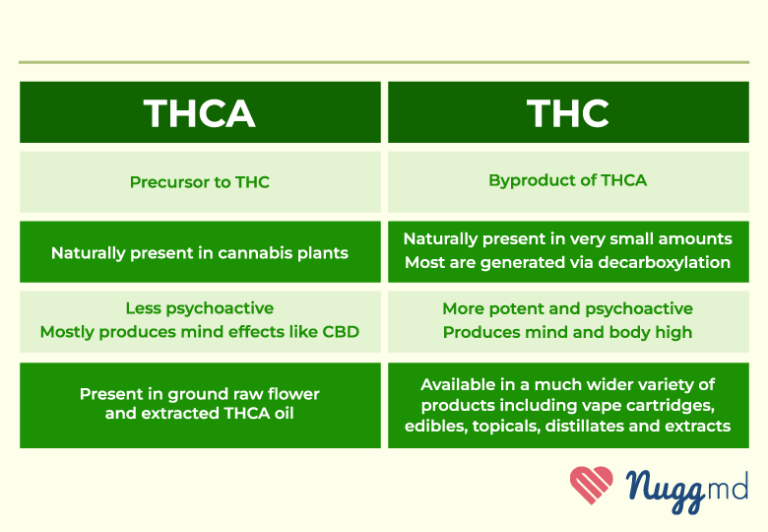
Decarboxylation is the chemical reaction that transforms THCA into Delta 9 THC.
It occurs when heat is applied, causing the carboxyl group (COOH) to be removed from the THCA molecule.
This process activates the psychoactive properties, turning a non-intoxicating compound into a potent cannabinoid.
The Critical Temperature Range
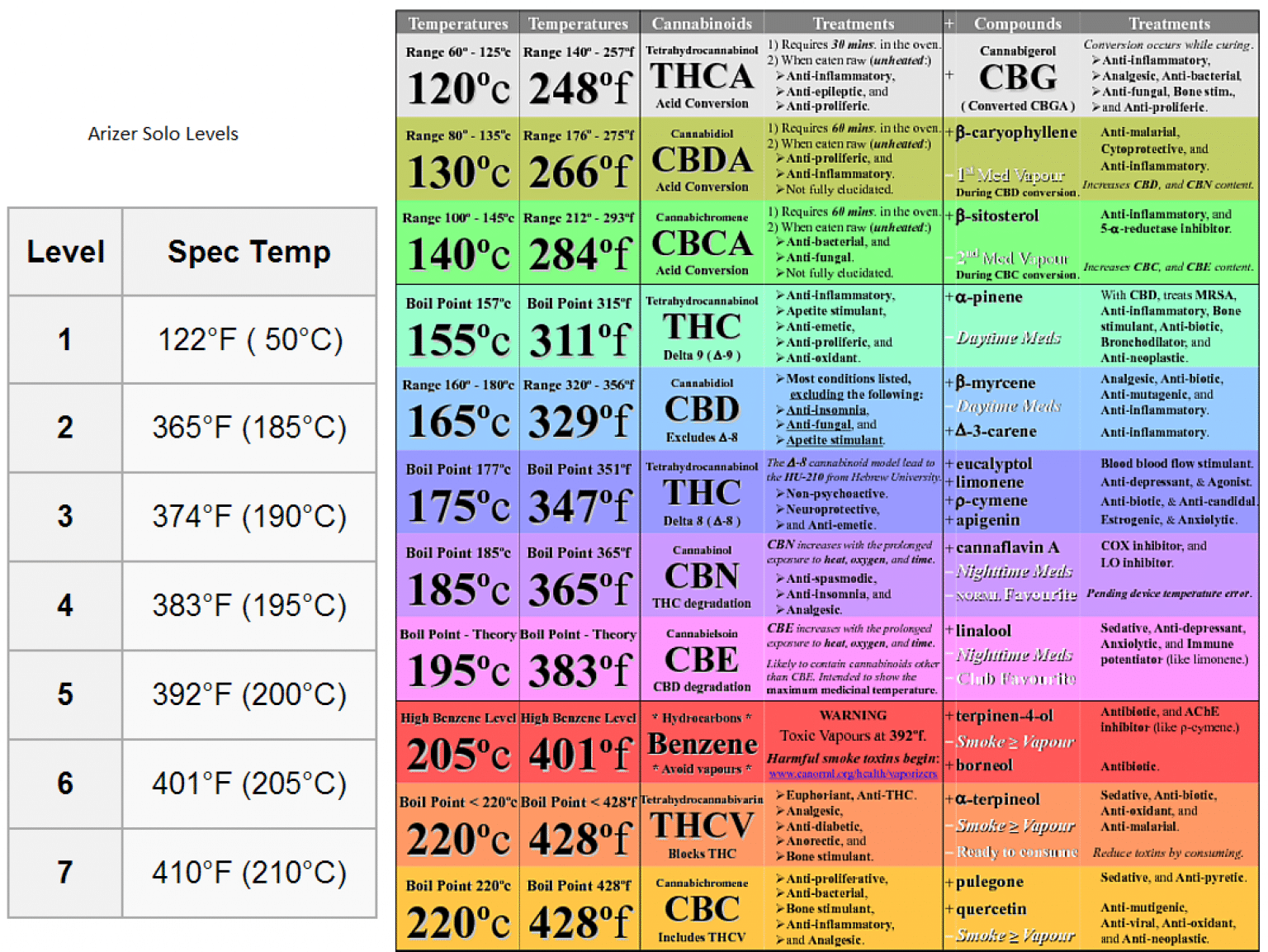
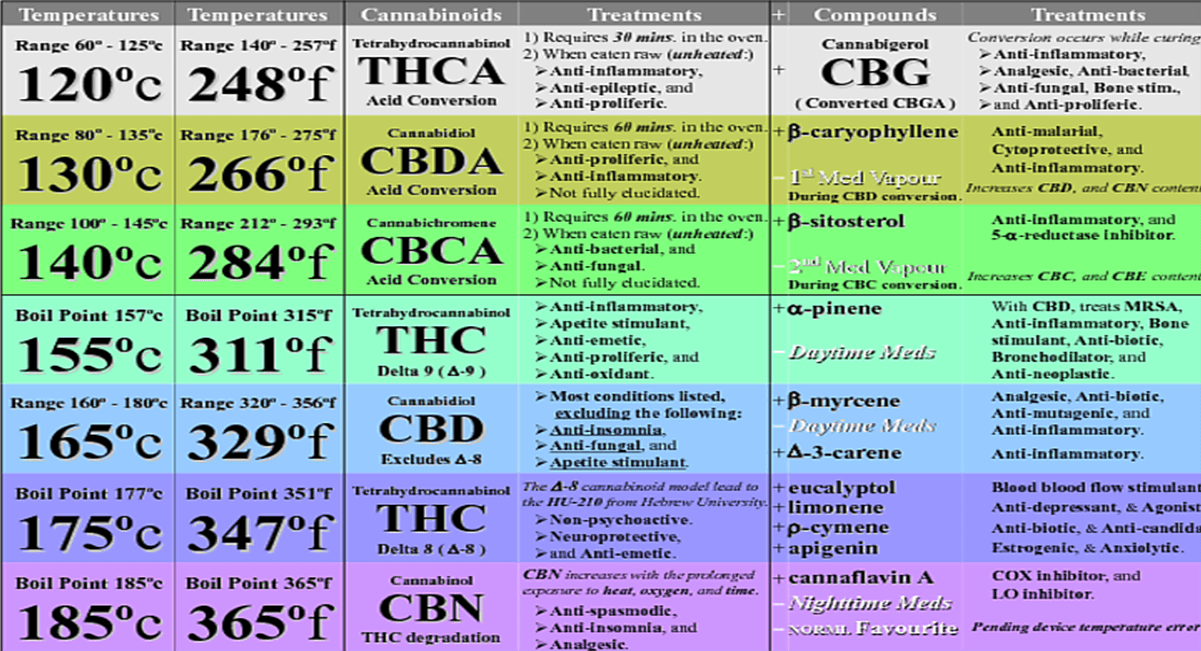
Multiple studies indicate that the ideal temperature range for THCA decarboxylation is 220-240°F (104-115°C).
Within this range, the conversion rate is optimized, ensuring maximum Delta 9 THC production while minimizing the degradation of other valuable cannabinoids and terpenes.
Temperatures below this range result in incomplete conversion, while higher temperatures can lead to the breakdown of Delta 9 THC into CBN (cannabinol) and other less desirable compounds.
Factors Affecting Conversion
Several factors influence the precise temperature and time required for complete decarboxylation.
These include the moisture content of the cannabis material, the surface area exposed to heat, and the specific strain being processed.
Moisture content: higher moisture may need to extend time, surface area is the coverage of the heat, and certain strains might react better with more precise heating times.
Time: Longer exposure to heat, even at lower temperatures, can eventually lead to decarboxylation.
However, prolonged heating increases the risk of terpene degradation and cannabinoid loss.
Environment: Oxygen present in the heating environment may further degrade cannabinoids.
Implications for Consumers
For consumers, understanding decarboxylation is crucial for accurate dosing and predictable effects.
When making edibles, proper decarboxylation of raw cannabis is essential to ensure the final product contains active Delta 9 THC.
Vaping devices and dab rigs also rely on controlled heating to activate cannabinoids.
Incomplete decarboxylation will lead to a less potent product, while excessive heat can degrade the desired compounds, diminishing the experience.
Consumer should research before they commit to using vaping or edibles.
If you are new to edibles, it is suggested to start with low dosage.
Implications for Industry Professionals
Commercial cannabis processors need to precisely control decarboxylation to ensure product consistency and potency.
Precise temperature control is essential for consistent results.
Accurate Delta 9 THC concentrations are critical for regulatory compliance and consumer safety.
Sophisticated decarboxylation equipment, often with vacuum sealing to prevent oxidation, is commonly used in commercial settings.
These tools allow for precise temperature and time control, minimizing degradation and maximizing Delta 9 THC yield.
Quality control is critical for compliance.
Scientific Evidence and Data
The data supporting the 220-240°F (104-115°C) temperature range for THCA decarboxylation comes from a combination of peer-reviewed studies and industry-validated research.
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is frequently used to analyze the cannabinoid content at different temperatures and time intervals.
This data reveals the rate of THCA conversion and the formation of other cannabinoids like CBN.
One notable study showed that heating THCA at 230°F (110°C) for 30-60 minutes resulted in optimal decarboxylation without significant degradation.
Another study highlighted the importance of moisture control, demonstrating that drier cannabis material decarboxylated more efficiently.
These results help to inform the range for decarboxylation.
Ongoing Developments
Research into decarboxylation continues to evolve, with a focus on optimizing the process for specific strains and product types.
Scientists are exploring the use of microwave and ultrasound technologies to achieve faster and more efficient decarboxylation.
These new methods are aimed at preserving terpenes and reducing the overall processing time.
The development of more precise and user-friendly decarboxylation devices for both home and commercial use is also underway.
These advancements will empower consumers and professionals alike to achieve consistent and predictable results.
These may lead to a new era of cannabis.
Conclusion
The optimal temperature for converting THCA to Delta 9 THC lies between 220-240°F (104-115°C), but careful attention must be paid to time, moisture content, and other factors to ensure the best possible outcome. Ongoing research aims to refine this process, promising further advancements in the future.
Consumers and industry professionals should stay informed about the latest findings to maximize the potential of cannabis products and ensure safety and consistency.
Look out for any studies that may change these facts.