Where Is The Electron Transport System Located

The fate of cellular energy production hangs in the balance! Scientists are urgently reiterating a fundamental question: Where exactly is the electron transport system (ETS) located?
This question, vital to understanding cellular respiration and energy production, isn't about new discovery, but about reinforcing foundational knowledge essential for students, researchers, and healthcare professionals. Knowing the precise location of the ETS is critical for grasping how cells generate the energy needed for life.
The Critical Location: Mitochondria
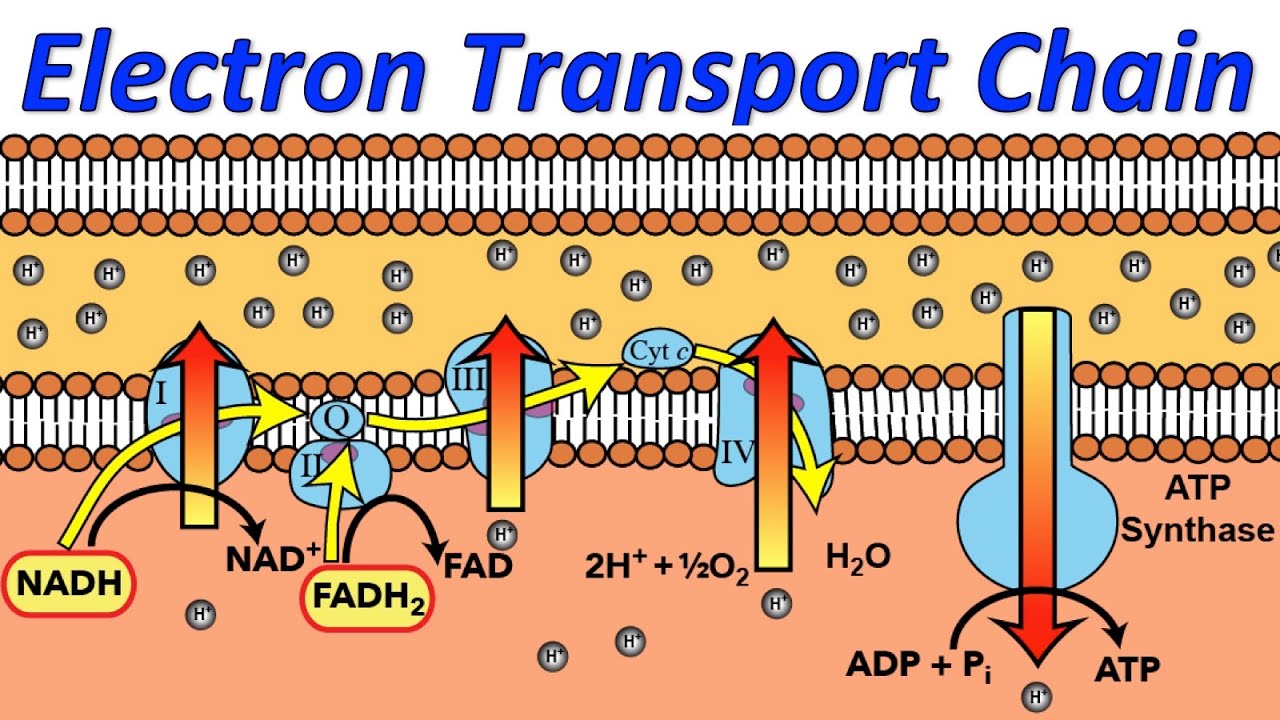
The answer is unequivocal: the electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This is not new information, but its constant emphasis is a must for the understanding of biological processes.
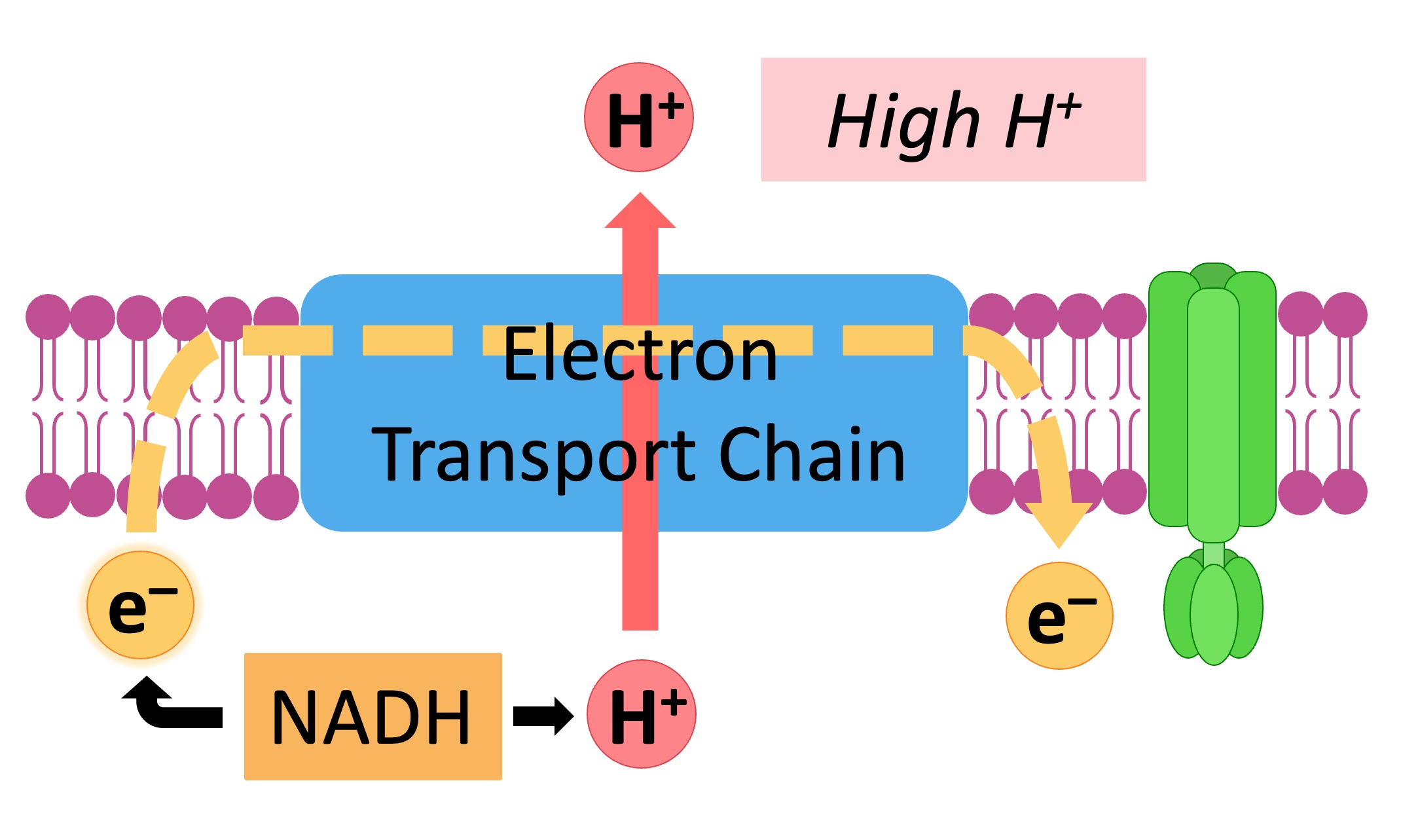
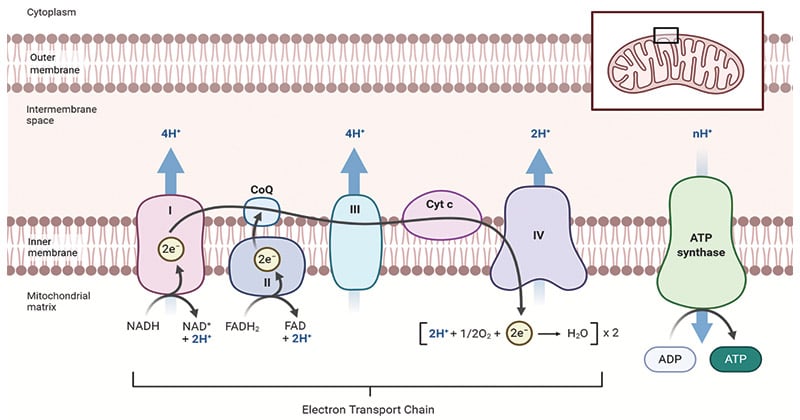
Specifically, the ETS resides within the cristae, the folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane. These folds significantly increase the surface area available for the electron transport chain and ATP synthase.
Why the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane?
The structure of the inner mitochondrial membrane is crucial for the ETS's function. It's impermeable to ions, allowing for the creation of a proton gradient. This gradient is the driving force behind ATP synthesis.
The location allows for compartmentalization. This ensures that the proton gradient, essential for chemiosmosis, can be established and maintained effectively.
Components of the ETS
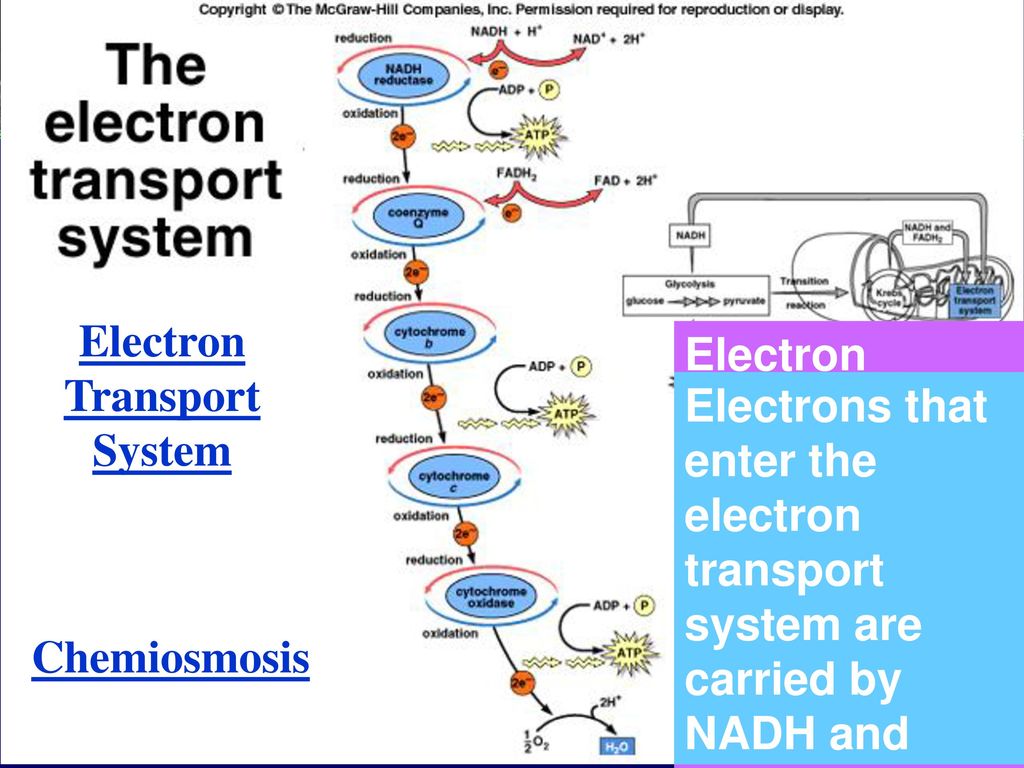
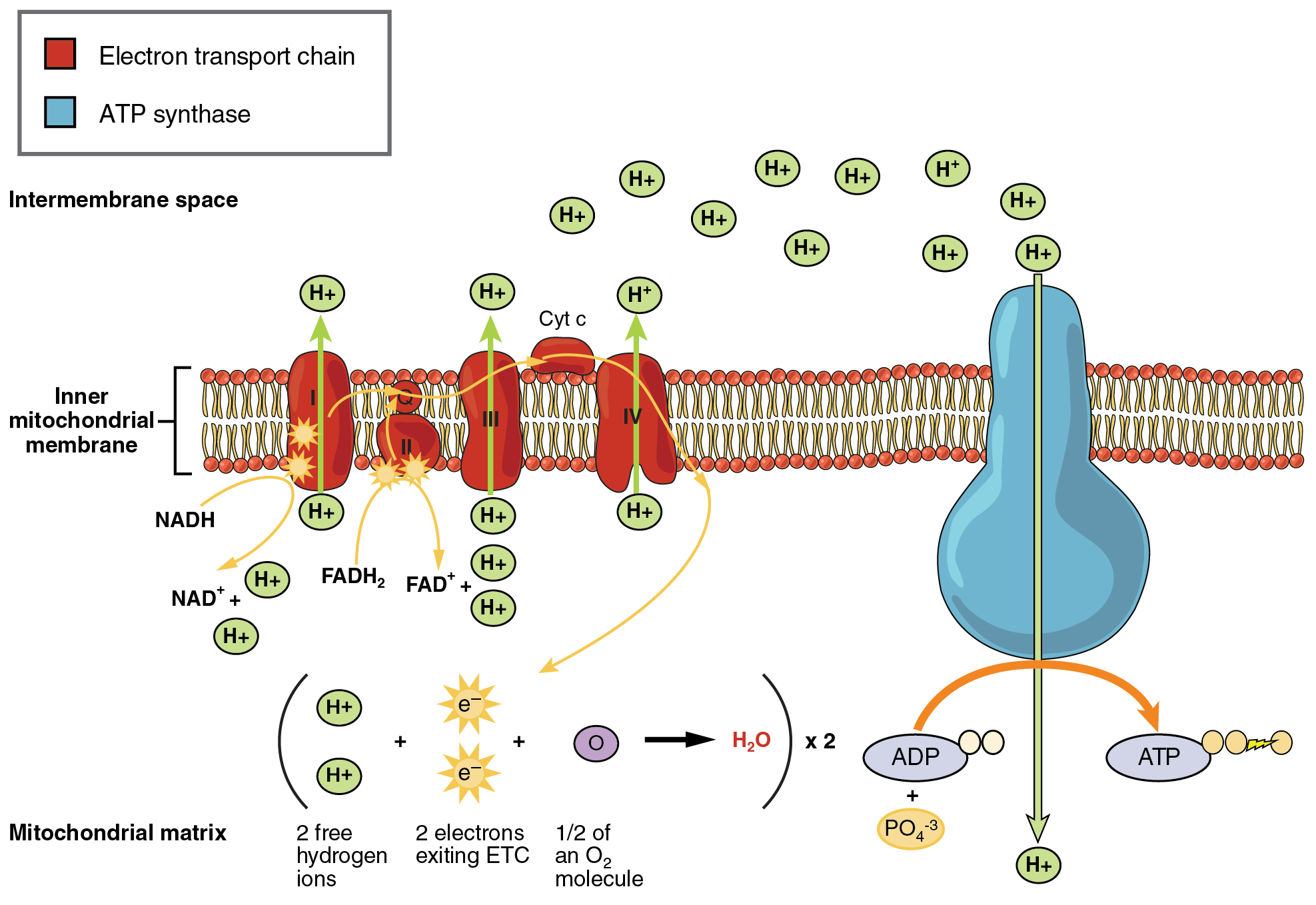
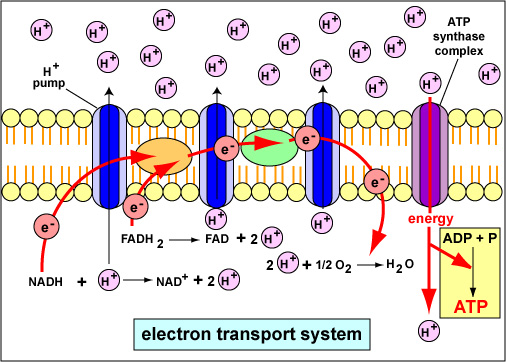
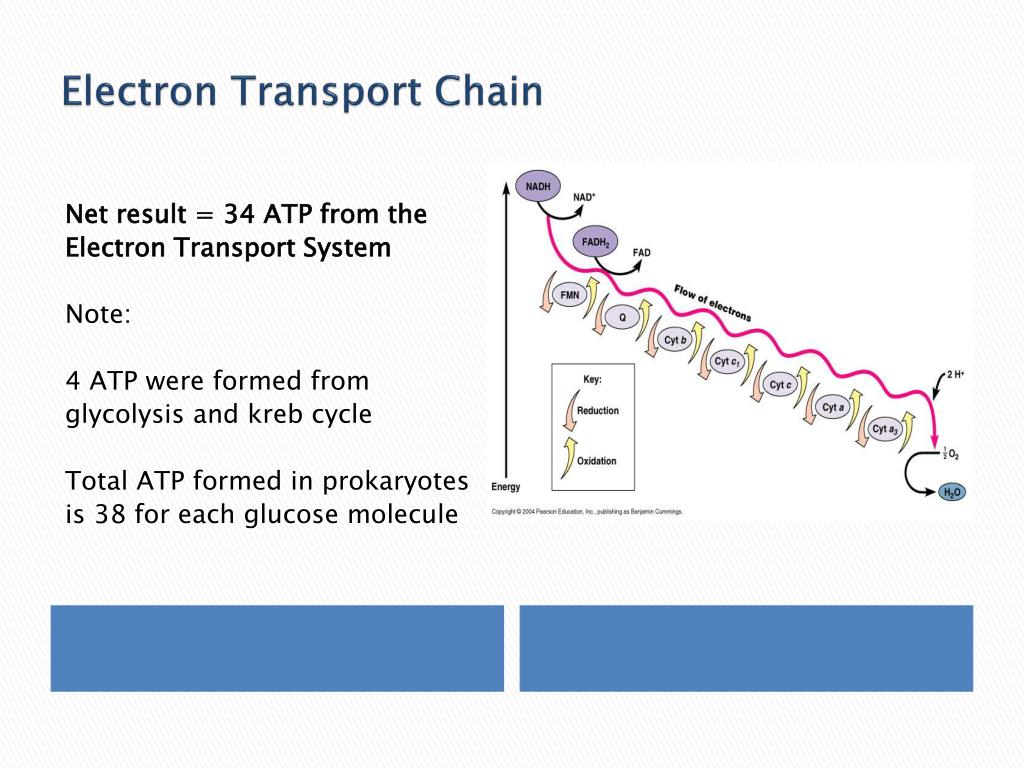
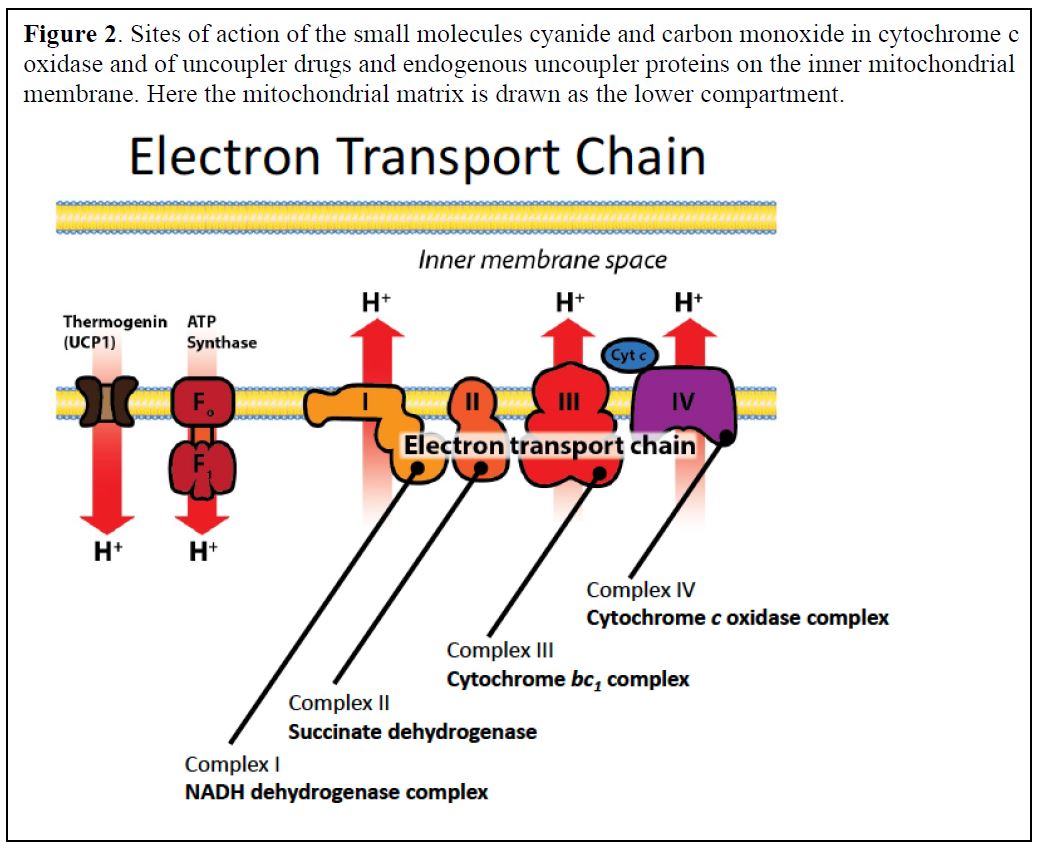
The ETS is composed of several protein complexes. These include Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase), Complex II (Succinate dehydrogenase), Complex III (Cytochrome bc1 complex), and Complex IV (Cytochrome c oxidase).
These complexes work sequentially to transfer electrons. They facilitate the pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, generating the electrochemical gradient.
Ubiquinone (Coenzyme Q) and Cytochrome c are mobile electron carriers. They shuttle electrons between the complexes, ensuring the smooth flow of electrons through the chain.
The Role of ATP Synthase
The proton gradient created by the ETS is harnessed by ATP synthase. ATP synthase is also embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
As protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, the energy released drives the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. This process is known as chemiosmosis.
The Big Picture: Cellular Respiration
The ETS is the final stage of aerobic cellular respiration. It follows glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), and pyruvate oxidation.
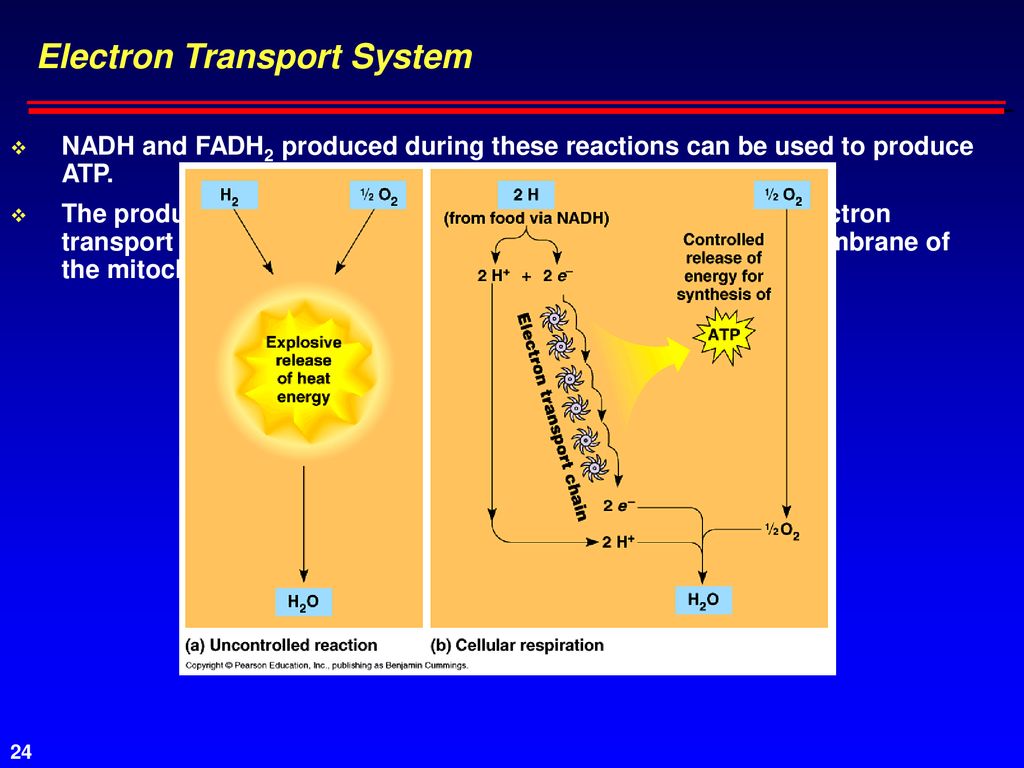
During cellular respiration, electrons are extracted from glucose and other fuel molecules. The electrons are then transferred through the ETS to ultimately reduce oxygen to water.
The energy released during electron transfer is used to generate a large amount of ATP. This ATP fuels various cellular activities.
Importance in Different Organisms
In eukaryotes, the ETS is found in the mitochondria. Prokaryotes lack mitochondria, so their ETS is located in the plasma membrane.
This difference in location highlights the evolutionary adaptations. Prokaryotes utilize their cell membrane for energy production, while eukaryotes have specialized organelles.
Relevance to Disease
Dysfunction of the ETS can lead to various diseases. Mitochondrial disorders often stem from defects in the components of the electron transport chain.
These disorders can manifest in a variety of ways, affecting tissues with high energy demands, such as the brain, heart, and muscles.
Understanding the precise location and function of the ETS is crucial for developing treatments for these diseases. It may help improve the quality of life for patients.
Future Directions and Reminders
Ongoing research focuses on understanding the intricacies of the ETS. Scientists are working to identify new therapeutic targets for mitochondrial diseases.
Reinforcing the fundamental knowledge of where the electron transport system is located – the inner mitochondrial membrane – remains paramount. It should be for students, researchers, and healthcare professionals alike.
Constant emphasis on this crucial fact is vital for progress in biological and medical fields. Remember: inner mitochondrial membrane, the site of life's energy engine.