Which Is A Key Component Of The Energy Molecule Atp

Imagine a world bustling with silent, microscopic activity. Within every cell of every living thing, from the towering redwood to the tiniest bacterium, a tireless engine hums. This engine relies on a single, critical fuel source, a molecule that powers virtually every biological process. Without it, life as we know it simply couldn't exist.
At the heart of this life-sustaining energy lies a key component of Adenosine Triphosphate, or ATP, the universal energy currency of cells. This crucial element is phosphate, and understanding its role in ATP is fundamental to grasping the very essence of life itself.
ATP, often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer, is a complex organic chemical. It participates in numerous processes essential to life. From muscle contraction to nerve impulse transmission, ATP is the driving force behind countless cellular activities.
A Closer Look at ATP's Structure
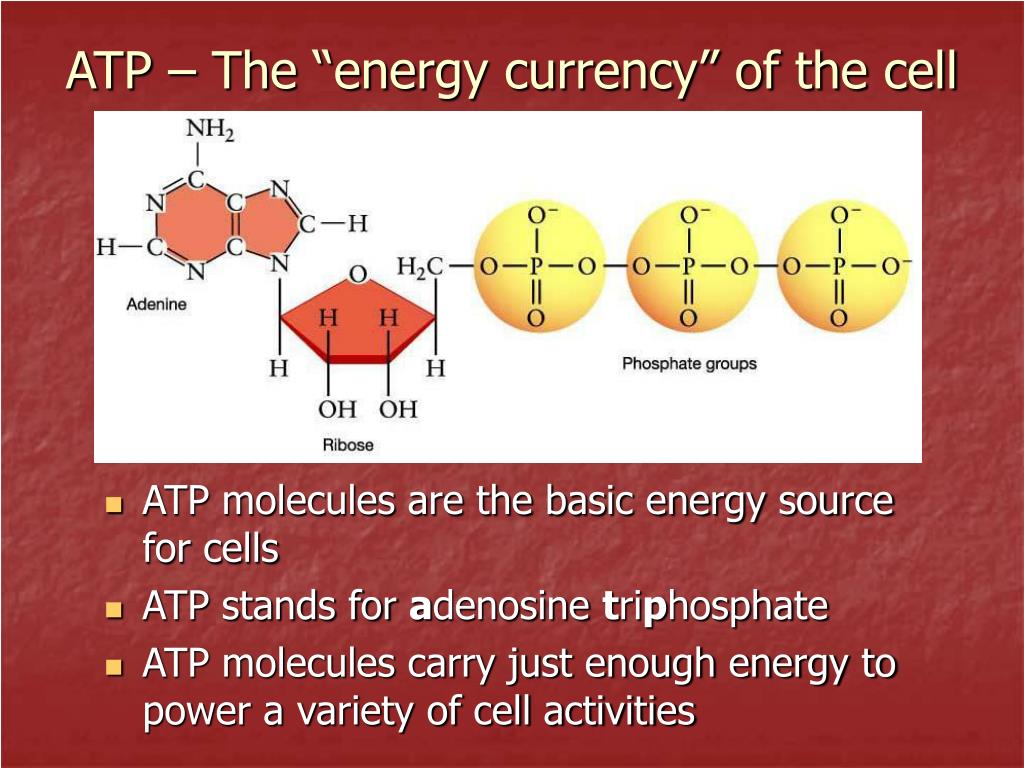
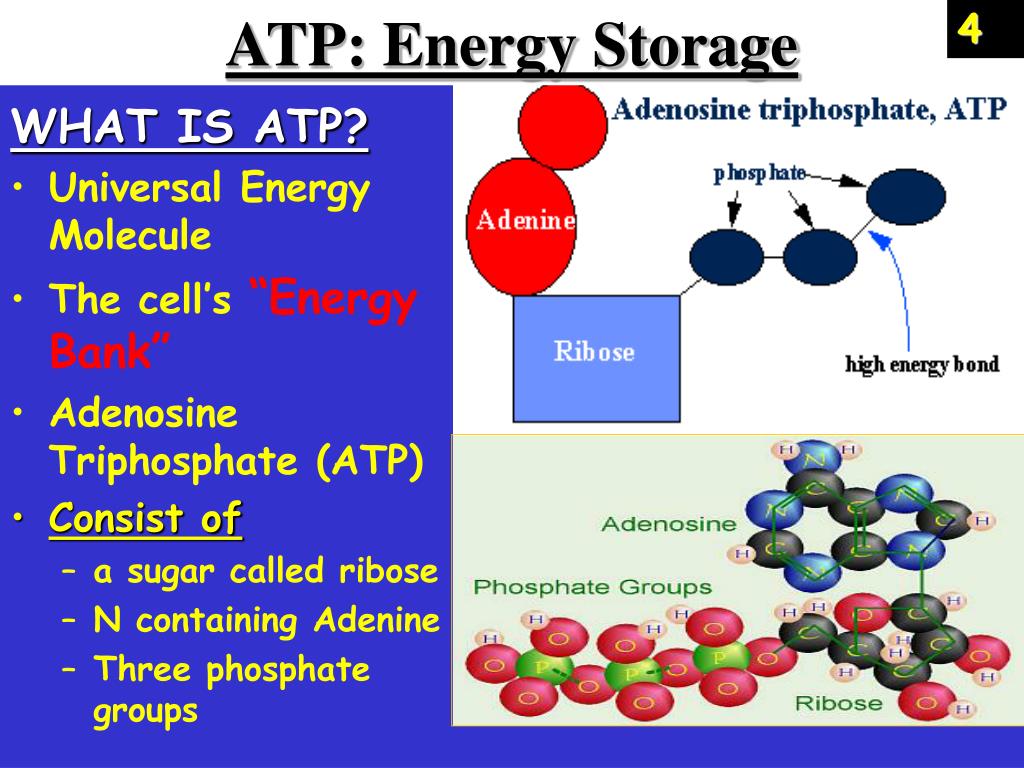
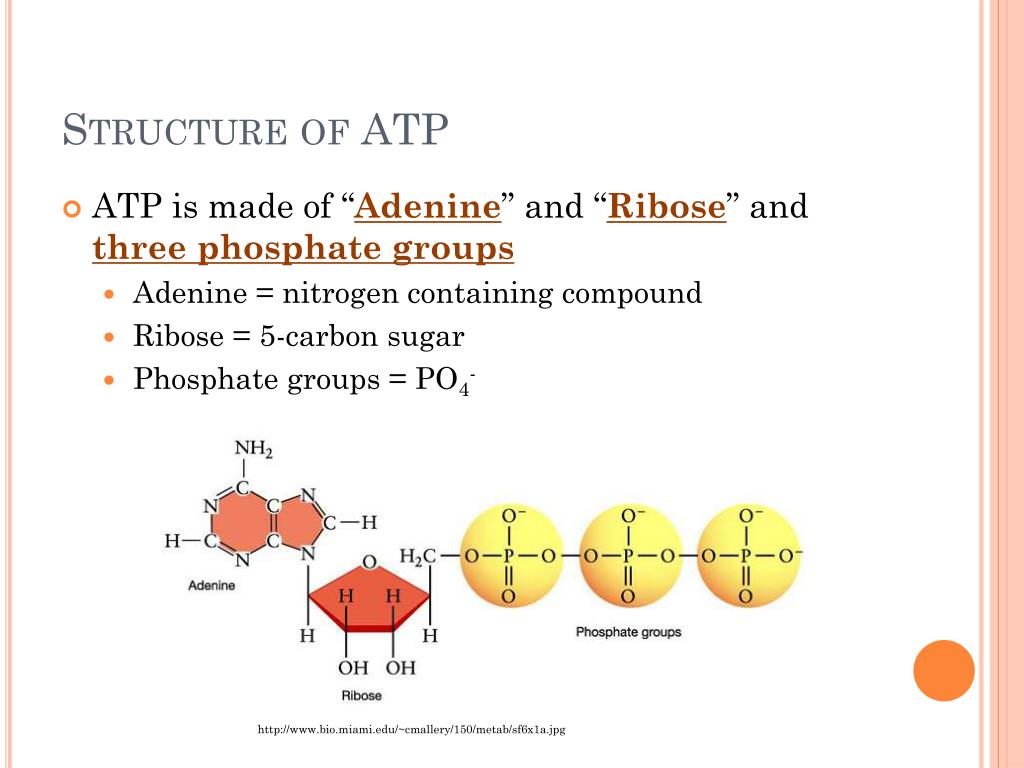
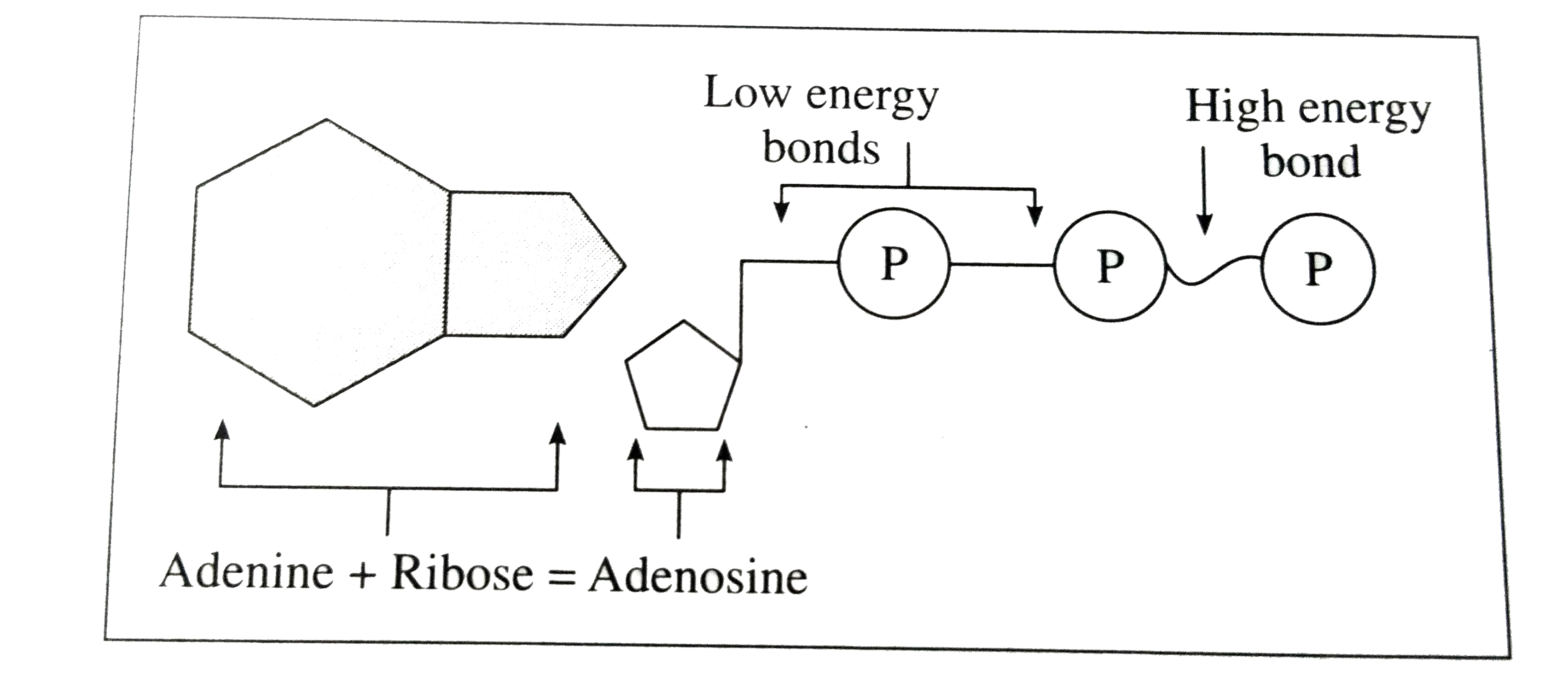
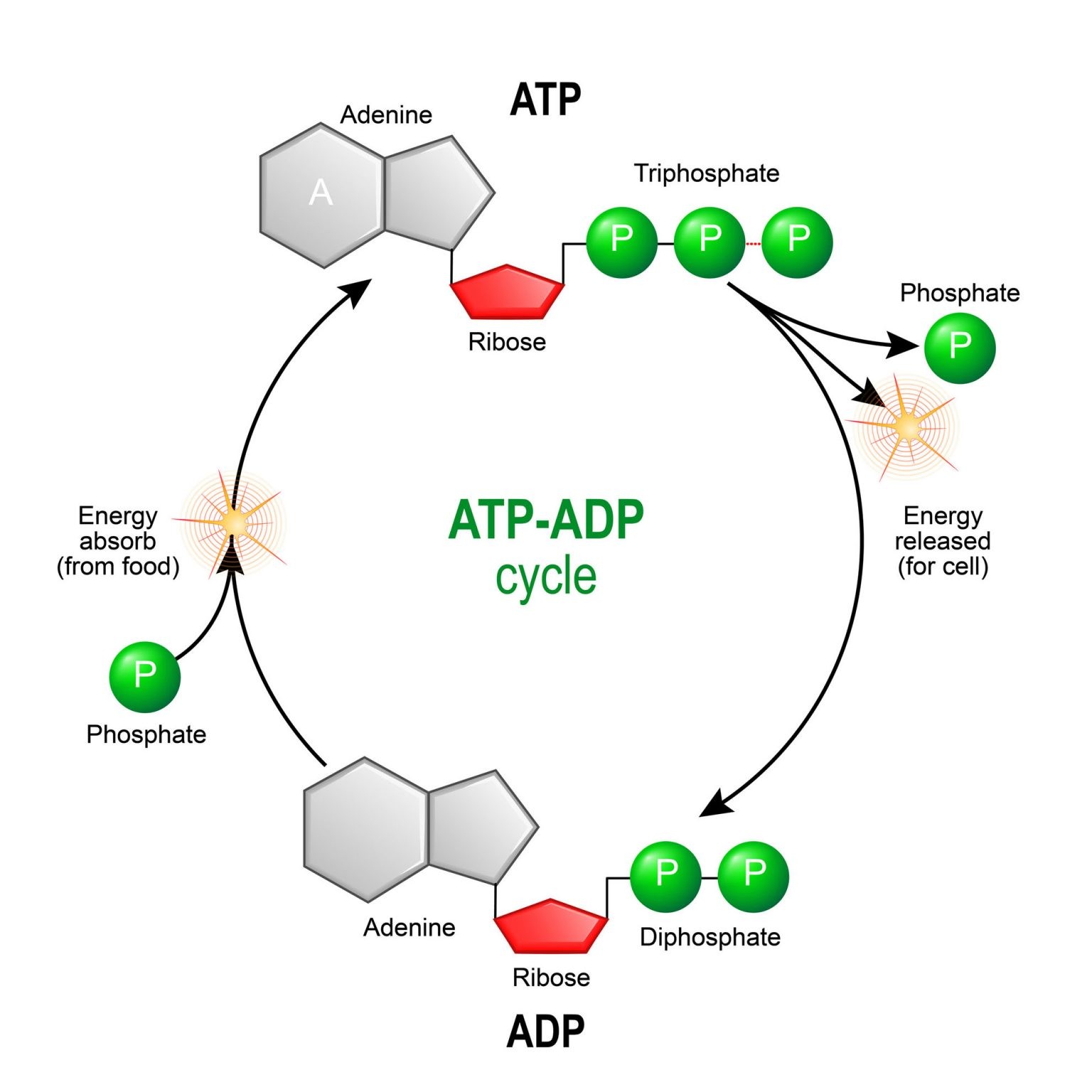
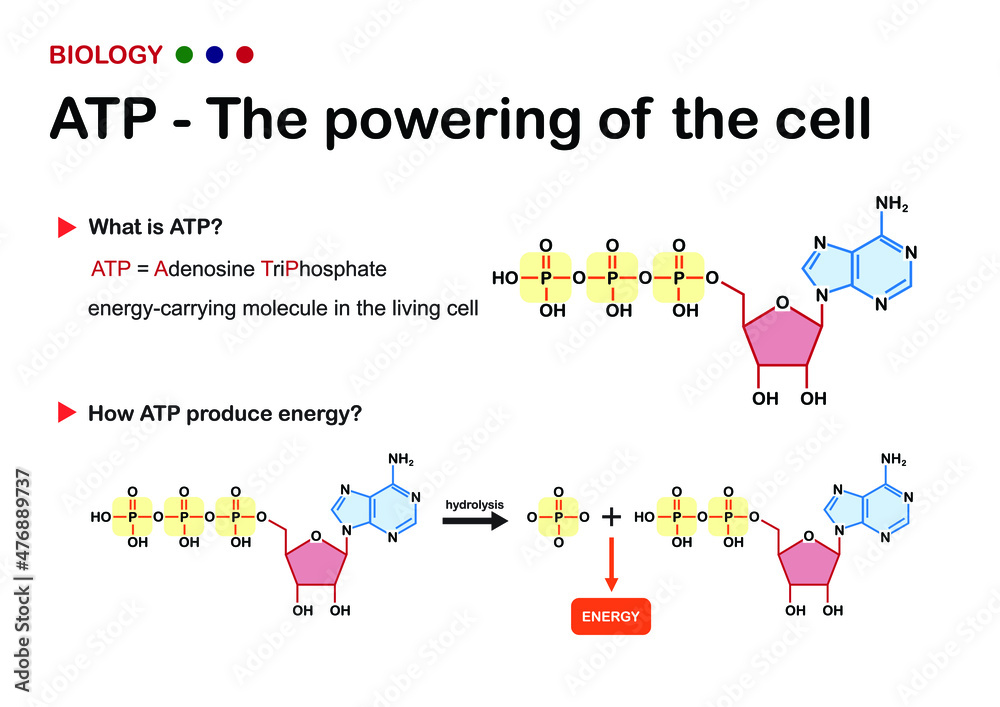
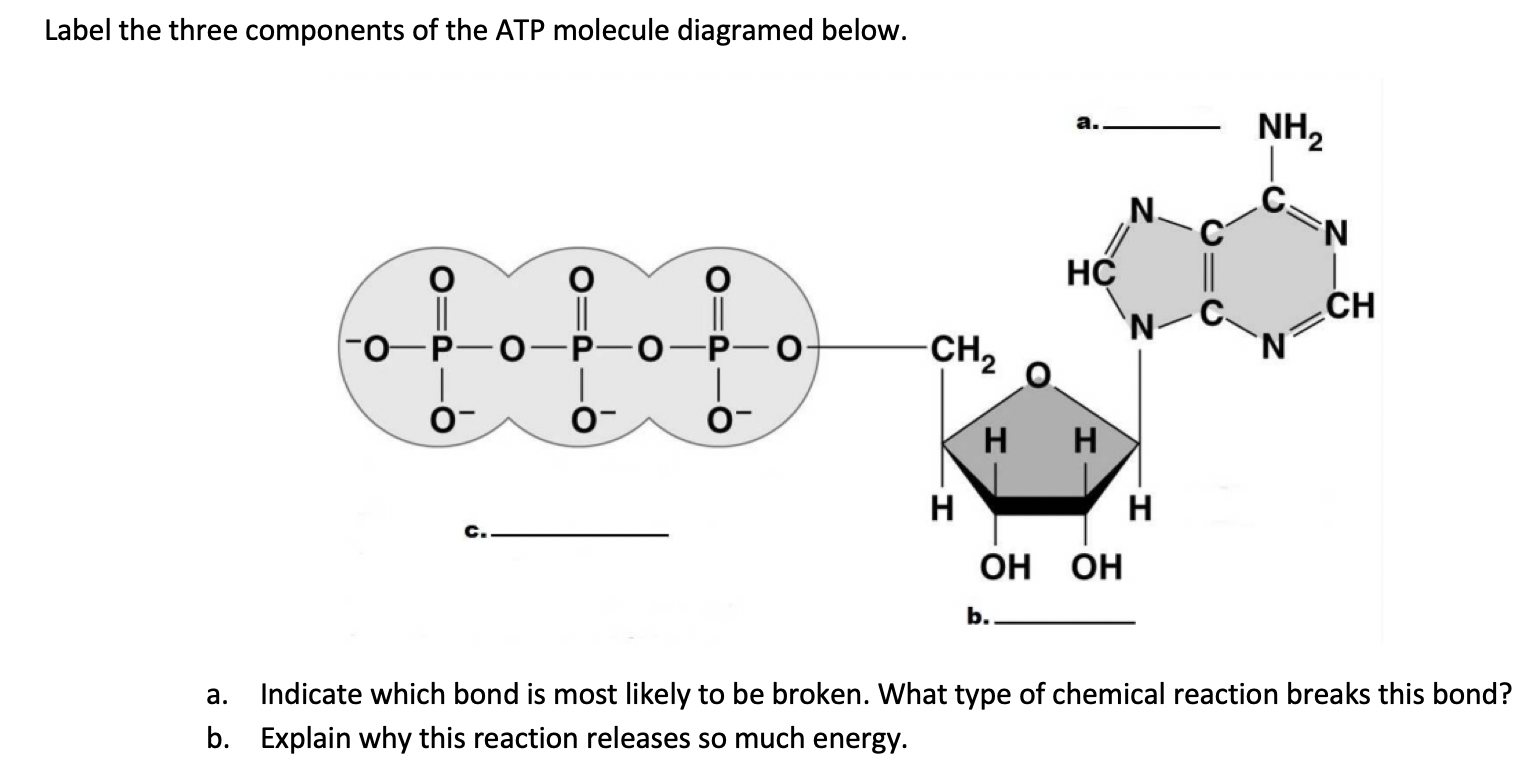
To truly understand phosphate's role, we must first examine ATP's structure. Adenosine Triphosphate consists of three main components: adenine, a nitrogenous base; ribose, a five-carbon sugar; and three phosphate groups.
These phosphate groups are linked together by high-energy bonds. It is within these bonds that the magic of ATP lies, and where phosphate plays its pivotal role.
The Significance of Phosphate
Phosphate is a chemical derivative of phosphoric acid. It's not just a structural component of ATP; it's the key to its energy-releasing capability.
The bonds between the phosphate groups are relatively weak and unstable. This instability is crucial because it allows for the controlled release of energy when one of these bonds is broken.
When ATP is hydrolyzed, meaning a water molecule is used to break a phosphate bond, it transforms into Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) and a free phosphate group. This process releases a significant amount of energy that the cell can then use to perform work.
"The energy released from ATP hydrolysis fuels a wide array of cellular processes, enabling organisms to grow, move, and maintain homeostasis," explains Dr. Emily Carter, a biochemist at the National Institutes of Health.
The free phosphate group, now separate from the ATP molecule, doesn't just vanish. It often attaches to other molecules in a process called phosphorylation.
Phosphorylation can alter the shape and activity of proteins, enzymes, and other cellular components. This serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism, switching proteins on or off to control cellular pathways.
The ATP Cycle: A Continuous Loop
The story of ATP doesn't end with its hydrolysis. The cell constantly regenerates ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate through a process called phosphorylation.
This regeneration is typically powered by energy derived from the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules during cellular respiration or photosynthesis.
Thus, ATP acts as a rechargeable battery, constantly cycling between its high-energy (ATP) and low-energy (ADP) forms. Phosphate is at the center of this cyclical energy transformation.
Beyond Energy: Phosphate's Other Roles
While its role in ATP is paramount, phosphate's importance extends beyond energy transfer. It is a fundamental building block of DNA and RNA, the molecules that carry genetic information.
Phosphate also plays a vital role in maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes. It is a component of phospholipids, the molecules that form the bilayer structure of these membranes.
Furthermore, phosphate is essential for bone and teeth formation. Calcium phosphate is the primary mineral component of these tissues, providing them with strength and rigidity.
The Environmental Significance of Phosphate
Phosphate is not only crucial for life at the cellular level but also plays a significant role in broader ecosystems. It is an essential nutrient for plant growth and a key component of fertilizers.
However, excess phosphate runoff from agricultural fields and sewage treatment plants can lead to eutrophication of waterways. This can cause algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels, harming aquatic life.
Therefore, responsible phosphate management is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring sustainable agriculture.
The Future of ATP Research
Scientists continue to explore the complexities of ATP and its role in various biological processes. Research focuses on understanding how ATP synthesis and hydrolysis are regulated. Researchers are also developing new therapeutic strategies that target ATP-dependent enzymes.
One promising area of research is the development of drugs that inhibit ATP synthesis in cancer cells. By disrupting their energy supply, these drugs could selectively kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissues.
Another exciting area is the development of bioluminescent ATP assays. These assays can be used to detect and quantify ATP levels in biological samples, providing valuable insights into cellular metabolism and disease processes.
As our understanding of ATP deepens, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of this fundamental energy molecule in medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science.
A Final Thought
The story of ATP is a testament to the elegance and efficiency of life's fundamental processes. This tiny molecule, with phosphate as its crucial component, powers virtually every activity within our cells.
From the simple act of breathing to the complex workings of our brains, ATP is the driving force behind it all. It's a reminder that even the smallest components can have the most profound impact on life itself.
So, the next time you marvel at the beauty of nature or the intricacies of the human body, remember the silent, tireless work of ATP, and the key role phosphate plays in keeping the engine of life running smoothly.










+is+composed+of+adenosine+and+three+inorganic+phosphates+(Pi)..jpg)
