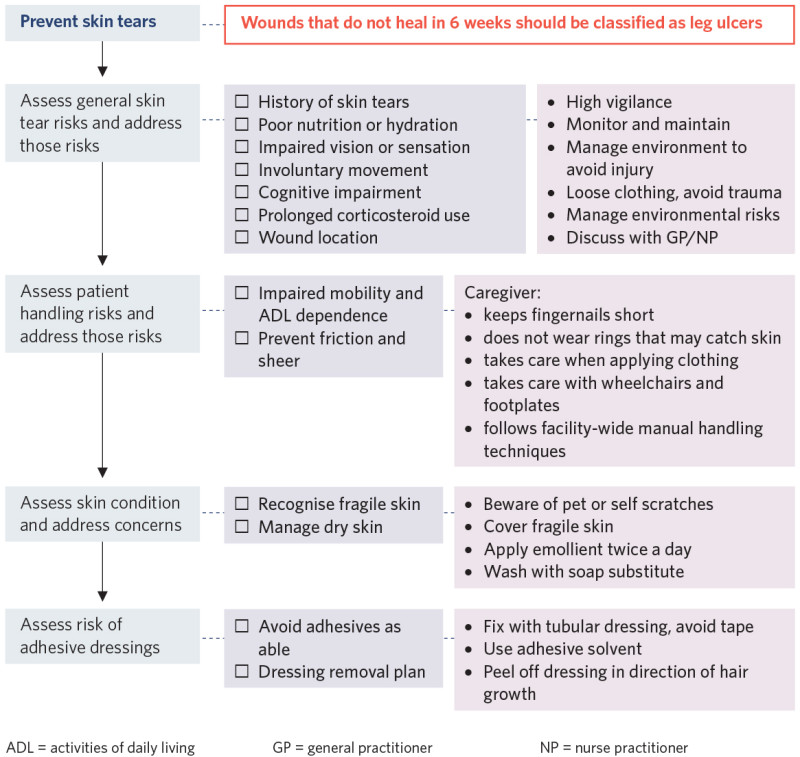
Which Of The Following Actions Helps To Prevent Skin Tears

For elderly individuals and those with fragile skin, the slightest bump or scrape can lead to a painful and debilitating injury: a skin tear. These wounds, characterized by the separation of the epidermis from the dermis or both layers from underlying structures, pose a significant threat to health and quality of life, often leading to infection, chronic pain, and increased healthcare costs. Preventing these injuries is paramount, and understanding the specific actions that can reduce risk is crucial for caregivers, healthcare professionals, and individuals themselves.
The following article will explore evidence-based strategies for preventing skin tears, drawing upon expert guidelines and research findings. We will examine key preventative measures, including proper skin hydration, protective clothing, safe transfer techniques, and environmental modifications. The information presented is intended to empower readers with the knowledge necessary to minimize the occurrence of skin tears and promote skin integrity.
Understanding Skin Tear Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of skin tears. Age is a primary risk factor as skin naturally becomes thinner and less elastic with age. This is due to a decrease in collagen and elastin production.
Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, malnutrition, and dehydration further compromise skin integrity. Medications like corticosteroids can also weaken the skin. A history of previous skin tears significantly elevates the risk of future occurrences.
Key Preventative Measures
Moisturizing and Hydration
Maintaining adequate skin hydration is essential for preventing skin tears. Dry skin is more prone to tearing. Regular application of emollients helps to restore and maintain the skin's moisture barrier.
According to the National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel (NPIAP), using a pH-balanced moisturizer at least twice daily is recommended. Focus on areas prone to dryness, such as arms and legs.
Internal hydration is equally crucial. Encouraging sufficient fluid intake can improve skin elasticity. Healthcare professionals often recommend at least eight glasses of water daily unless contraindicated by other medical conditions.
Protective Clothing and Padding
Wearing appropriate clothing can significantly reduce the risk of skin tears. Long sleeves and pants offer a protective barrier against minor bumps and abrasions. Consider using specialized limb protectors or padding for individuals at high risk, especially those prone to falls.
Occupational therapists often play a key role in recommending and fitting protective gear. They can assess individual needs and provide tailored solutions.
Safe Transfer Techniques
Improper transfer techniques are a leading cause of skin tears, particularly in elderly care settings. Always use proper lifting and transfer techniques. Avoid pulling or dragging individuals across surfaces.
Healthcare providers and caregivers should receive comprehensive training in safe patient handling. Using assistive devices such as transfer boards or mechanical lifts can minimize friction and shear forces on the skin.
Environmental Modifications
Modifying the environment to reduce hazards is crucial in preventing skin tears. Remove or pad sharp edges on furniture. Ensure adequate lighting to prevent falls.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) recommends performing routine safety checks of the environment. Pay close attention to potential hazards in high-traffic areas such as hallways and bathrooms.
Skin Care Best Practices
Gentle cleansing is vital for maintaining skin integrity. Avoid using harsh soaps or scrubbing vigorously. Use mild, pH-balanced cleansers. Pat the skin dry instead of rubbing.
Careful attention to wound care is crucial if a skin tear does occur. Follow established protocols for cleansing and dressing wounds to promote healing and prevent infection.
Consulting with a wound care specialist is recommended for complex or slow-healing skin tears. They can provide specialized treatment and management strategies.
Addressing Specific Risk Factors
Individualized care plans are essential for addressing specific risk factors. Nutritional assessments can identify and correct deficiencies that compromise skin health. Regular monitoring of medications that may weaken the skin is important.
For individuals with cognitive impairments, providing clear and simple instructions during transfers can reduce agitation and resistance. This minimizes the risk of accidental injuries.
The Role of Education
Education is a cornerstone of skin tear prevention. Healthcare professionals, caregivers, and individuals at risk should receive comprehensive training on preventative measures. This includes proper skin care techniques, safe transfer methods, and environmental modifications.
Patient and family education materials should be readily available and easy to understand. Reinforcing key concepts through visual aids and practical demonstrations can enhance comprehension and adherence.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research is focused on developing new and improved methods for preventing and treating skin tears. This includes exploring novel wound dressings and preventative skin care products. Investigating the effectiveness of various educational interventions is also a priority.
Advancements in technology, such as wearable sensors that monitor skin hydration and pressure, hold promise for personalized prevention strategies. These technologies could provide real-time feedback and alerts to prevent skin tears before they occur.
Conclusion
Preventing skin tears requires a multifaceted approach that addresses individual risk factors and implements evidence-based strategies. By focusing on skin hydration, protective measures, safe transfer techniques, environmental modifications, and education, we can significantly reduce the incidence of these debilitating injuries. Continued research and innovation will further enhance our ability to protect vulnerable individuals and promote skin integrity, improving their overall well-being and quality of life. Proactive prevention is the most effective strategy in combating skin tears, safeguarding the health and independence of those at risk.