Which Of The Following Are True Of Information Governance
In today's data-driven world, understanding information governance (IG) is increasingly critical for organizations of all sizes. But what exactly does information governance entail, and what statements accurately reflect its core principles? The rise in data breaches, stringent regulatory requirements, and the sheer volume of information being generated daily have thrust IG into the spotlight.
This article explores the fundamental aspects of information governance, clarifying its key characteristics and dispelling common misconceptions. It aims to provide a clear understanding of IG, its importance, and its practical application in modern organizations.
Defining Information Governance: What It Is and Isn't
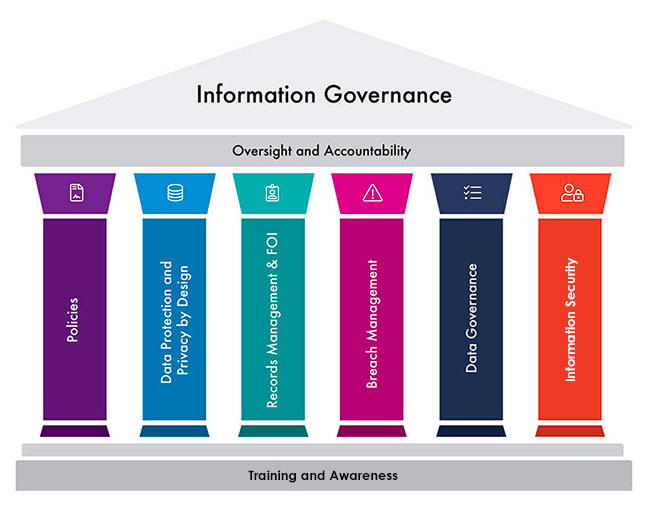
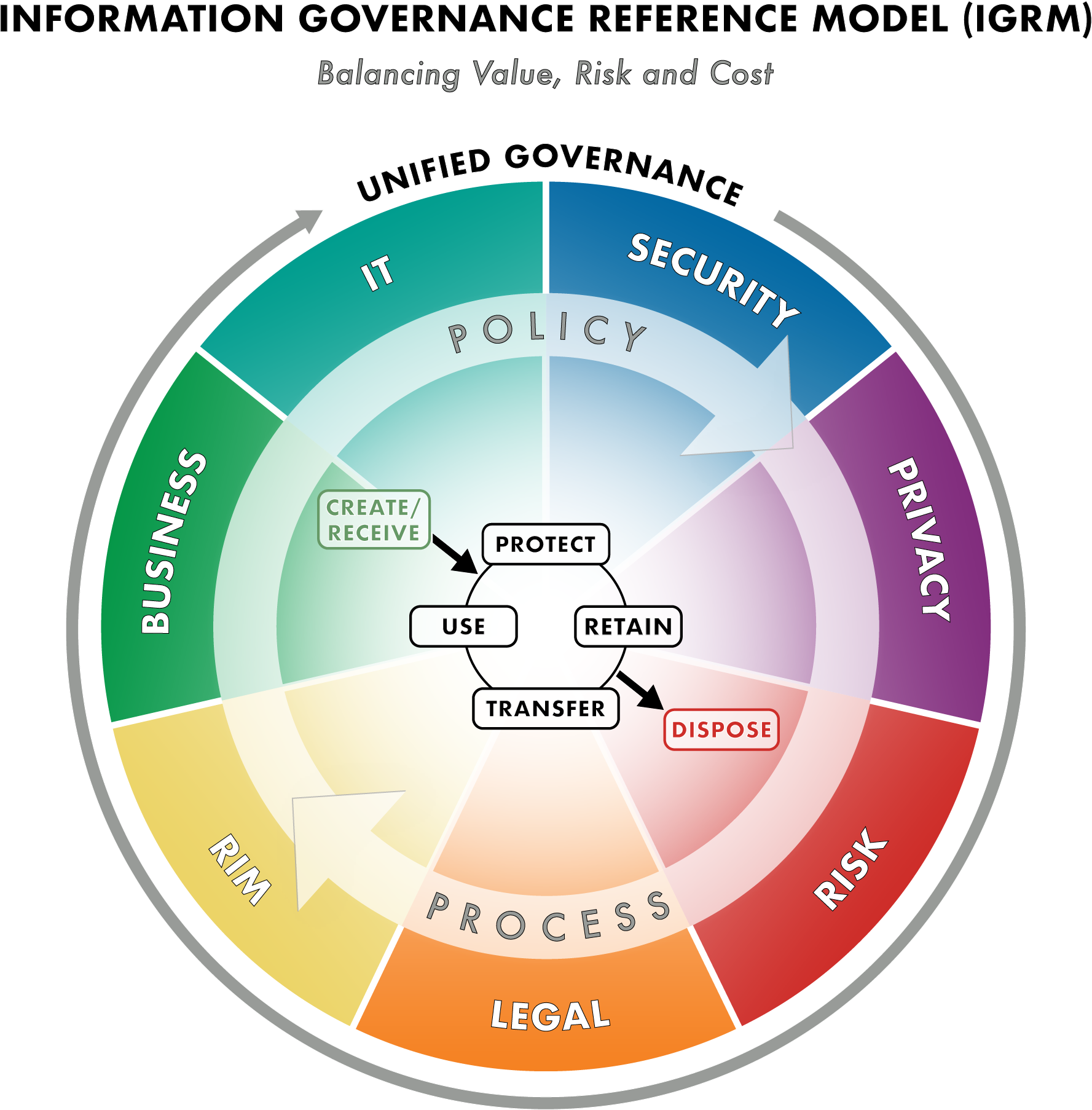
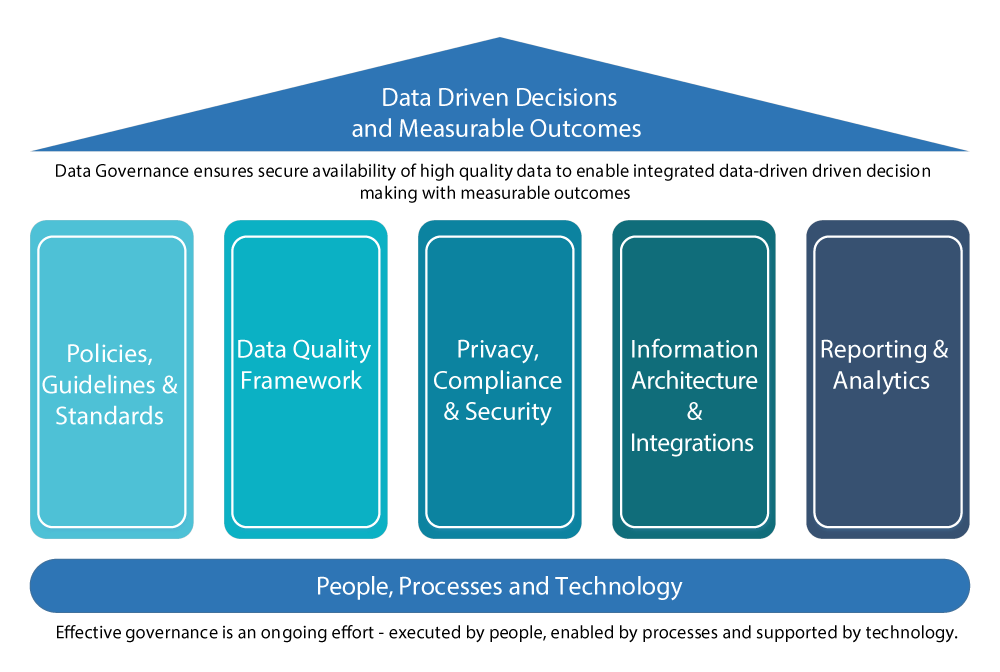
At its core, information governance is a strategic framework. It establishes policies and procedures for managing information assets throughout their lifecycle. This lifecycle includes creation, storage, usage, archiving, and eventual disposal.
Key Concept: Information governance is *not* simply about IT infrastructure or records management. It's a broader, enterprise-wide approach.
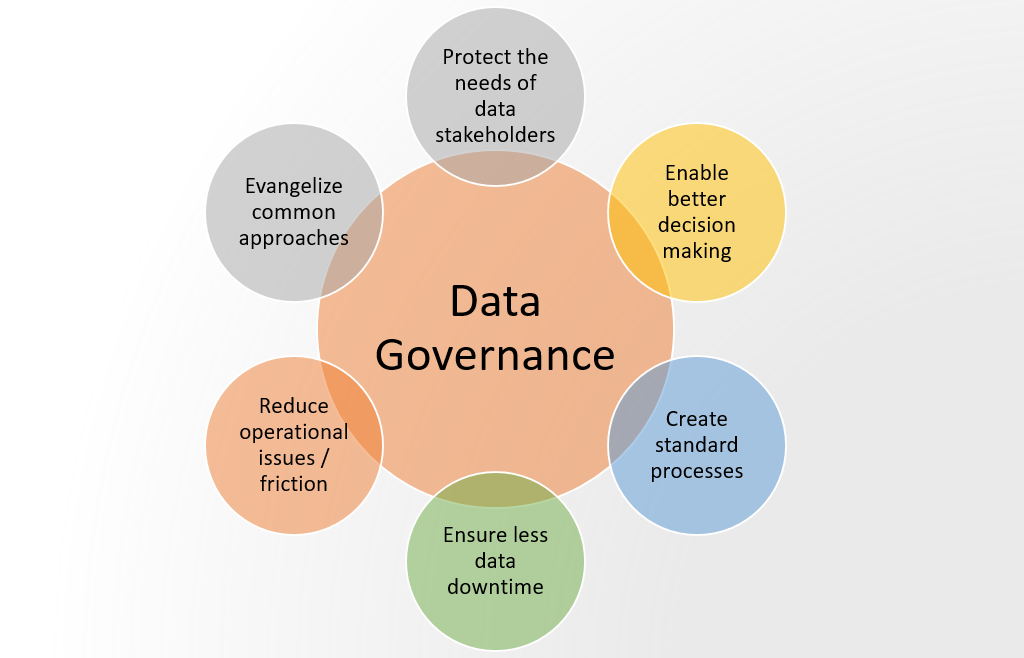
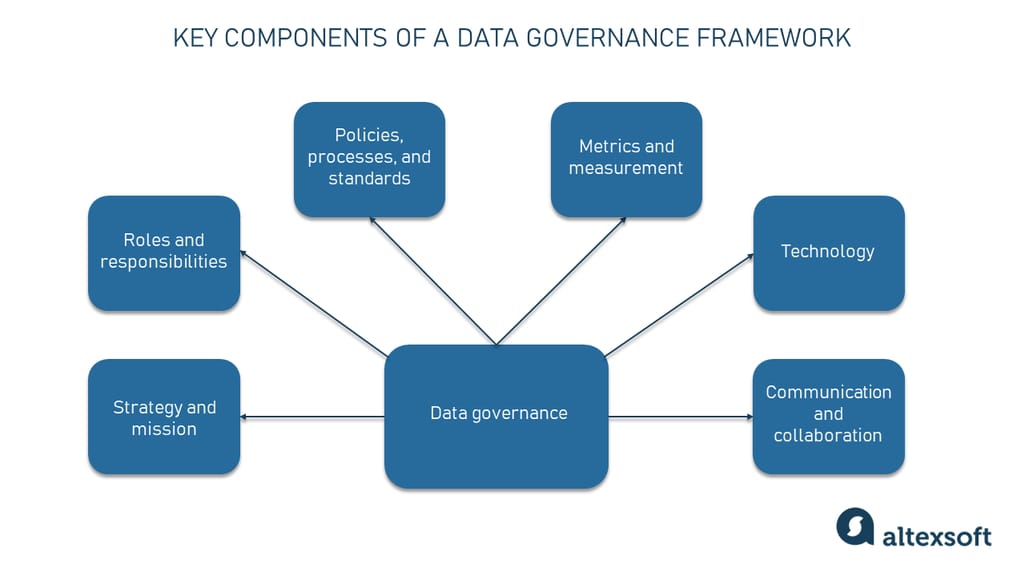
Core Principles of Effective Information Governance
Several principles underpin successful information governance programs. Understanding these principles is essential for determining the validity of different statements about IG.
Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are crucial. Someone must be ultimately responsible for the IG program's success.
Transparency: Policies and procedures should be readily accessible and understandable to all relevant stakeholders. This promotes trust and compliance.
Integrity: Information must be accurate, reliable, and protected from unauthorized modification. Data integrity is paramount for informed decision-making.
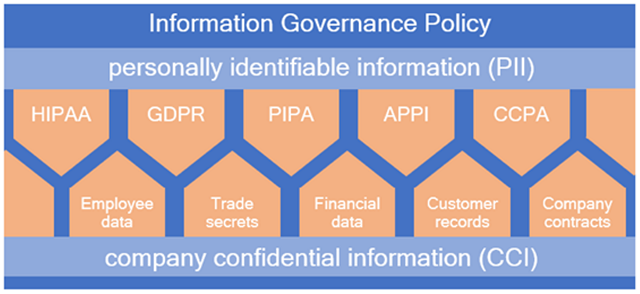
Protection: Sensitive information must be adequately secured to prevent breaches and comply with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Compliance: IG programs must ensure adherence to all applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
Availability: Information should be accessible to authorized users when and where they need it. This supports efficient business operations.
Retention: Establish appropriate retention schedules for different types of information. This avoids unnecessary storage costs and legal risks.
Disposition: Implement secure disposal methods for information that is no longer needed. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and regulatory non-compliance.
Analyzing Common Statements About Information Governance
Based on these principles, we can analyze common statements about information governance to determine their accuracy. Let's examine a few examples.
"Information governance is solely the responsibility of the IT department."
This statement is false. While IT plays a crucial role in implementing and maintaining IG systems, it's a shared responsibility across the entire organization. Legal, compliance, and business units are all integral parts of the IG process.
"Information governance is only necessary for large corporations."
This is also false. Regardless of size, any organization that handles data needs information governance. Even small businesses face data security risks and regulatory requirements.
"An effective information governance program improves decision-making."
This statement is true. By ensuring data quality and accessibility, IG empowers organizations to make more informed decisions. This leads to better business outcomes.
"Information governance primarily focuses on preventing data breaches."
This is partially true, but incomplete. Data protection is a critical aspect, but IG encompasses much more. It also includes managing data for business intelligence, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
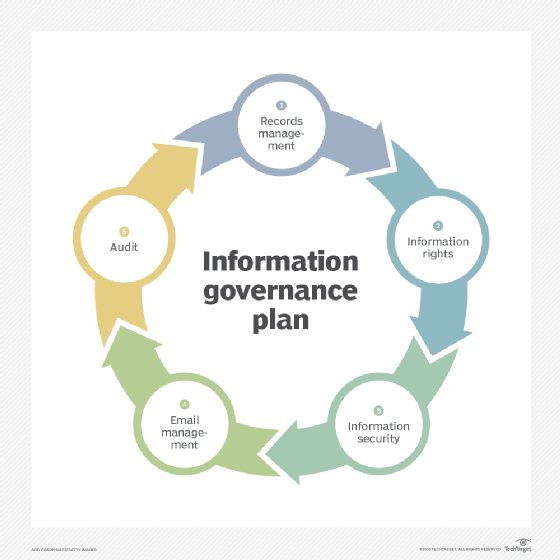
"Implementing information governance is a one-time project."
This statement is definitively false. Information governance is an ongoing process. It requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement to remain effective.
The Impact of Effective Information Governance
Implementing a robust information governance program yields numerous benefits. These extend far beyond simple regulatory compliance.
Improved data quality leads to better insights and more accurate reporting. This supports more strategic decision-making.
Reduced storage costs result from efficient data retention and disposal practices. This frees up resources for other initiatives.
Enhanced security reduces the risk of data breaches and reputational damage. This builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Streamlined processes improve operational efficiency and productivity. This allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
Better compliance minimizes legal and regulatory risks, protecting the organization from fines and penalties.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to Information
In conclusion, understanding what constitutes true information governance is essential for modern organizations. It's not just about IT or compliance; it's about treating information as a strategic asset.
By embracing the core principles of accountability, transparency, integrity, and protection, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data. This leads to better decision-making, reduced risks, and improved business outcomes. Ultimately, effective information governance is not just a best practice, but a necessity in today's information-driven world.