Which Of The Following Are Types Of Barriers To Communication

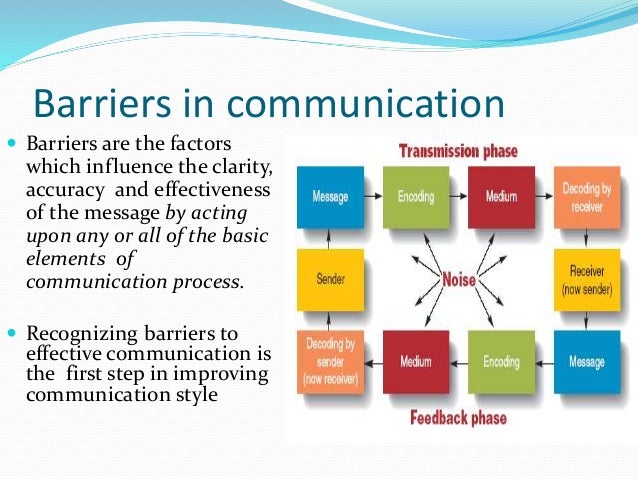
Effective communication is the bedrock of human interaction, essential for building relationships, fostering understanding, and achieving common goals. However, the path to clear communication is often fraught with obstacles known as barriers to communication, hindering the accurate transmission and reception of information.
Understanding these barriers is crucial for individuals and organizations alike to improve communication effectiveness and minimize misunderstandings. These barriers can manifest in various forms, stemming from linguistic differences to psychological factors and even physical environments.
Types of Barriers to Communication
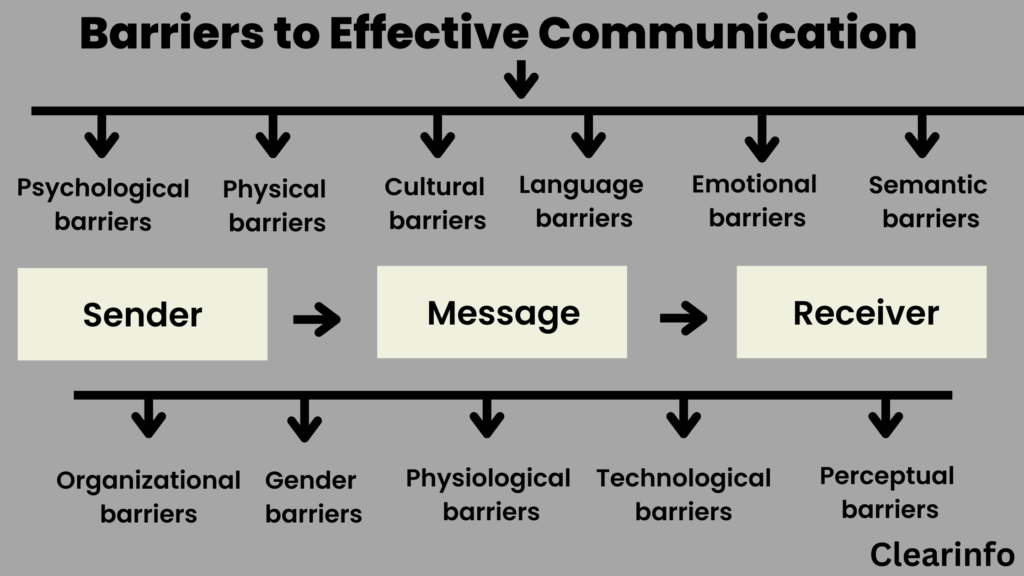
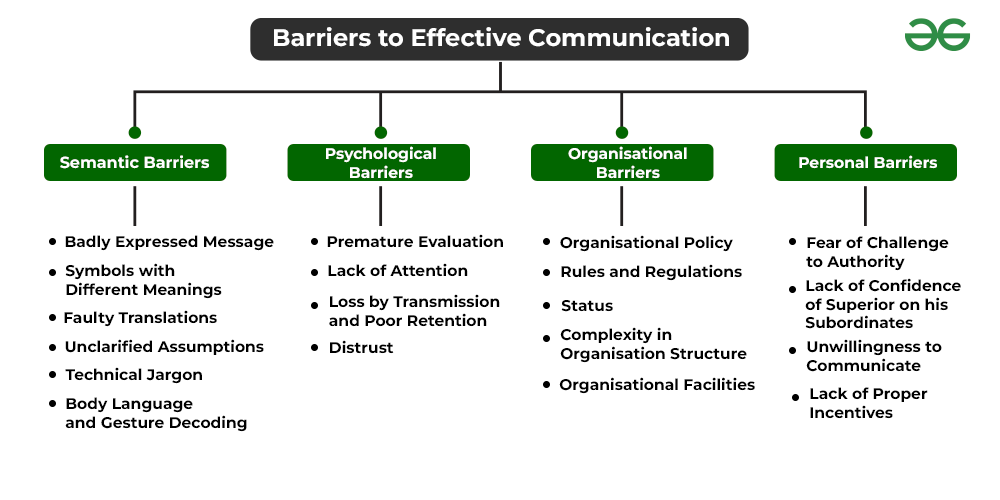
Barriers to communication are multifaceted and can be broadly categorized. These categories include physical, semantic, psychological, emotional, cultural, and organizational barriers. Recognizing these distinct categories is the first step towards mitigating their impact.
Physical Barriers
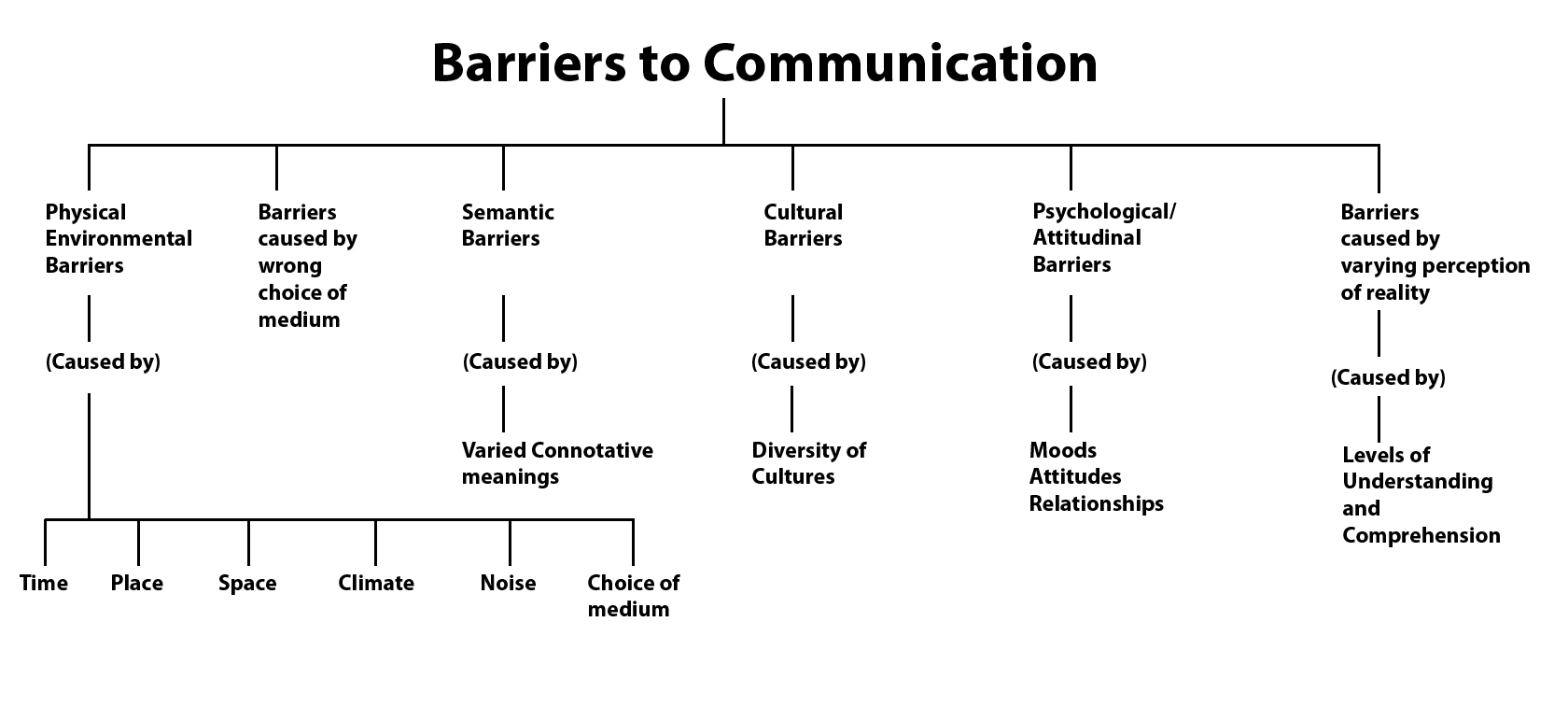
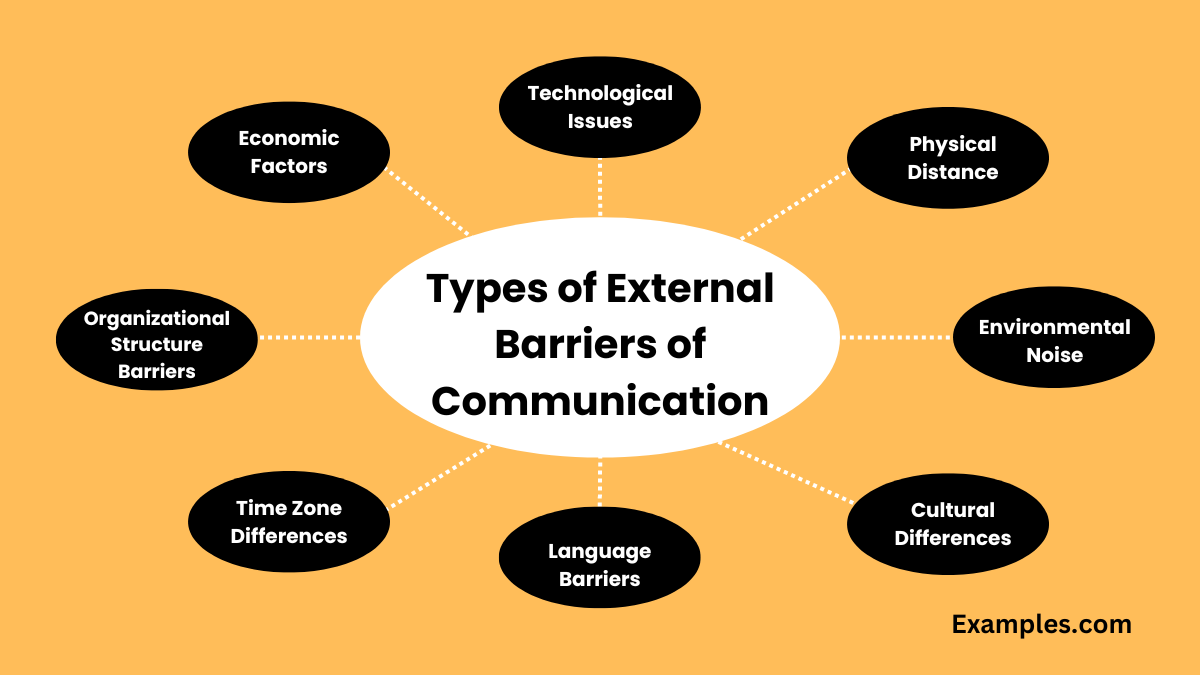
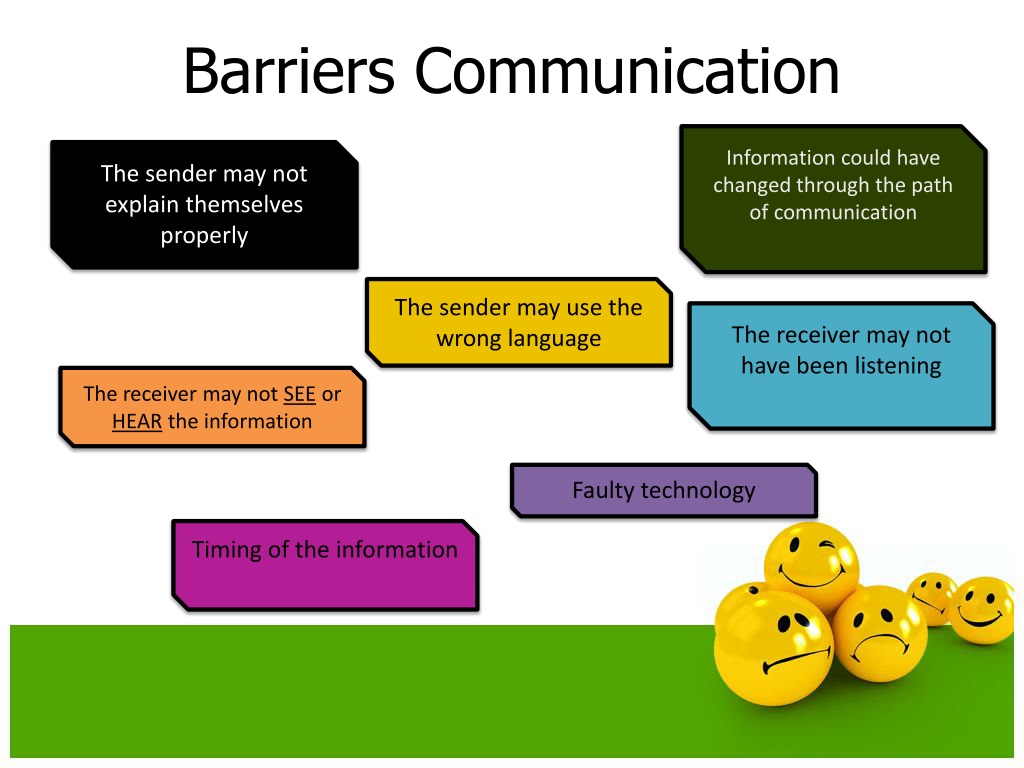
Physical barriers are perhaps the most tangible and easily identifiable. These encompass environmental factors that obstruct the communication process, such as noise, distance, and technological malfunctions. Examples include poor acoustics in a meeting room, a noisy construction site hindering verbal communication, or a dropped phone call interrupting a crucial conversation.
Semantic Barriers
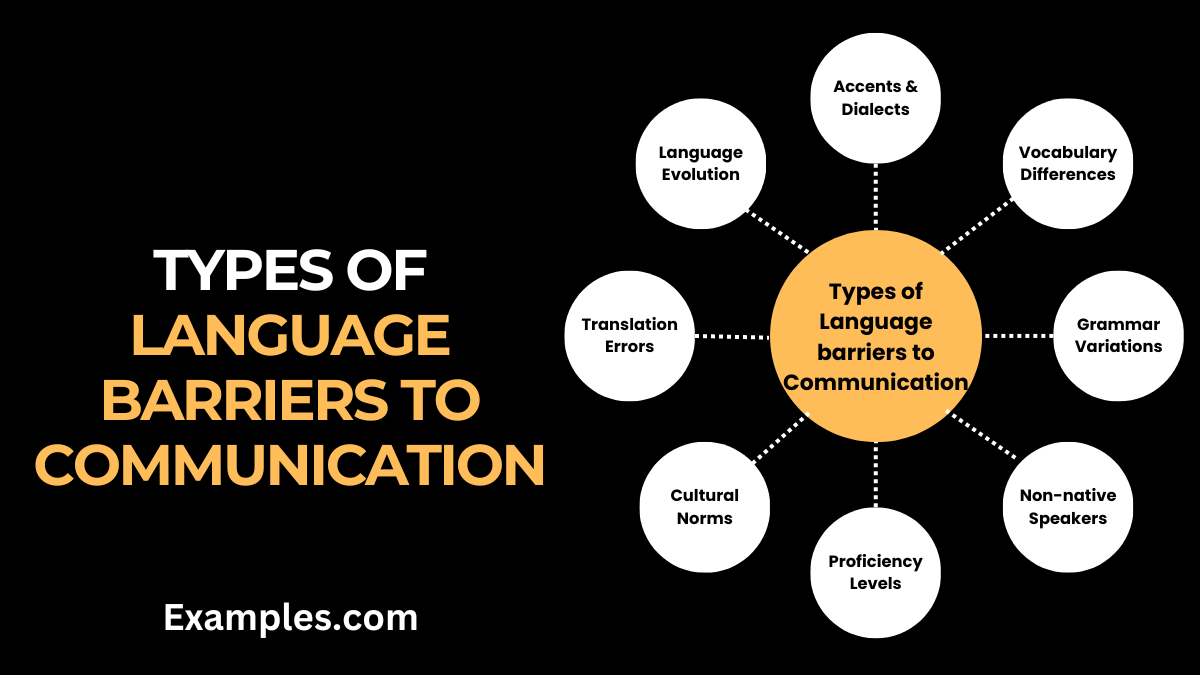
Semantic barriers arise from misunderstandings related to the meaning of words or symbols. Language differences, jargon, and ambiguous terminology can all contribute to semantic barriers. For instance, using highly technical jargon with an audience unfamiliar with the terms can lead to confusion and a breakdown in communication.
Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers are internal factors that affect an individual's ability to receive or transmit information effectively. These can include biases, preconceived notions, and personal anxieties. A listener who dismisses a speaker based on a prior negative experience is an example of a psychological barrier in action.
Emotional Barriers
Emotional barriers are closely linked to psychological barriers but are specifically driven by feelings. Anger, fear, distrust, and defensiveness can cloud judgment and impede communication. Attempting to convey complex information to someone in a state of high emotional distress is often ineffective.
Cultural Barriers
Cultural barriers stem from differences in cultural norms, values, and beliefs. Nonverbal cues, communication styles, and attitudes towards authority can vary significantly across cultures. These differences can lead to misinterpretations and misunderstandings if not carefully considered.
"Cross-cultural communication requires sensitivity and awareness of cultural nuances," states Dr. Anya Sharma, a professor of intercultural communication at the University of California, Berkeley. "Assumptions should be minimized, and active listening should be prioritized."
Organizational Barriers
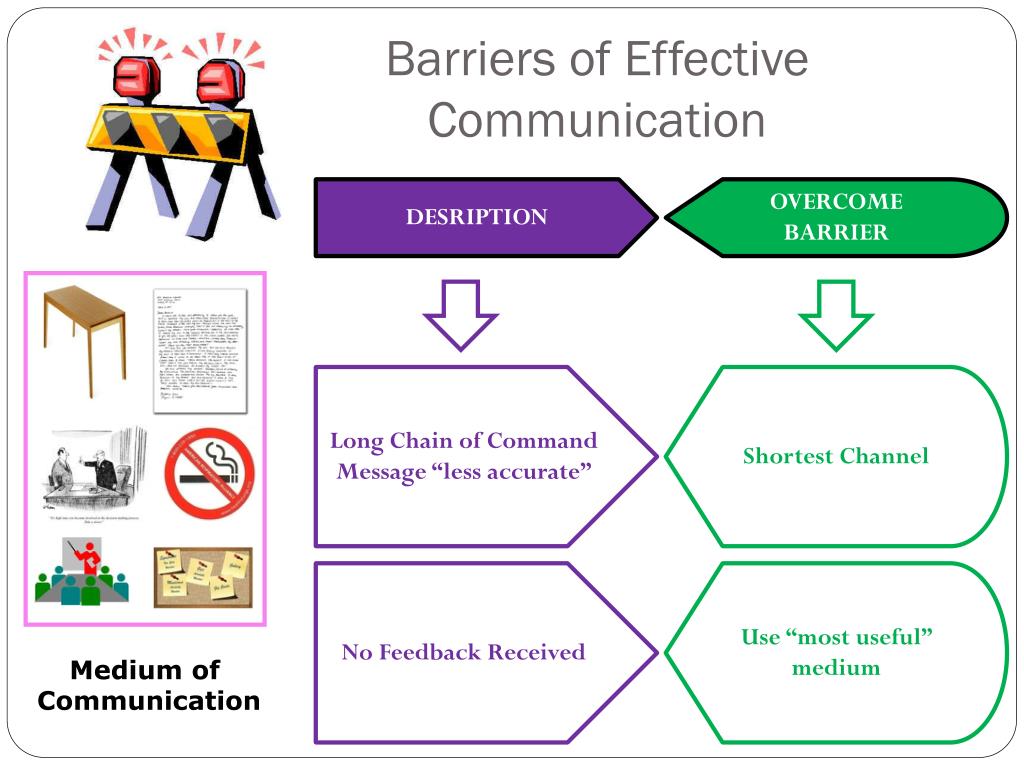
Organizational barriers are specific to the structure and hierarchy of an organization. Poor communication channels, information overload, and a lack of transparency can hinder the flow of information within an organization. Examples include a top-down management style that discourages feedback or a complex reporting structure that slows down decision-making.
Addressing these barriers is an ongoing process. It requires a proactive approach from both senders and receivers of information, emphasizing clarity, empathy, and active listening.
Ultimately, understanding and actively mitigating these barriers is paramount to achieving effective communication in all aspects of life. By consciously addressing these potential pitfalls, individuals and organizations can foster stronger relationships, improve collaboration, and create a more inclusive and understanding society.