Which Of The Following Can Directly Impact Fluid Balance

Fluid balance is a critical aspect of human health, and several factors can directly disrupt this delicate equilibrium, leading to serious consequences.
Key Factors Impacting Fluid Balance
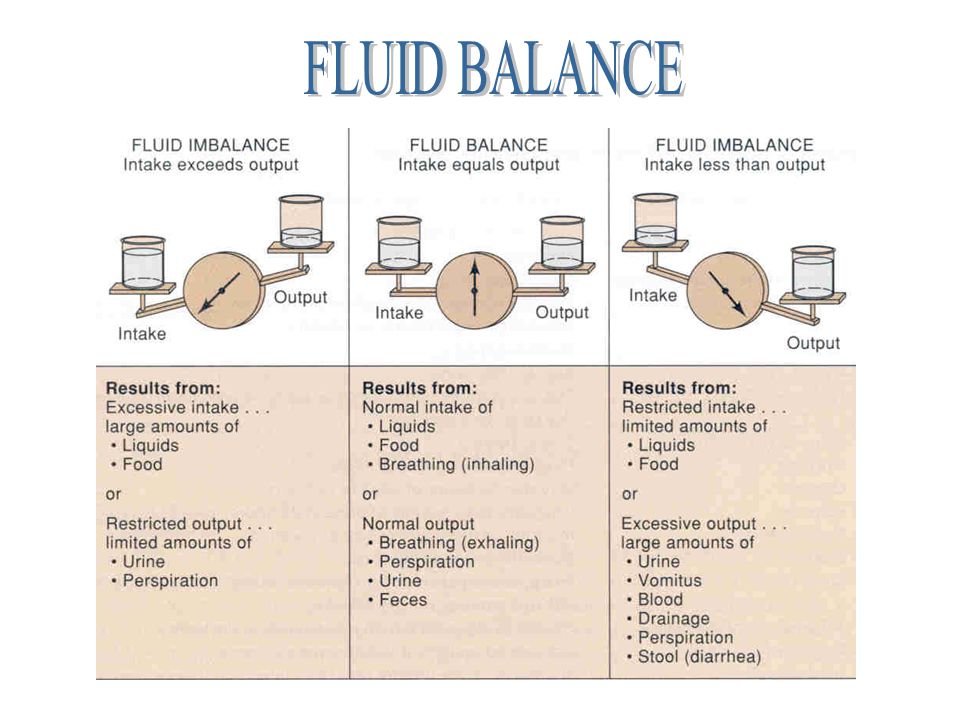
Maintaining a healthy fluid balance is essential for numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and temperature regulation. Disruptions to this balance can quickly lead to dehydration or fluid overload, both of which can have severe health implications.
Sodium Intake
Sodium plays a primary role in regulating fluid volume in the body. Increased sodium intake prompts the body to retain water to maintain a proper sodium concentration in the blood.
Conversely, low sodium levels can lead to fluid loss. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), excessive sodium consumption is common in the American diet, contributing to fluid retention and potentially high blood pressure.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, directly influence how much water the kidneys retain. ADH signals the kidneys to conserve water, reducing urine output.
Conditions like diabetes insipidus, characterized by insufficient ADH production or action, result in excessive water loss and severe dehydration. Conversely, conditions leading to excessive ADH production can cause fluid retention and hyponatremia.
Kidney Function
The kidneys are central to fluid balance. They filter blood and regulate the excretion of water and electrolytes.
Kidney diseases, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) or acute kidney injury (AKI), impair the kidneys' ability to perform these functions, leading to either fluid retention or excessive fluid loss. Data from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) show that impaired kidney function is a significant cause of fluid imbalances in the elderly.
Fluid Intake
Adequate fluid intake is fundamental for maintaining fluid balance. Dehydration occurs when fluid intake is insufficient to replace fluid losses from respiration, perspiration, and excretion.
Certain populations, like athletes and individuals living in hot climates, require higher fluid intakes to compensate for increased fluid losses. Recommendations from organizations such as the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) emphasize the importance of monitoring fluid intake during strenuous activity to prevent dehydration.
Certain Medications
Certain medications can also significantly impact fluid balance. Diuretics, for example, are prescribed to increase urine production, thereby reducing fluid volume in the body.
However, excessive diuretic use can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Other medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can affect kidney function and indirectly impact fluid balance.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Conditions like vomiting and diarrhea lead to rapid fluid loss, potentially causing severe dehydration. These conditions also disrupt electrolyte balance, further complicating the situation.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), effective management of these conditions involves rapid rehydration with electrolyte-rich solutions to restore fluid and electrolyte balance.
Heart Failure
Heart failure can disrupt fluid balance by reducing the kidneys' ability to excrete sodium and water. This often leads to fluid retention and edema (swelling).
The American Heart Association (AHA) notes that fluid restriction and diuretic medications are often necessary to manage fluid overload in patients with heart failure.
Immediate Actions and Ongoing Monitoring
Understanding these key factors allows for proactive measures to maintain fluid balance. Regular monitoring of fluid intake and output, coupled with awareness of individual risk factors (such as underlying health conditions and medication use), is crucial.
If you suspect a fluid imbalance, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and promote optimal health.







.jpg)