Which Of The Following Increases Heart Rate

Imagine you're hiking a mountain trail, the sun kissing your face, birds serenading you from the canopy above. Your breath deepens, your muscles engage, and you feel that familiar thrum in your chest, a steady rhythm pushing you onward and upward. This vibrant symphony within your body, the beating of your heart, is responding to the demands of the moment.
Understanding what makes our heart tick faster – which is to say, which activities or stimuli increase our heart rate – is essential knowledge for maintaining overall health and well-being. This knowledge helps us make informed decisions about lifestyle choices and recognize when our heart might be signaling a need for attention. From the obvious culprits like exercise to more subtle influences like stress and even the temperature around us, a multitude of factors play a role in shaping our heart rate.
The Basics: What is Heart Rate?
Heart rate, measured in beats per minute (BPM), represents the number of times your heart contracts in a minute to pump blood throughout your body. It's a vital sign that provides valuable insights into cardiovascular health and overall physiological function.
A normal resting heart rate generally falls between 60 and 100 BPM for adults, though this can vary based on age, fitness level, and other individual factors. Elite athletes, for instance, often have resting heart rates below 60 BPM due to their highly efficient cardiovascular systems.
Exercise: The Obvious Accelerator
It's no surprise that physical activity significantly elevates heart rate. As you exercise, your muscles require more oxygen, prompting your heart to beat faster and pump more blood to meet that demand. The intensity of the exercise directly correlates with the increase in heart rate.
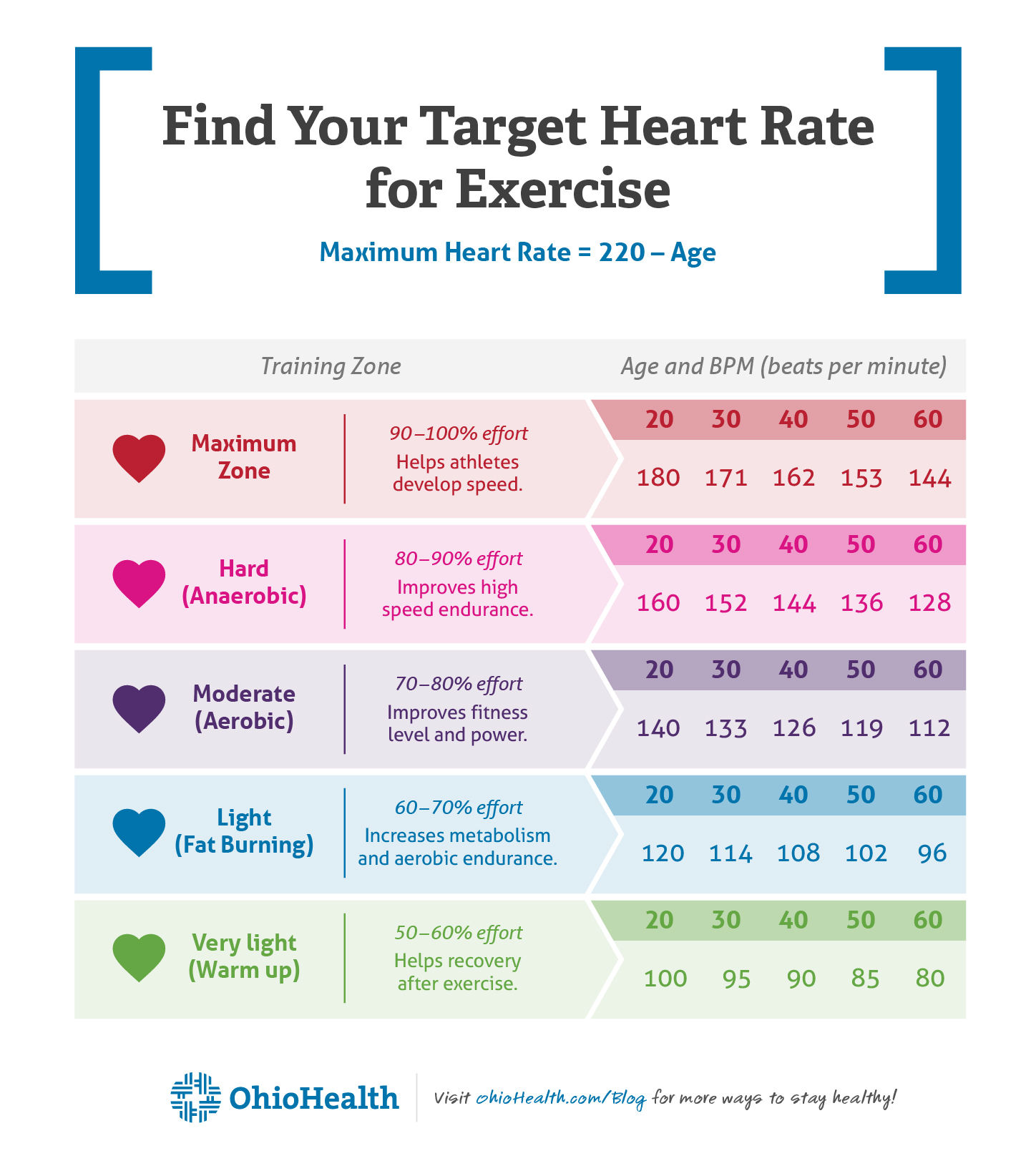
Activities like running, swimming, cycling, and even brisk walking can all cause a substantial rise in BPM. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week to maintain cardiovascular health.
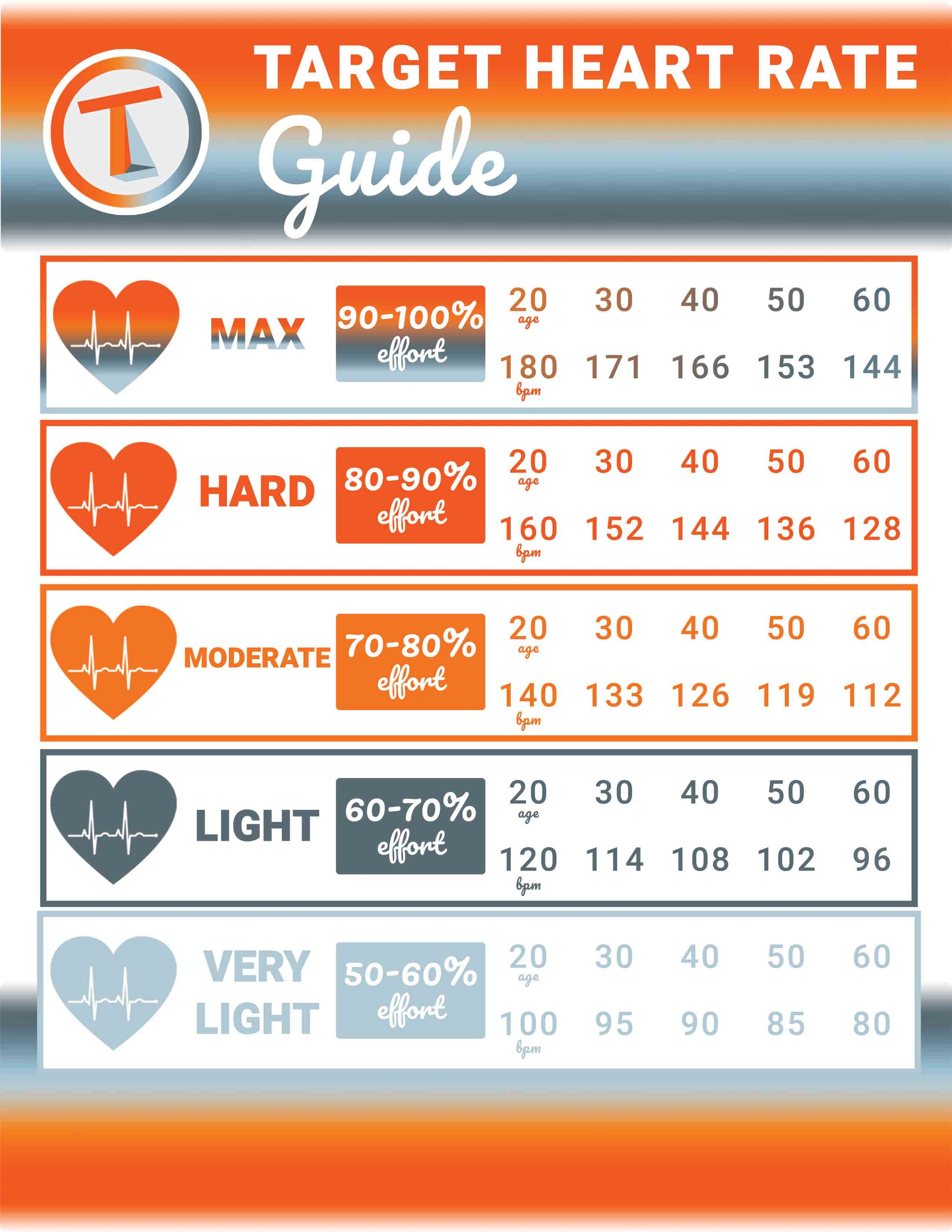
Target heart rate zones, calculated based on age and maximum heart rate, are often used to guide exercise intensity and ensure workouts are both effective and safe. These zones help individuals optimize their cardiovascular benefits while minimizing the risk of overexertion.
Stress and Anxiety: The Emotional Rollercoaster
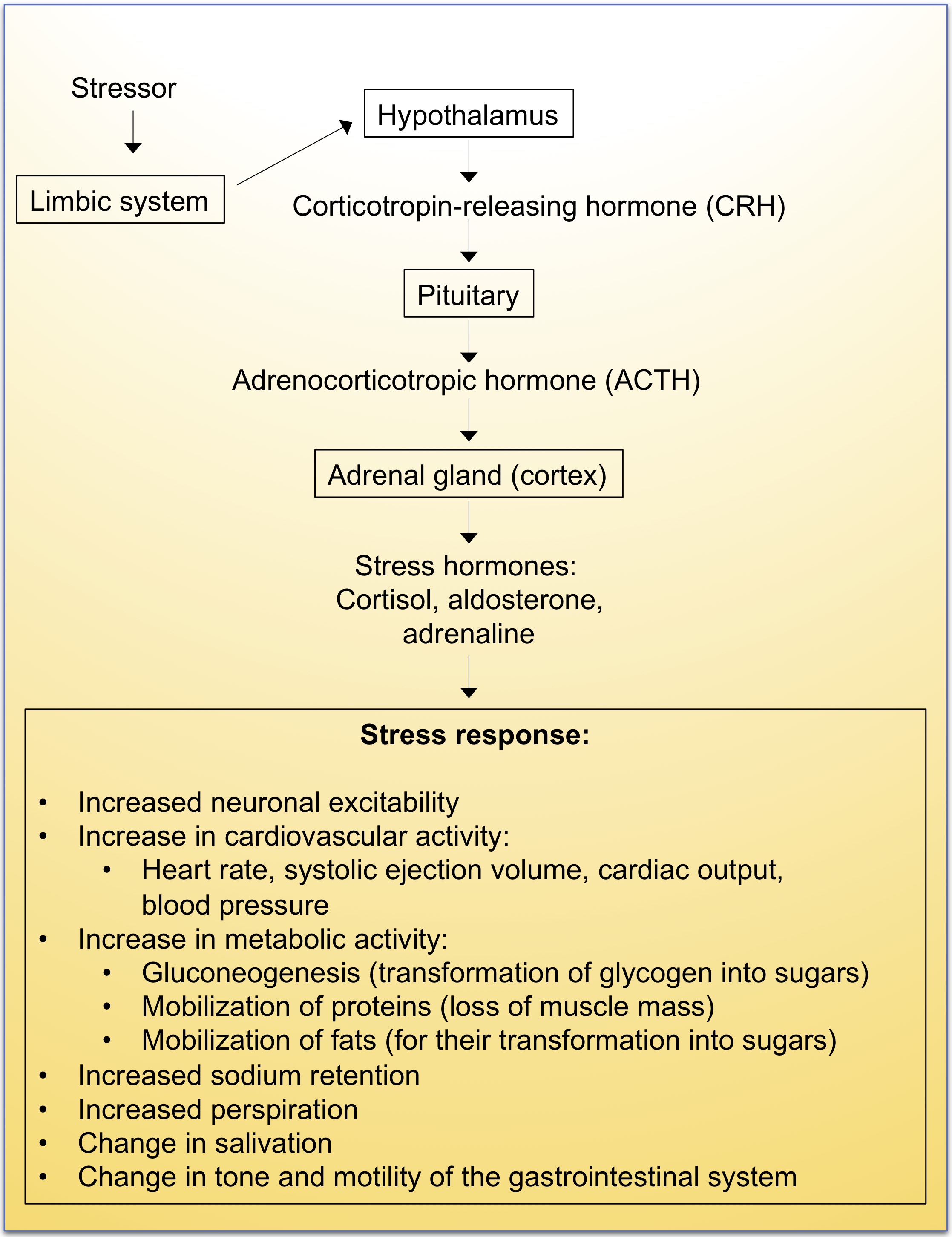
Beyond physical exertion, emotional stress and anxiety can also trigger a significant increase in heart rate. When faced with stressful situations, the body activates the sympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response.
This activation releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which increase heart rate and blood pressure to prepare the body for immediate action. Chronic stress can lead to persistently elevated heart rate and blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Mindfulness techniques, deep breathing exercises, and other stress-reduction strategies can help regulate the nervous system and mitigate the impact of stress on heart rate. Seeking support from therapists or counselors can also be beneficial in managing anxiety and its physical manifestations.
Caffeine and Stimulants: The Energizing Boost (and the Potential Downside)
Caffeine, a stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and some medications, is known to increase heart rate. It works by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and slows down nerve activity.
While moderate caffeine consumption is generally considered safe for most adults, excessive intake can lead to palpitations, anxiety, and other adverse effects. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends that healthy adults consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day.
Other stimulants, such as nicotine and certain medications, can also elevate heart rate. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions should exercise caution when using stimulants and consult with their healthcare provider.
Medications and Medical Conditions: The Hidden Influences
Certain medications can significantly impact heart rate as a side effect. Decongestants, thyroid medications, and some antidepressants are among those that can cause an increase in BPM.
Underlying medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, anemia, and heart arrhythmias, can also affect heart rate. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or unexplained changes in your heart rate, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
Regular check-ups with your doctor can help identify and manage any underlying health issues that may be contributing to an elevated heart rate.
Temperature and Hydration: The Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature and hydration levels, can also play a role in heart rate regulation. In hot weather, the body works harder to cool itself, leading to an increased heart rate. Dehydration can further exacerbate this effect by reducing blood volume and making it more difficult for the heart to pump blood efficiently.
Staying hydrated and avoiding strenuous activity during the hottest parts of the day can help prevent excessive increases in heart rate. Similarly, spending prolonged periods in very cold environments can also impact heart rate as the body works to maintain its core temperature.
Ensuring adequate hydration and dressing appropriately for the weather conditions can help minimize the impact of environmental factors on heart rate.
Dehydration: A Subtle Stressor
Dehydration is a often overlooked factor. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, blood volume decreases, making it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. To compensate, the heart beats faster, increasing heart rate.
Even mild dehydration can lead to a noticeable increase in BPM, especially during physical activity or in hot weather. Paying attention to your thirst cues and drinking enough water throughout the day is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart rate.
Electrolyte imbalances, often associated with dehydration, can also affect heart function. Consuming electrolyte-rich drinks after intense exercise can help restore balance and support healthy heart rate regulation.
After Eating: The Digestive Process
Believe it or not, the simple act of eating can also cause a temporary increase in heart rate. This phenomenon, known as postprandial heart rate increase, is due to the digestive system's increased energy demands. As the body processes food, blood flow to the digestive organs increases, requiring the heart to work harder and beat faster.
The type of food consumed can also influence the extent of this increase. Meals high in carbohydrates, sugars, and processed foods tend to cause a more significant rise in heart rate compared to balanced meals with plenty of fiber and lean protein.
Paying attention to portion sizes and choosing nutritious foods can help minimize the postprandial heart rate increase and support overall cardiovascular health.
The Bottom Line: Listening to Your Body
Understanding what increases heart rate is a critical step toward proactive heart health. While some factors, like exercise, are beneficial and necessary, others, like chronic stress and excessive caffeine intake, can have detrimental effects. By paying attention to your body's signals and making informed lifestyle choices, you can help maintain a healthy heart rate and promote long-term cardiovascular well-being.
Remember, knowledge is power. Monitoring your heart rate during various activities and situations can provide valuable insights into your body's responses and help you tailor your lifestyle accordingly. If you have any concerns about your heart rate, don't hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance. Your heart is a tireless engine, deserving of your utmost care and attention.










.jpg)

