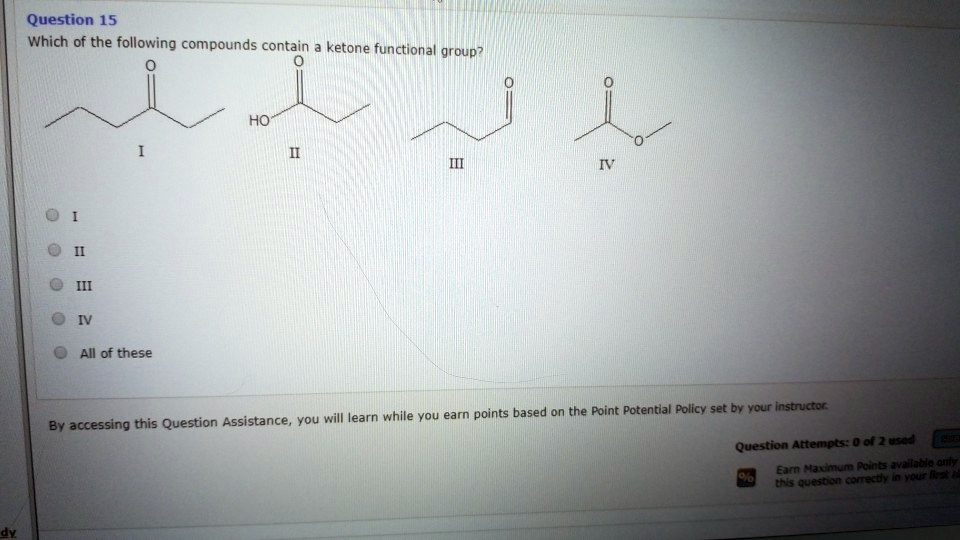
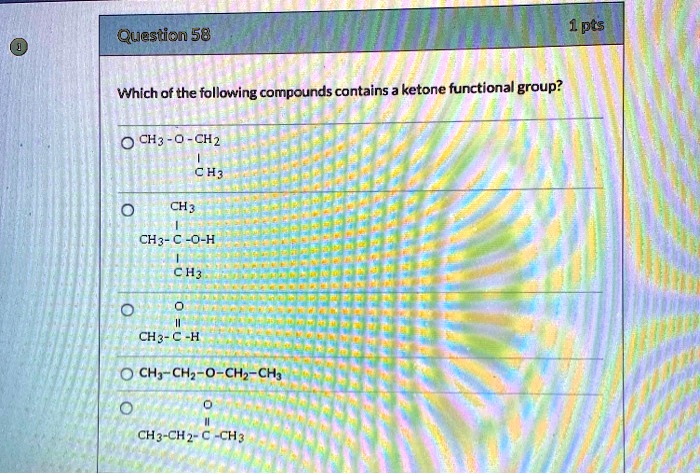
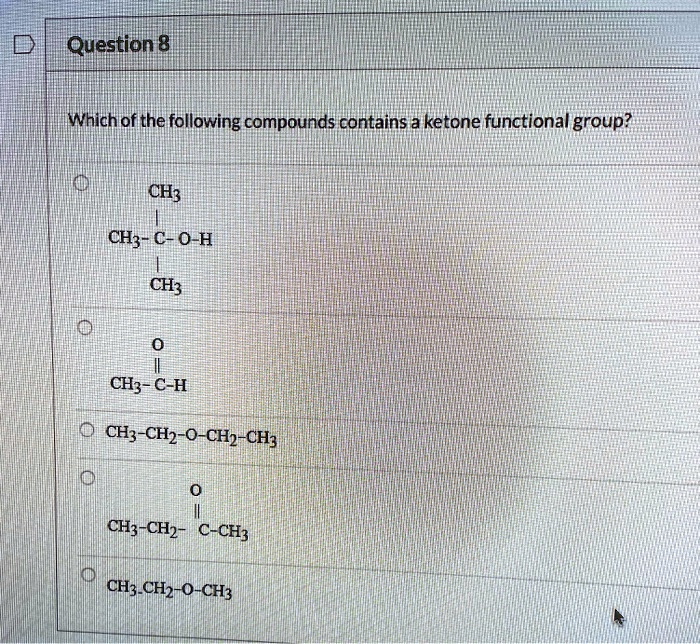
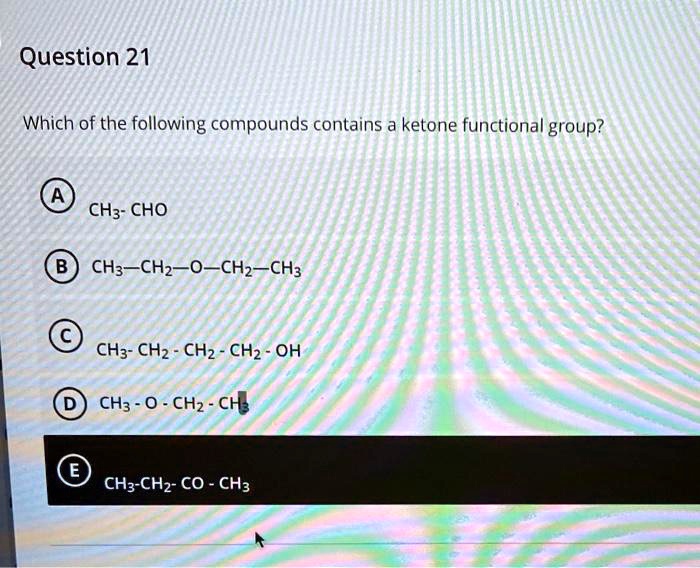
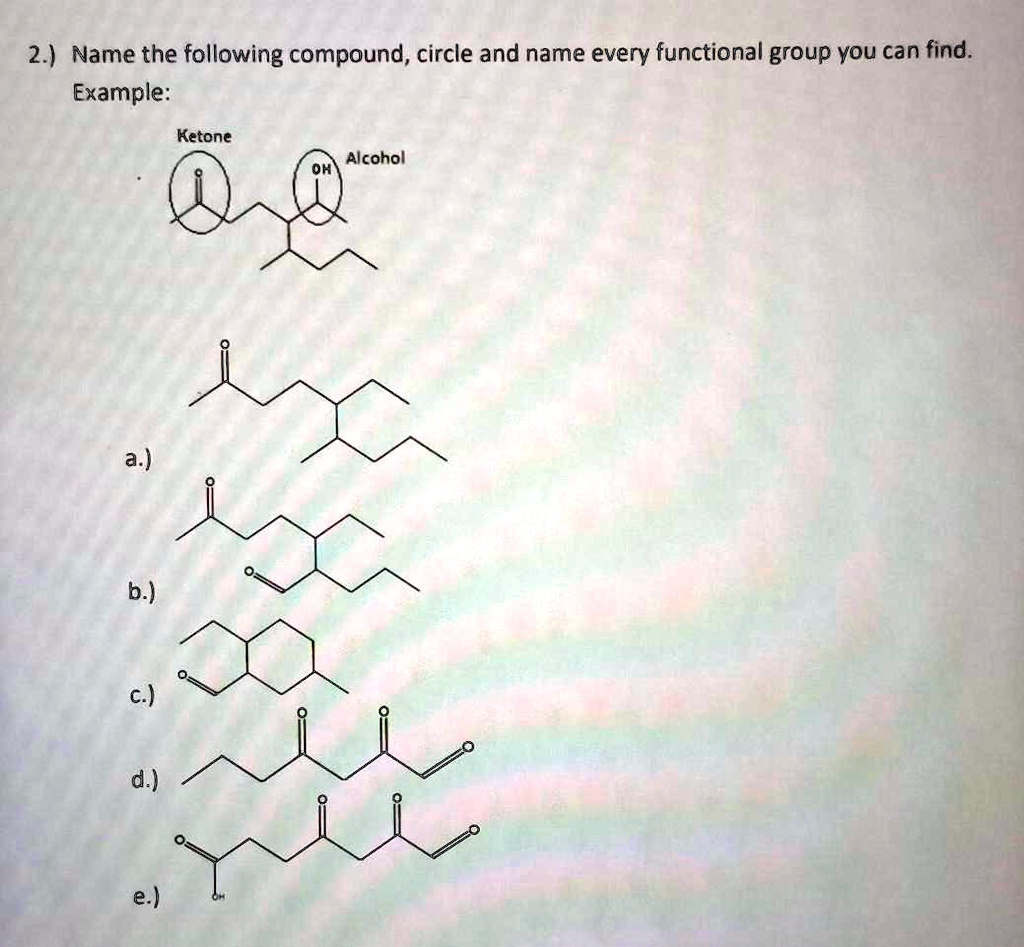
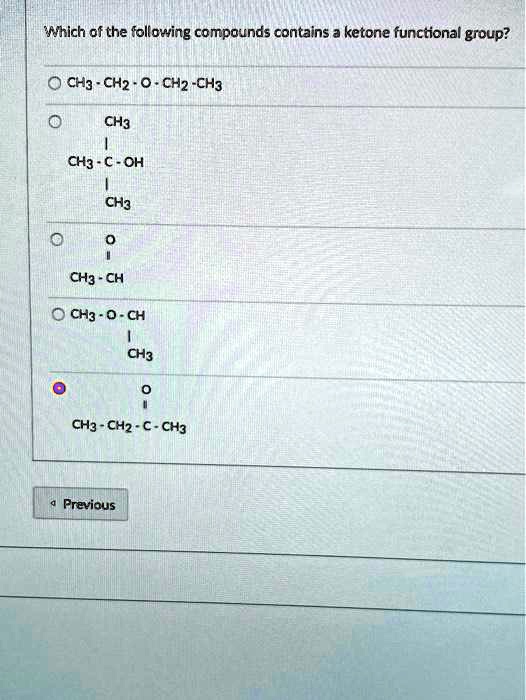
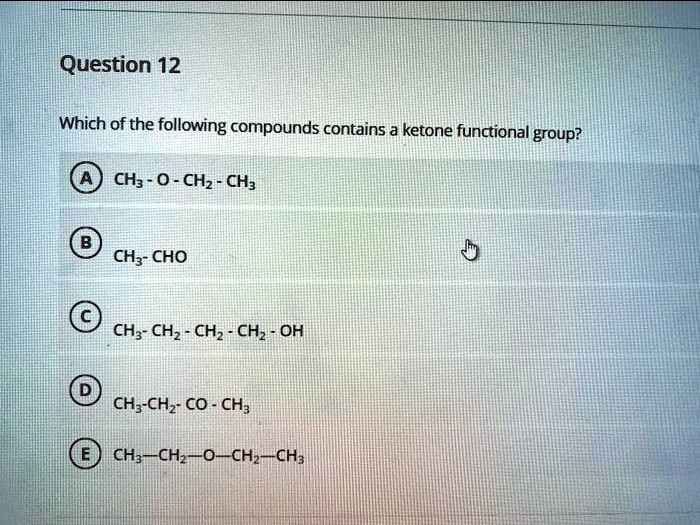
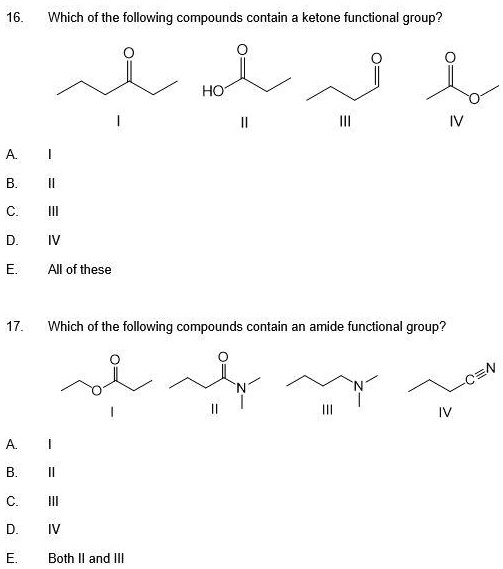
Which Of The Following Compounds Contains A Ketone Functional Group
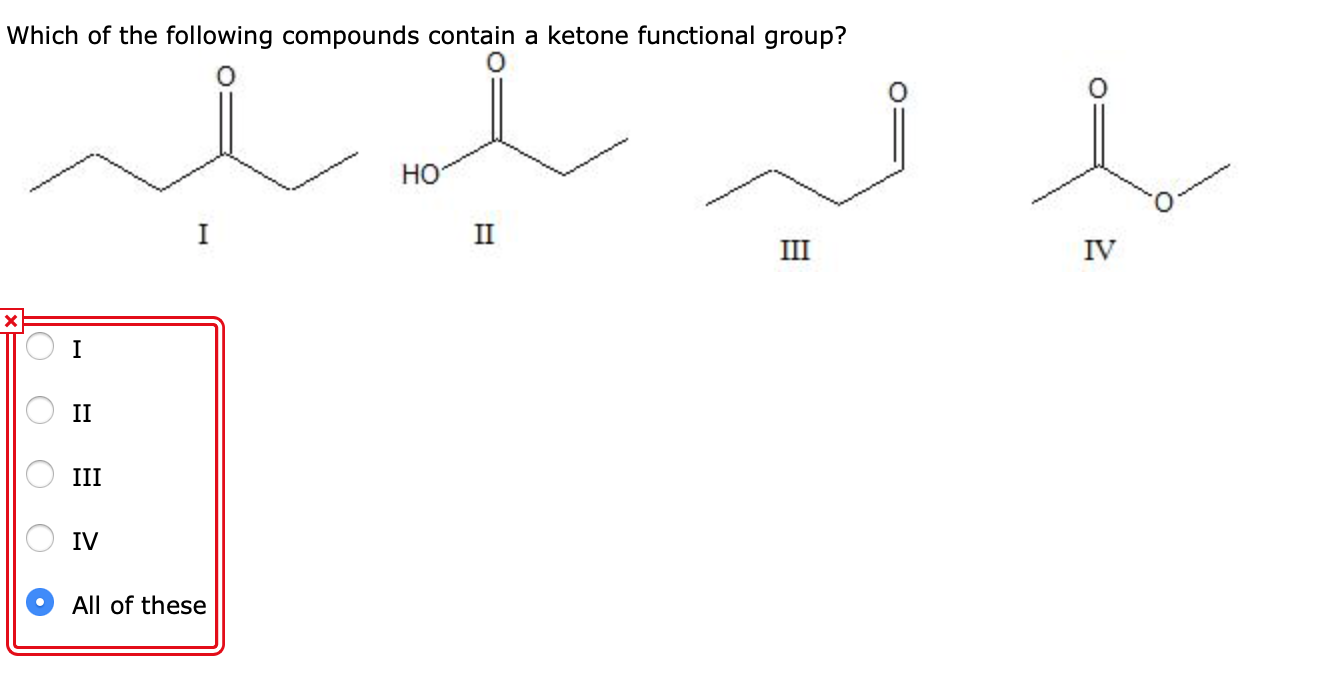
The world of organic chemistry can often feel like a complex puzzle, particularly when differentiating between functional groups. A recent online search spike has focused on a fundamental question: "Which of the following compounds contains a ketone functional group?" This inquiry highlights a widespread need for clear and accessible information on basic chemical concepts.
This article aims to clarify what a ketone is, how to identify it within a chemical structure, and why understanding this concept is important. The demand for this information suggests a gap in public understanding, possibly driven by students studying chemistry, or individuals interested in the chemical compositions of everyday products.
What is a Ketone?
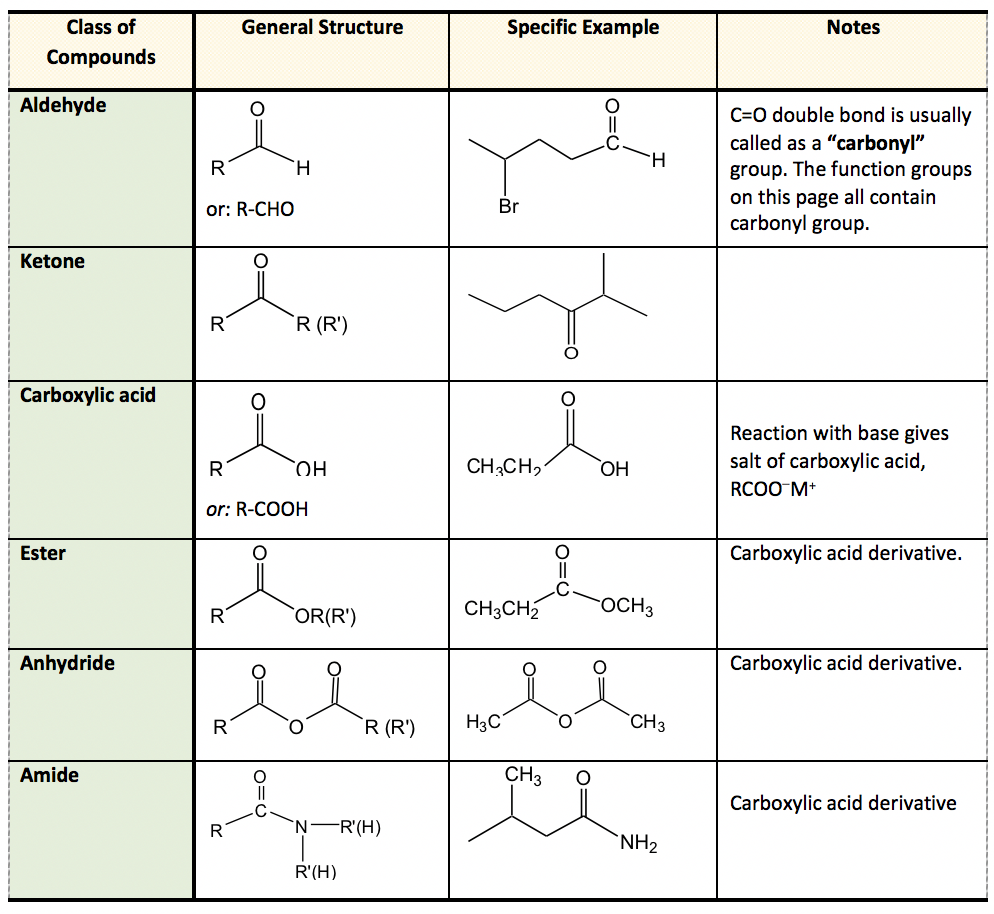
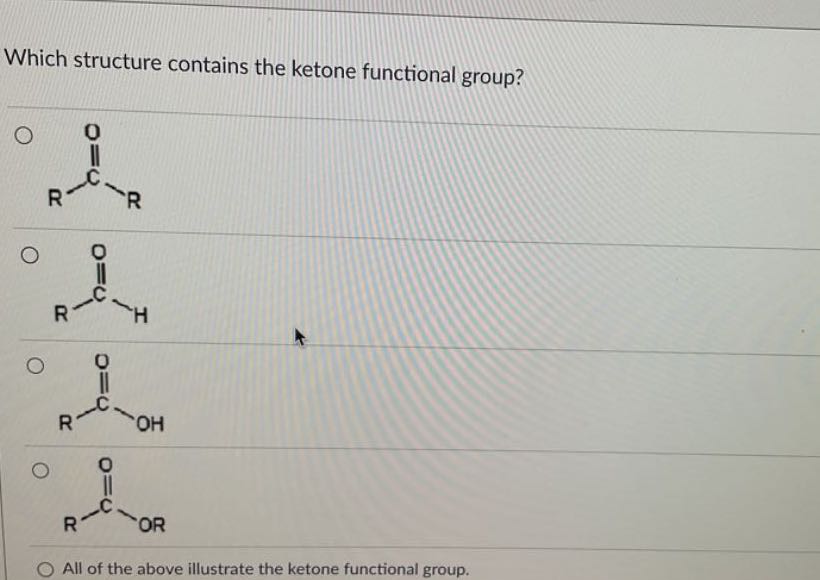
At its core, a ketone is a functional group characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. This arrangement distinguishes it from other carbonyl-containing groups like aldehydes, where the carbonyl carbon is bonded to at least one hydrogen atom.
The general formula for a ketone is R-(C=O)-R', where R and R' represent alkyl or aryl groups. These groups can be the same or different.
How to Identify a Ketone
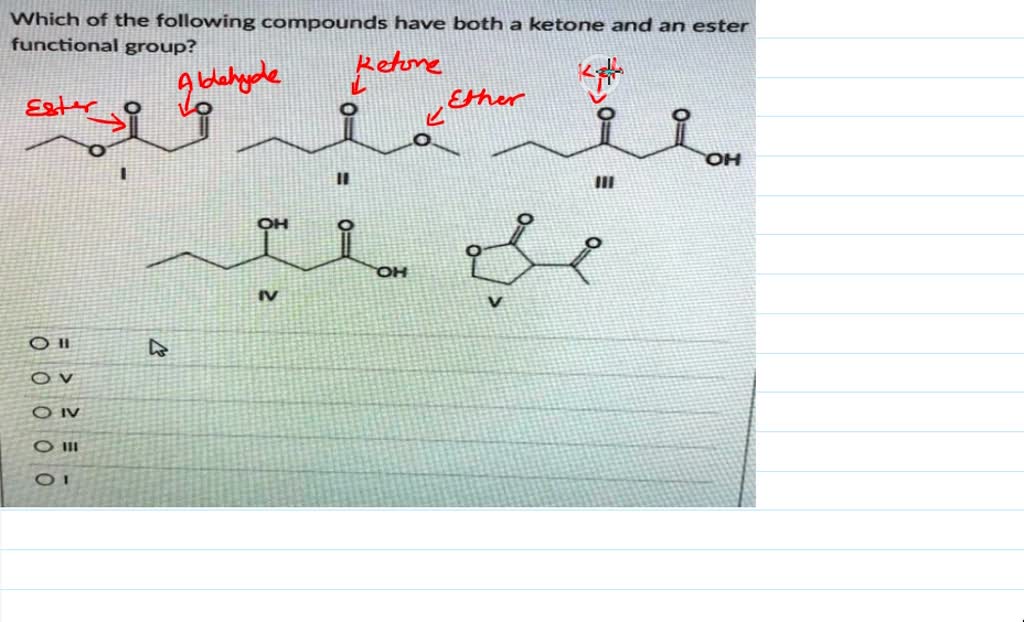
The key to identifying a ketone lies in recognizing the carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms within the molecule’s structure. Look for the "C=O" in the middle of a carbon chain, not at the end.
For instance, acetone (propanone) is a common example of a ketone. Its chemical formula is CH3COCH3, clearly showing the carbonyl group nestled between two methyl groups.
Other ketones can range from simple molecules like butanone to more complex compounds found in biological systems and industrial processes. Visual representations or chemical diagrams are often the easiest way to confirm the presence of a ketone functional group.
Why is Understanding Ketones Important?
Ketones are prevalent in numerous applications, ranging from solvents to pharmaceuticals. Understanding their structure and properties is crucial in fields like chemistry, biology, and medicine.
Acetone, for example, is a widely used solvent in nail polish remover and various industrial processes. Ketones also play a significant role in metabolic processes; ketone bodies, such as acetoacetate, are produced during periods of fasting or in individuals with diabetes.
Furthermore, many pharmaceuticals contain ketone functional groups, which contribute to their biological activity. The presence of a ketone can influence how a drug interacts with its target within the body.
Examples and Applications
Beyond acetone, numerous other compounds feature ketone functional groups. These examples help illustrate the diverse applications of ketones across different industries.
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is another common solvent used in paints, coatings, and adhesives. Cyclohexanone is a cyclic ketone used in the production of nylon.
In biology, steroids like testosterone and progesterone contain ketone groups, which are essential for their hormonal functions. The synthesis and modification of these compounds often involve reactions at the ketone functional group.
The importance of ketones extends to everyday life. Many natural and synthetic fragrances contain ketone compounds that contribute to their characteristic scents.
The Online Interest Explained
The heightened online interest in identifying ketone functional groups likely stems from a combination of factors. Students studying organic chemistry are often tasked with identifying functional groups in various compounds.
Also, individuals interested in understanding the ingredients and chemical compositions of products they use might research specific functional groups to better grasp their properties and effects.
Furthermore, online resources and educational platforms are increasingly popular learning tools, which may drive searches for specific chemistry topics like this one.
Resources for Further Learning
Numerous resources are available for those wanting to deepen their understanding of ketones and other functional groups. Textbooks, online chemistry courses, and reputable websites offer comprehensive information.
University websites and educational organizations often provide free learning materials, including diagrams and explanations of organic chemistry concepts.
Interactive tools and simulations can also aid in visualizing chemical structures and understanding the properties of different functional groups. Seek information from reputable and verified sources.
Conclusion
Identifying a ketone functional group involves recognizing the carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. The recent surge in online searches for this information underscores the importance of accessible and clear educational resources.
Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply curious, understanding ketones is a fundamental step in navigating the world of organic chemistry. Recognizing this functional group opens doors to understanding the properties, applications, and biological roles of countless compounds.
By leveraging available resources and focusing on the basic principles, anyone can confidently identify a ketone and appreciate its significance in the world around us. This is a cornerstone of basic chemical literacy.
![Which Of The Following Compounds Contains A Ketone Functional Group [FREE] Which of the following compounds contains a ketone functional](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:750/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d94/4259154932ae84f41e965f49952f4ced.png)