Which Of The Following Disorders Is An Inflammation
Urgent health alert: Confusion surrounds the inflammatory nature of several common disorders, demanding immediate clarification for effective diagnosis and treatment. The question, "Which of the following disorders is an inflammation?" is more complex than it appears, impacting patient care worldwide.
This report cuts through the misinformation, pinpointing specific disorders characterized by inflammation. Understanding the root cause – inflammation – is crucial for targeted intervention and improved patient outcomes.
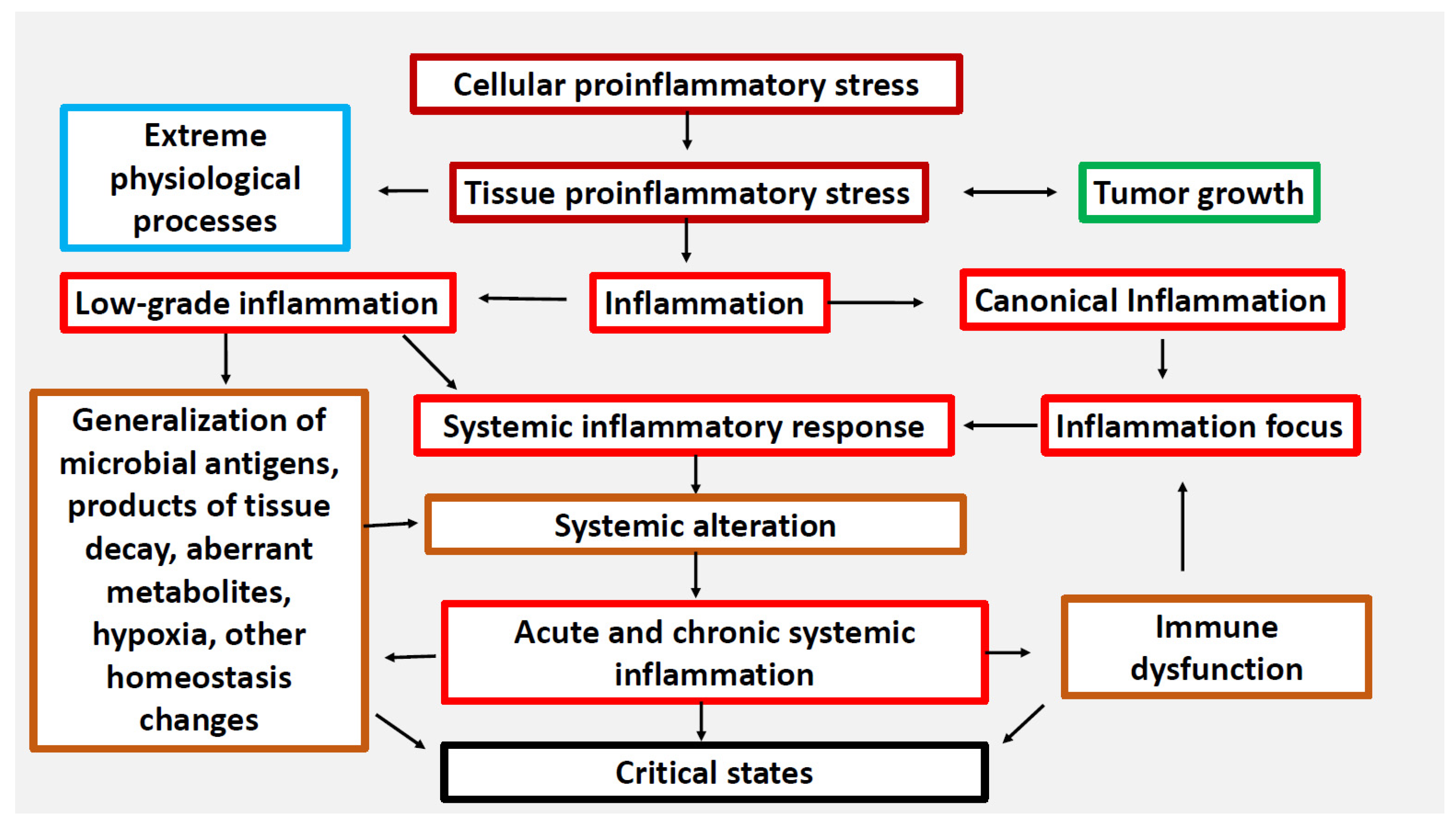
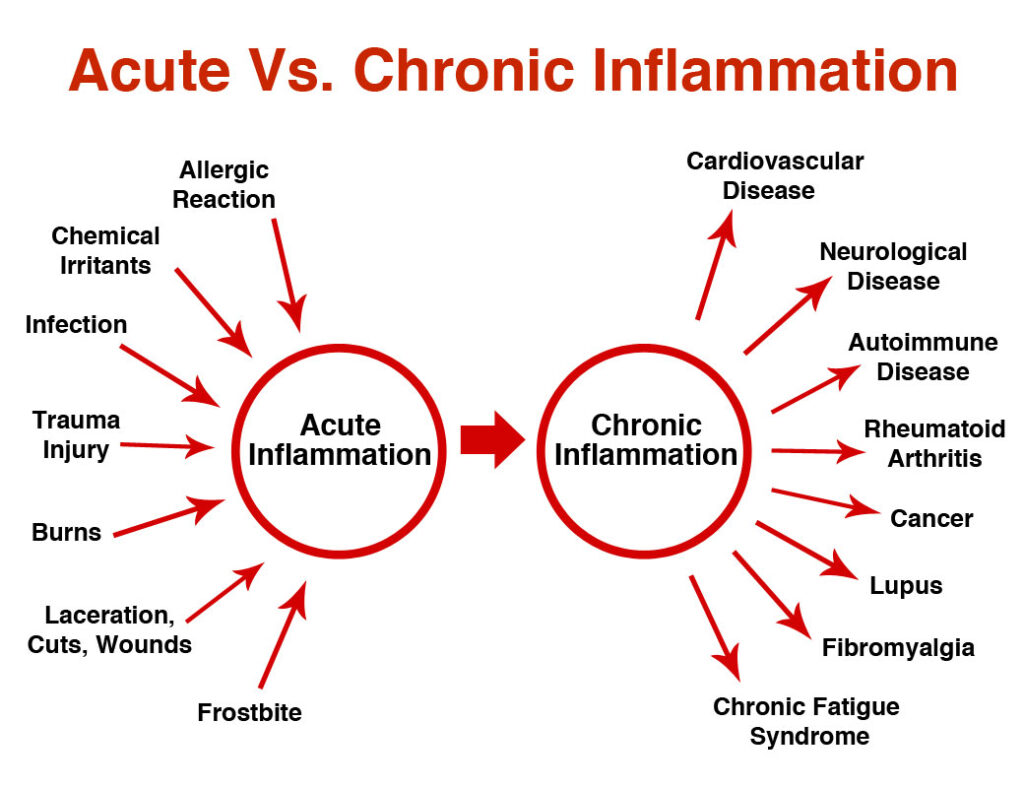
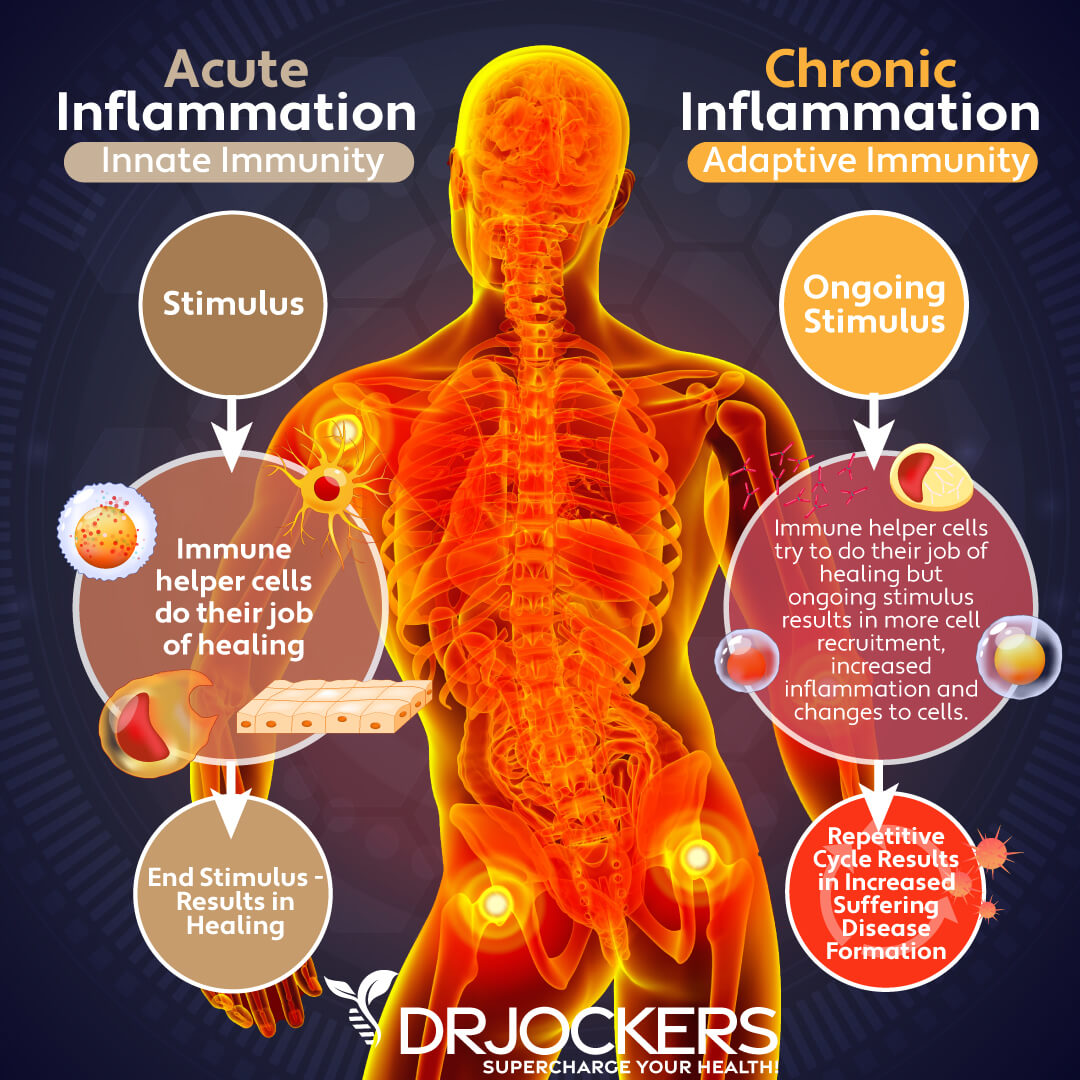
Inflammation: A Central Biological Process
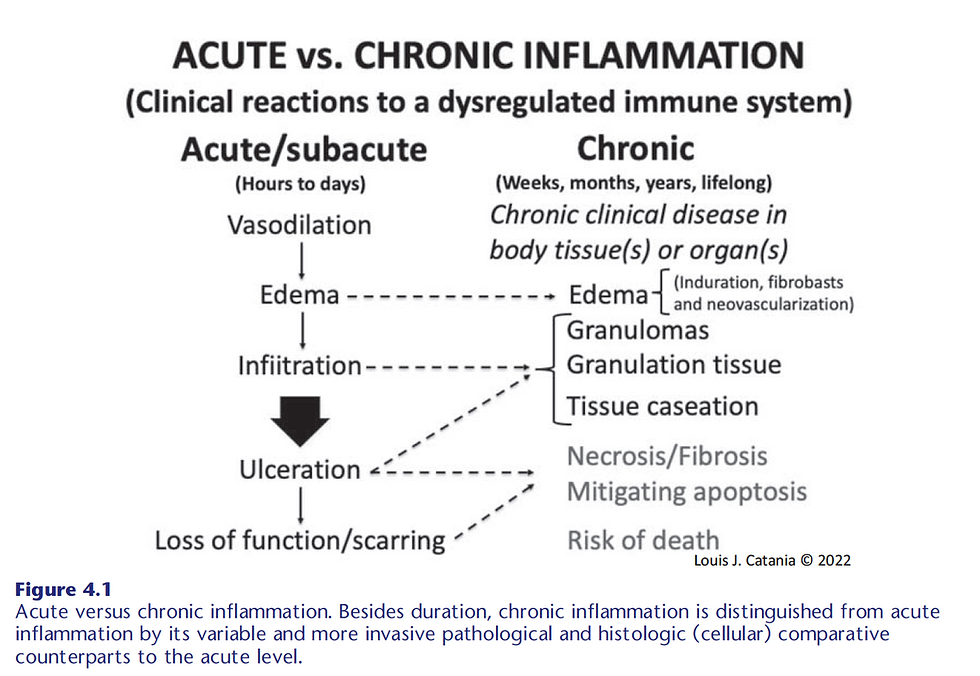
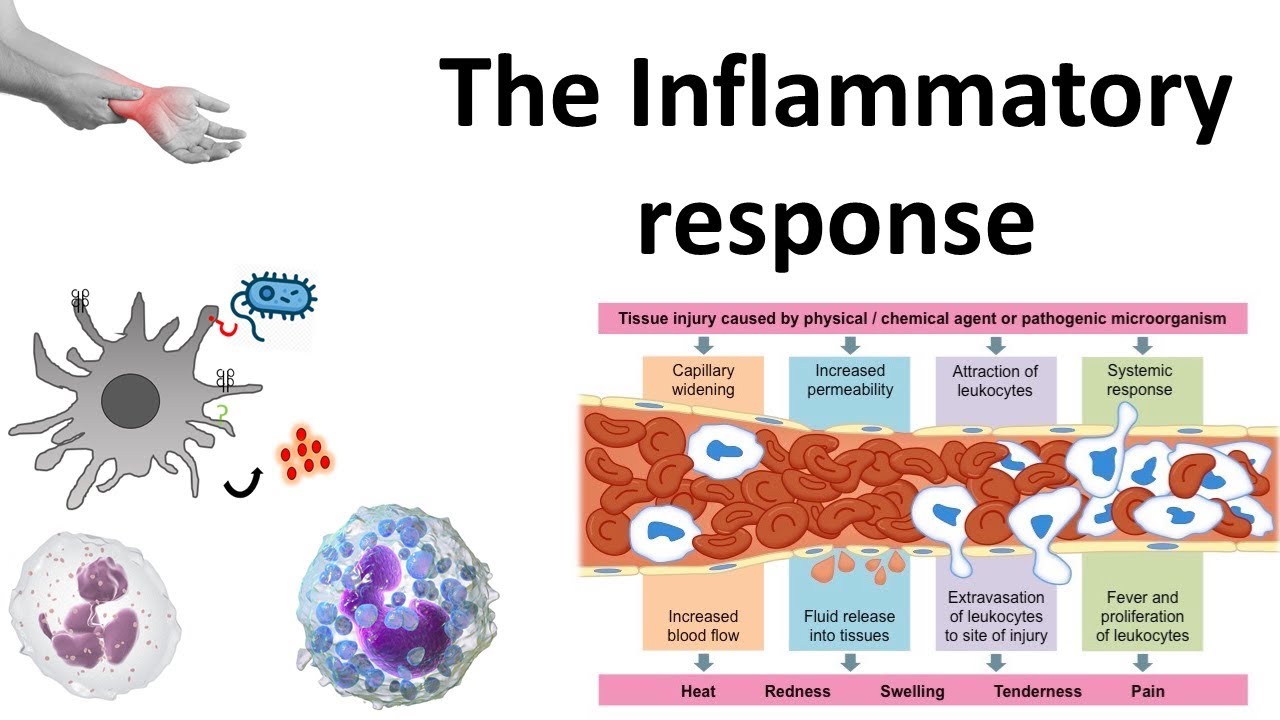
Inflammation is a fundamental biological response to injury or infection. It's the body's attempt to protect itself and begin the healing process.
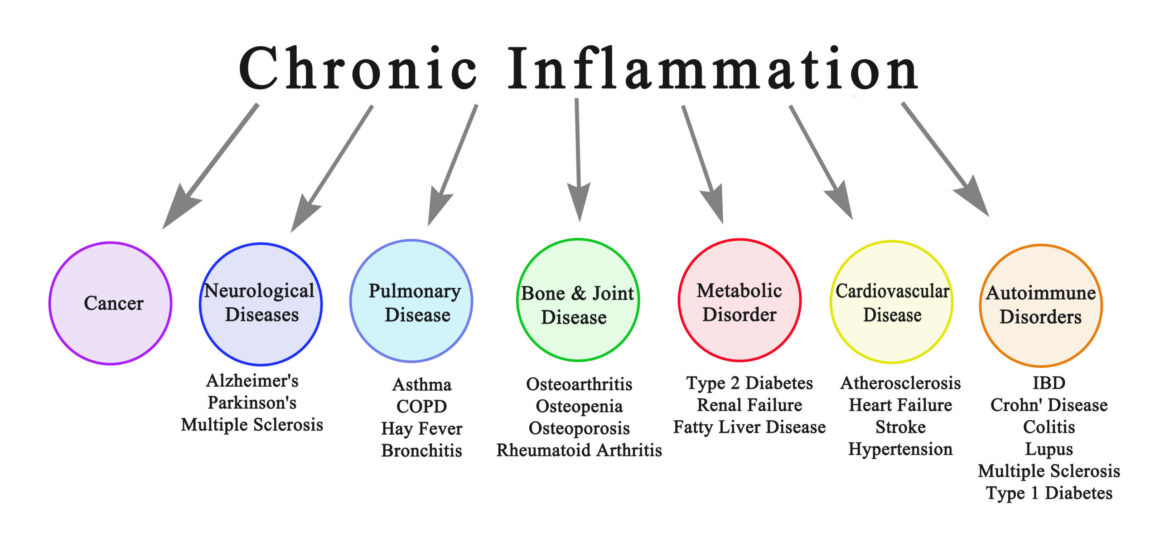
However, when inflammation becomes chronic or misdirected, it can contribute to a wide range of disorders.
Identifying Inflammatory Disorders
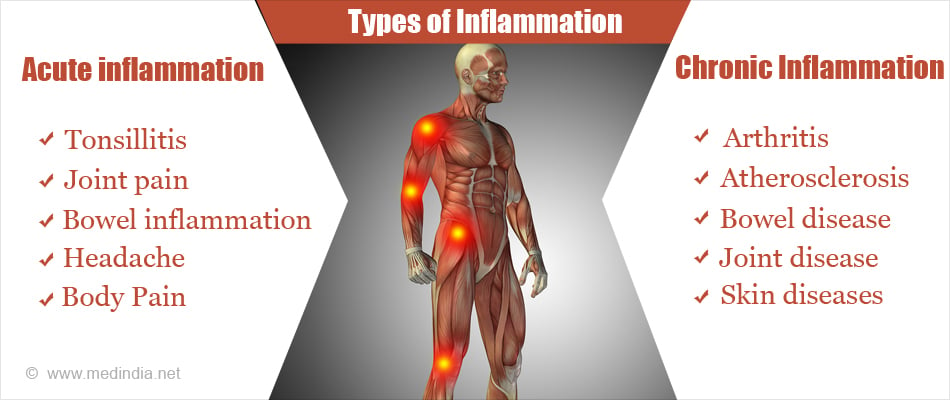
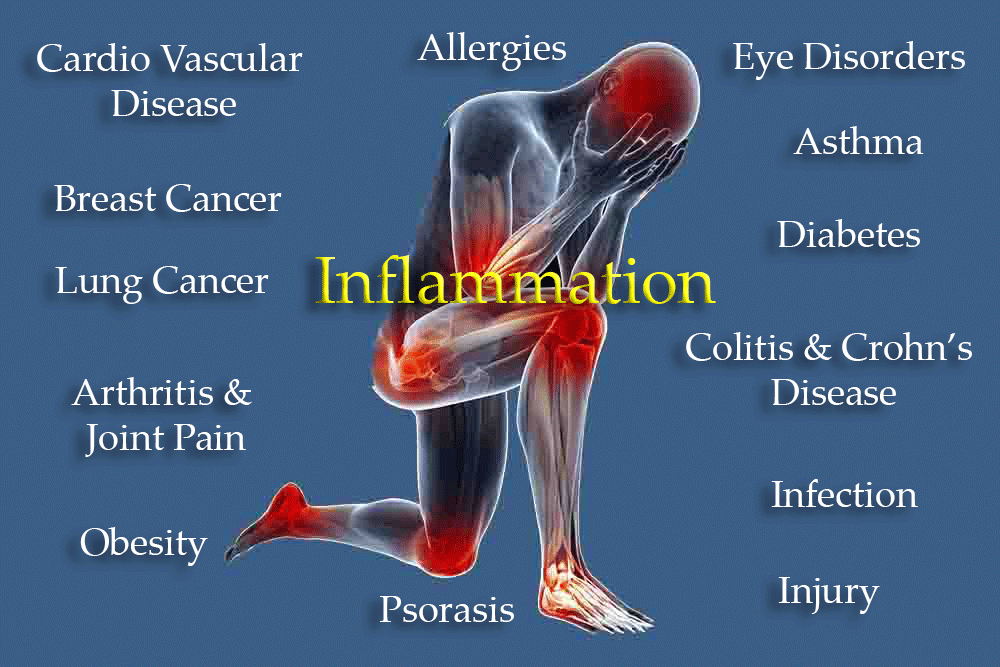
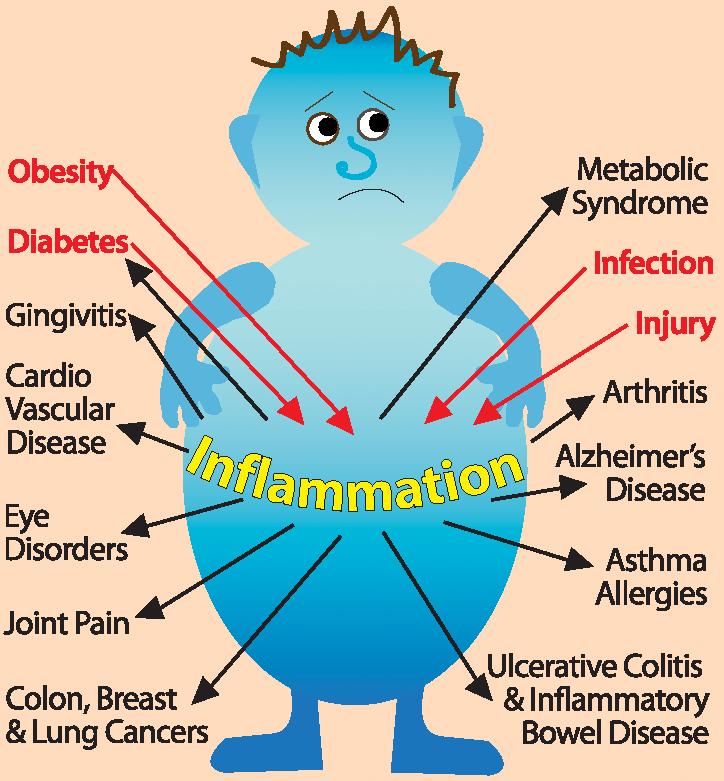
Several disorders are fundamentally characterized by inflammation. These can range from localized to systemic conditions.
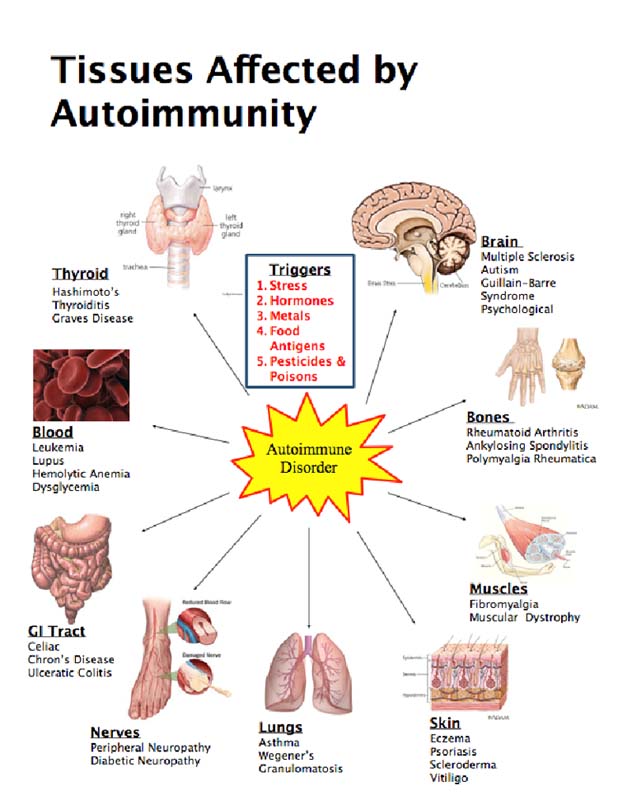
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder primarily affecting the joints. The immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium – the lining of the joints – causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness.
RA is a systemic disease, meaning it can affect other organs, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, RA affects an estimated 1.3 million adults in the United States.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) encompasses conditions characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The two main types are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Crohn's disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, while ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon and rectum.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that approximately 3 million adults in the US have IBD.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways in the lungs. Inflammation causes the airways to narrow and swell, producing extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
Triggers for asthma attacks can include allergens, irritants, exercise, and respiratory infections.
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA) reports that asthma affects more than 25 million Americans.
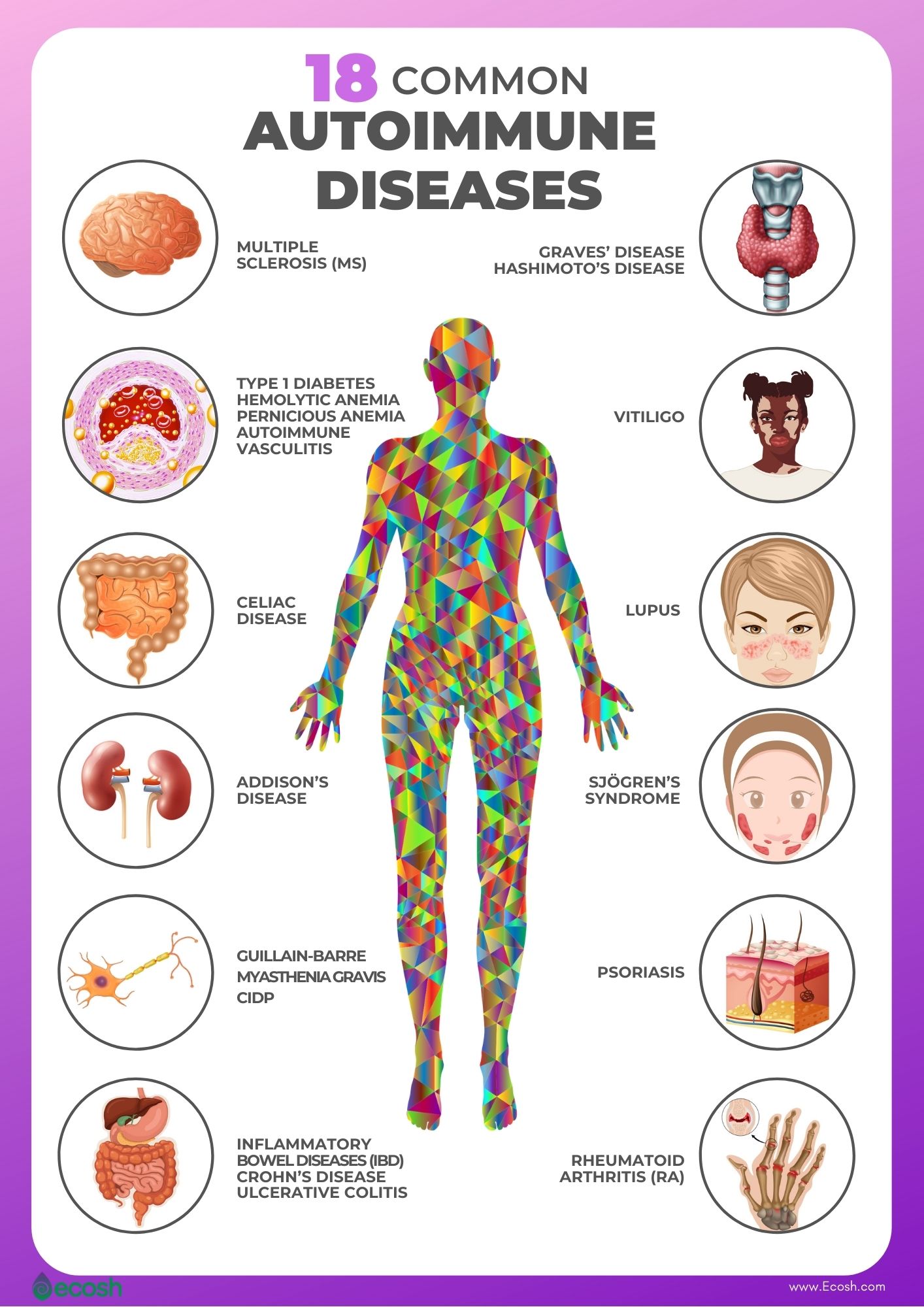
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath that covers nerve fibers. This inflammation disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
Symptoms of MS can vary widely and include fatigue, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and vision problems.
The National Multiple Sclerosis Society estimates that nearly 1 million people live with MS in the United States.
Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This triggers intense pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected joint, most often the big toe.
Risk factors for gout include obesity, high blood pressure, and kidney disease.
According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), gout affects more than 8 million adults in the United States.
Distinguishing Inflammation from Other Disease Processes
It's crucial to distinguish inflammatory disorders from those with other primary etiologies, such as infectious diseases caused by bacteria or viruses. While infection can *trigger* inflammation, the infection itself is the primary disease process, not inflammation.
Similarly, some conditions like osteoarthritis, although involving joint pain and stiffness, have a primary mechanism of cartilage degradation rather than primary inflammation.
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate identification of inflammation as a key component of a disorder is vital for appropriate treatment strategies. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and biologics, are frequently used to manage these conditions.
However, treatment must be tailored to the specific disorder and the individual patient.
The Urgency of Correct Information
Misunderstanding the role of inflammation in different diseases can lead to inappropriate or delayed treatment. This can significantly impact patient outcomes and quality of life.
Further research and education are essential to improve understanding and management of inflammatory disorders.
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
Healthcare professionals are urged to stay updated on the latest research and clinical guidelines regarding inflammatory disorders. Continued research is focused on developing more targeted and effective therapies.
Patients experiencing symptoms suggestive of inflammation should seek prompt medical evaluation for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.







00322-3/asset/094176be-0bf0-4e49-9a58-bd74f7911888/main.assets/gr1_lrg.jpg)
