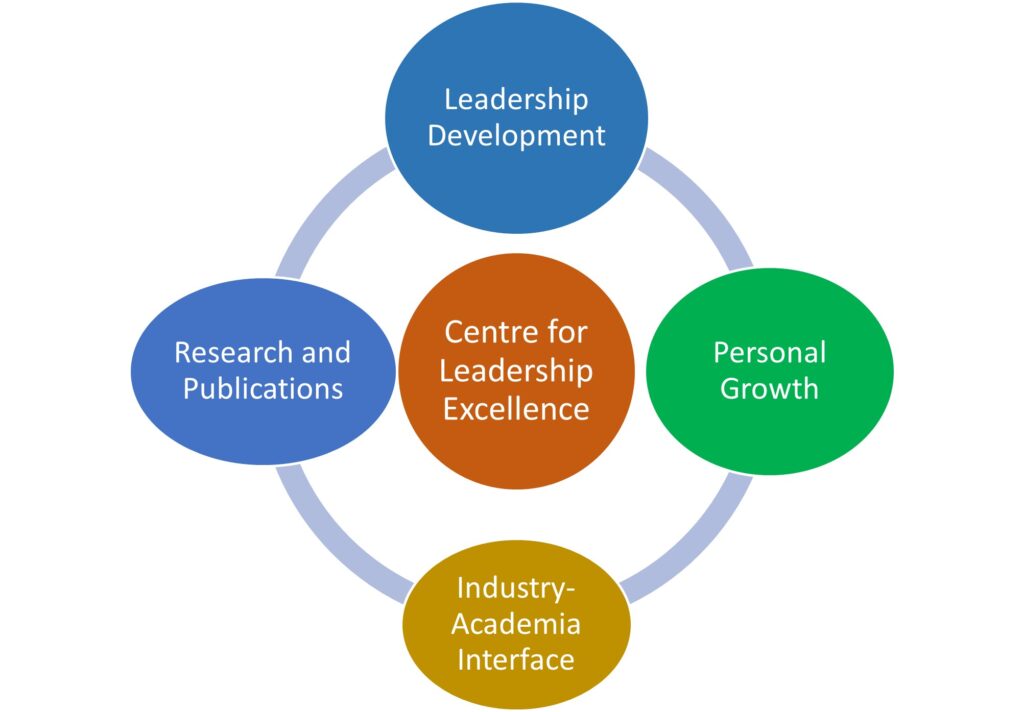
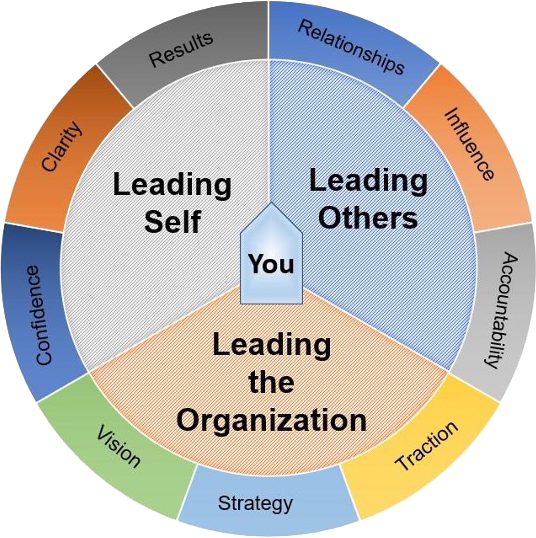
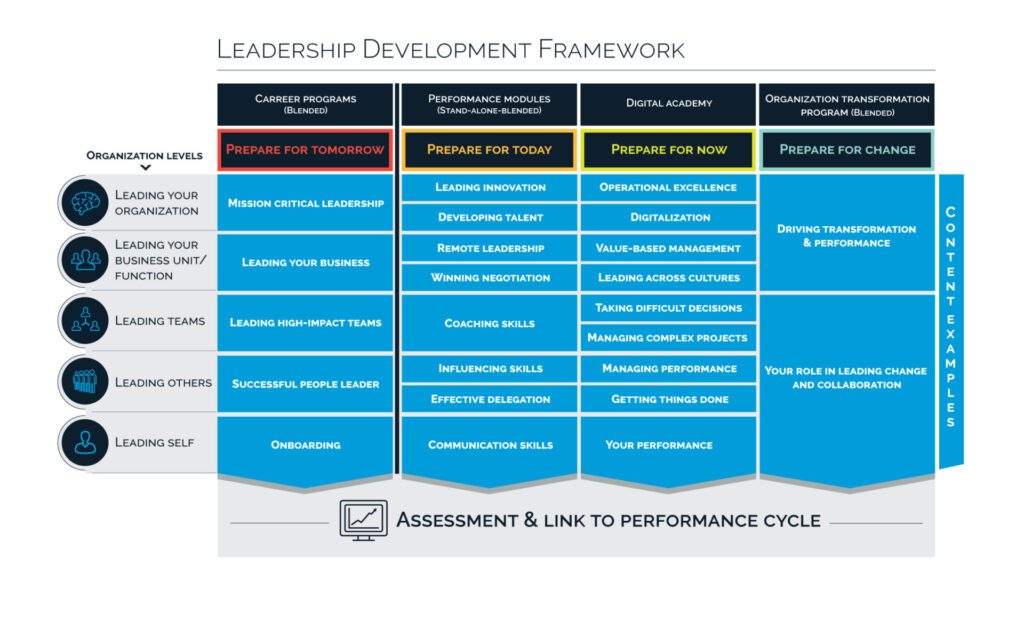
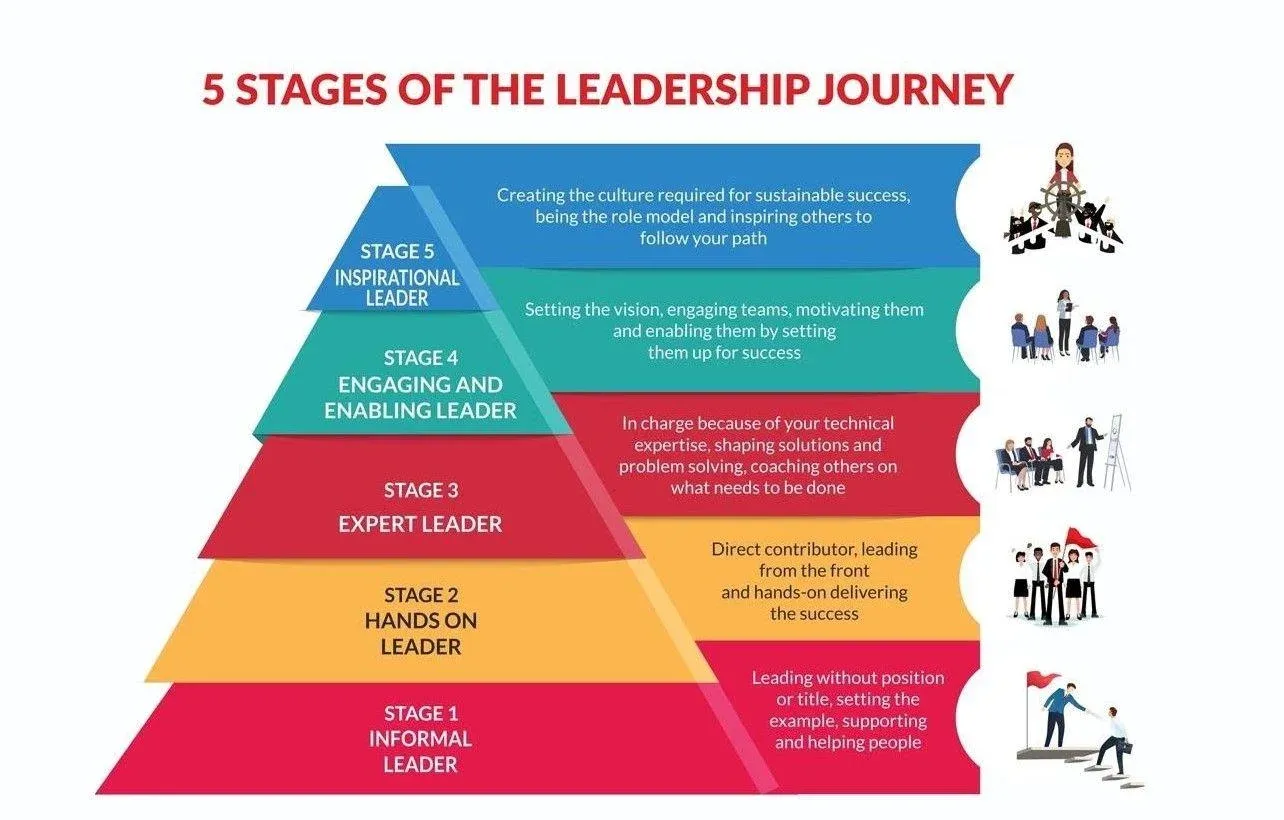
Which Of The Following Illustrates Leader Development
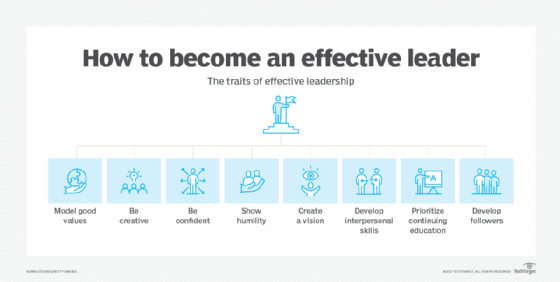
In today's complex world, the ability to cultivate effective leadership is not merely advantageous, but essential for organizational survival and societal progress. From corporate boardrooms to military command centers, identifying and nurturing individuals capable of inspiring, guiding, and making critical decisions under pressure is a perpetual challenge.
This article dissects the multifaceted concept of leader development, exploring various approaches and initiatives employed across diverse sectors. We will analyze the key characteristics that distinguish genuine leader development from simple training programs, examining the role of experiential learning, mentorship, and continuous self-reflection in shaping future leaders.
The Essence of Leader Development
Leader development extends far beyond the acquisition of technical skills or management techniques. It represents a holistic process aimed at fostering the personal growth, strategic thinking, and ethical grounding necessary to effectively lead and influence others. This transformative journey requires a commitment to lifelong learning and a willingness to embrace challenges as opportunities for growth.
The distinction between leader development and management training lies in the focus. Training equips individuals with specific competencies, while development focuses on cultivating the underlying character, judgment, and vision that enable effective leadership in a variety of contexts.
Experiential Learning: The Crucible of Leadership
Many experts consider experiential learning to be a cornerstone of effective leader development. Immersing individuals in challenging situations, where they must apply their knowledge and skills in real-time, provides invaluable opportunities for growth.
Action Learning, a process where individuals or teams tackle real organizational problems and reflect on their experiences, is one such approach. By analyzing their successes and failures, participants gain a deeper understanding of their own leadership strengths and weaknesses.
Military organizations, for example, routinely employ field exercises and simulations to test the leadership abilities of their officers. These high-stakes environments provide critical insights into how individuals perform under pressure, revealing their capacity for strategic thinking and decisive action.
Mentorship and Coaching: Guiding the Next Generation
The role of mentorship and coaching in leader development cannot be overstated. Pairing emerging leaders with experienced professionals provides a crucial support system and a valuable source of guidance.
A mentor can offer advice based on their own experiences, helping mentees navigate the complexities of their roles and avoid common pitfalls. Coaching, on the other hand, focuses on enhancing specific skills and improving performance through targeted feedback and support.
Companies like Google and Microsoft have established formal mentorship programs to cultivate talent and foster a culture of learning and development. These programs provide opportunities for employees to connect with senior leaders and receive personalized guidance.
Self-Reflection: The Inner Journey of Leadership
Effective leader development requires a commitment to continuous self-reflection. Individuals must be willing to examine their own beliefs, values, and behaviors, identifying areas for improvement and growth.
Practices such as journaling, mindfulness, and 360-degree feedback can help individuals gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their impact on others. 360-degree feedback, in particular, provides valuable insights from peers, subordinates, and supervisors, offering a more comprehensive assessment of an individual's leadership effectiveness.
Harvard Business Review frequently publishes articles emphasizing the importance of self-awareness in leadership. Leaders who are aware of their strengths and weaknesses are better equipped to make sound decisions and build strong relationships.
Examples of Leader Development in Action
Several specific examples illustrate the principles of leader development in practice. Consider a program where mid-level managers are given cross-functional assignments to broaden their understanding of the organization.
This allows them to develop a more holistic perspective and build relationships with colleagues in different departments. Another example involves providing emerging leaders with opportunities to lead challenging projects, requiring them to manage resources, motivate teams, and overcome obstacles.
The Center for Creative Leadership (CCL) offers a variety of programs designed to foster leadership development at all levels. Their programs emphasize experiential learning, feedback, and self-reflection, helping participants develop the skills and mindset necessary to lead effectively.
The Future of Leader Development
The future of leader development will likely be shaped by several key trends. The increasing complexity of the global landscape will require leaders to be more adaptable, resilient, and culturally aware.
Technology will play an increasingly important role in leader development, with online learning platforms and virtual simulations providing access to a wider range of resources and experiences. There will also be a greater emphasis on developing inclusive leaders who can effectively manage diverse teams and create a culture of belonging.
As organizations grapple with rapid change and unprecedented challenges, the ability to cultivate effective leadership will become even more critical. By embracing a holistic approach that incorporates experiential learning, mentorship, self-reflection, and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can develop the leaders they need to thrive in the years to come.