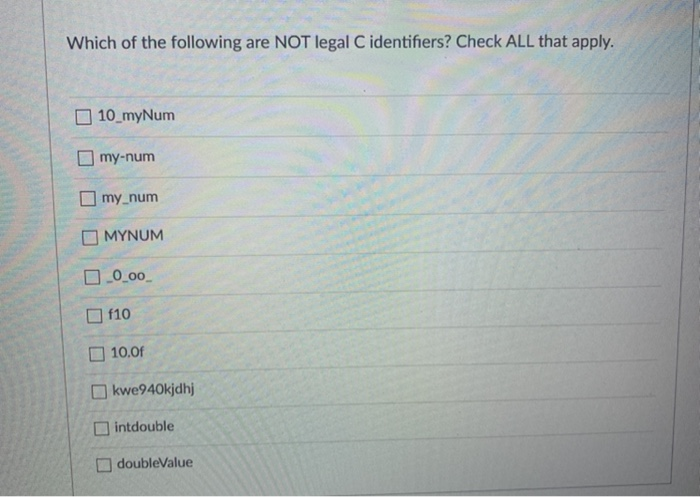
Which Of The Following Is A Legal Identifier
Confusion reigns as individuals and businesses grapple with the legal boundaries of personal identification. The question on everyone's mind: Which data points are legally permissible for use as unique identifiers?
This article cuts through the noise, providing a clear and concise breakdown of legally recognized identifiers, focusing on compliance and avoiding potential legal pitfalls.
Permissible Identifiers: A Legal Landscape
What constitutes a legal identifier? The answer depends heavily on the specific context and jurisdiction. Nationally, in the United States, for example, a Social Security number (SSN) is heavily regulated and generally restricted from widespread use as a universal identifier.
However, some data points enjoy broader legal acceptance. A driver's license number, while geographically limited, serves as a recognized identifier within its issuing state. Similarly, a passport number offers international identification.
Acceptable Identifiers: The Nuances
Full Name and Date of Birth, while seemingly innocuous, require cautious handling. When combined, they possess a higher risk of identifying an individual and can fall under the purview of privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in healthcare or the CCPA/CPRA in California.
Email Addresses are commonly used for online identification but are not universally recognized as legal identifiers in a strict regulatory sense. Terms of service and privacy policies dictate their permissible use, and reliance on them for high-stakes identification purposes is generally discouraged.
Physical Addresses, similar to names and dates of birth, gain significance when combined with other data. Alone, they may not constitute a definitive identifier, but their association with specific names or purchase histories can elevate their sensitivity.
Identifiers Under Scrutiny: What to Avoid
Certain data points carry significant legal restrictions. As mentioned before, the broad and unrestricted use of Social Security Numbers (SSNs) is generally prohibited due to the high risk of identity theft. Storing or transmitting them without appropriate security measures can lead to severe penalties.
Biometric data, including fingerprints, facial recognition scans, and iris scans, falls under heightened regulatory scrutiny. Laws like the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) impose strict requirements on the collection, storage, and use of such data.
Protected Health Information (PHI) under HIPAA also constitutes a sensitive category. Any data related to an individual's health condition, treatment, or payment information cannot be used as a general identifier.
The Impact of Regulations: GDPR and Beyond
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe has profoundly impacted the handling of personal data worldwide. Under GDPR, any information that can directly or indirectly identify a person is considered personal data, requiring lawful justification for processing.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and its amendment, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), grant California residents broad rights over their personal information, including the right to know, access, and delete their data.
These regulations require organizations to implement robust data protection measures and provide transparency about their data processing practices. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and reputational damage.
Best Practices for Data Handling
Data Minimization is paramount. Collect only the data necessary for a specific purpose. Avoid gathering excessive information that could create unnecessary risk.
Encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Use strong encryption algorithms to safeguard data from unauthorized access.
Access Controls should be implemented to restrict access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only. Implement role-based access controls to limit data exposure.
Moving Forward: Navigating the Legal Complexities
The legal landscape surrounding personal identifiers is constantly evolving. Organizations must stay informed about the latest regulations and best practices.
Consulting with legal counsel specializing in data privacy is essential for ensuring compliance and mitigating potential risks. Regular audits and risk assessments can help identify and address vulnerabilities.
The ongoing debate about data privacy and the definition of personal identifiers underscores the need for vigilance and proactive measures. Staying ahead of the curve is crucial for protecting individuals' rights and maintaining public trust.




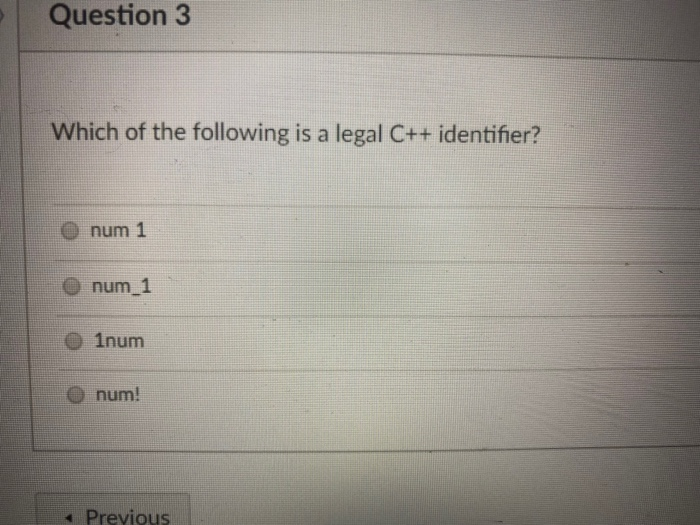
![Which Of The Following Is A Legal Identifier Solved Question 3 [03] Which of the following is NOT a legal | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/5ca/5ca9fe9a-a4f8-42ef-91f9-8e7a7c6589df/image.png)