Which Of The Following Is A Qualitative Forecasting Method
In the realm of business and economic planning, forecasting is a crucial element, allowing organizations to anticipate future trends and make informed decisions. Among the array of forecasting techniques, qualitative methods stand out for their reliance on expert opinions and subjective assessments rather than purely numerical data. Deciding which technique is best depends on the specific context, available data, and the nature of the forecast being made.
Understanding the nuances of qualitative forecasting methods is essential for businesses, economists, and policymakers seeking to navigate uncertain futures. This article will delve into the key characteristics of qualitative forecasting, providing a clear understanding of its application and significance.
Qualitative Forecasting: A Deep Dive
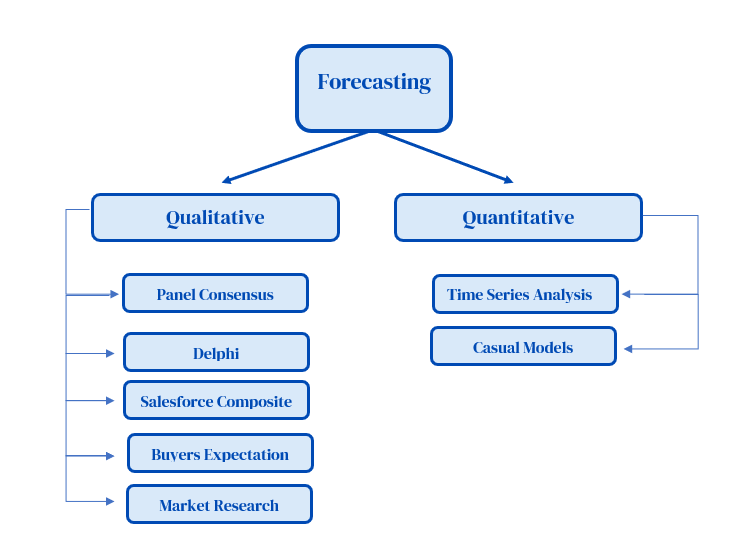
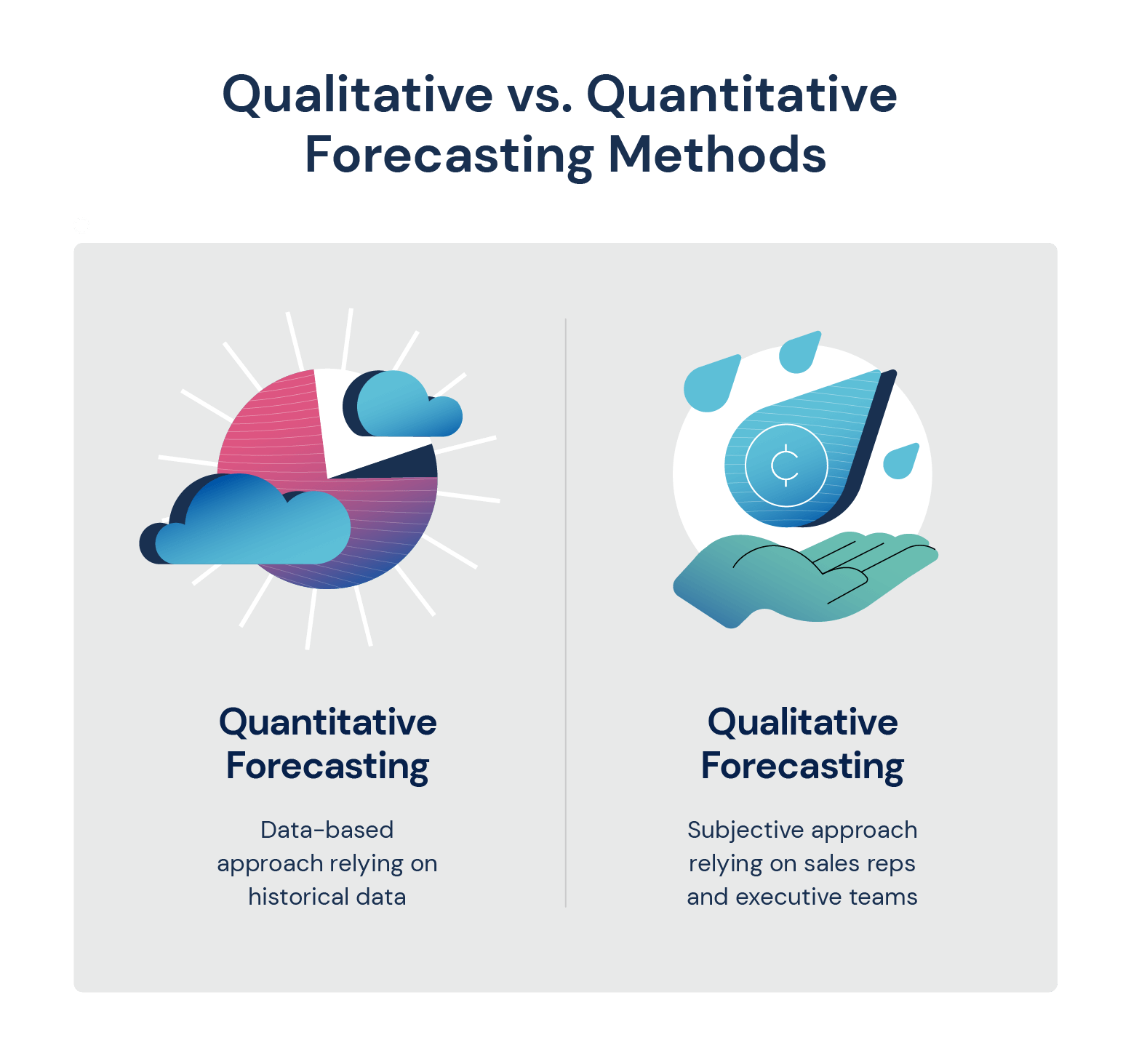
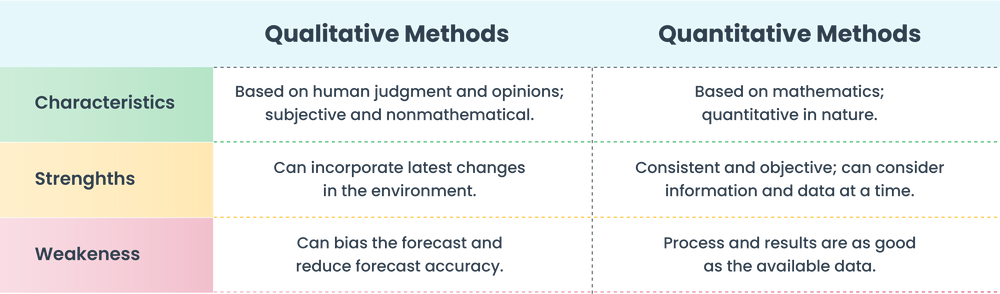
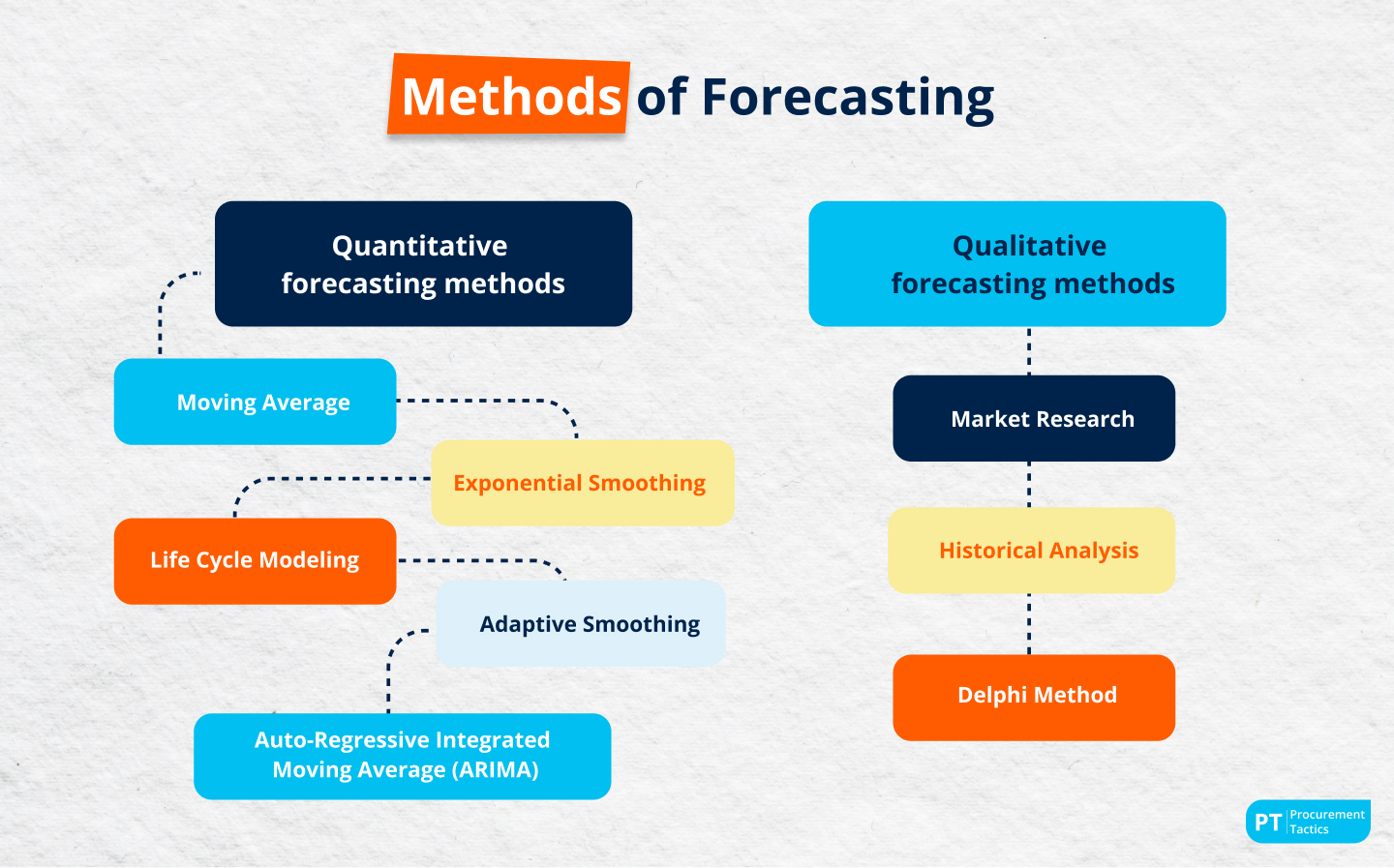
Qualitative forecasting methods are predictive techniques that rely primarily on judgment, intuition, surveys, and comparative studies. Unlike quantitative methods, which utilize historical data and statistical analysis, qualitative approaches are most valuable when historical data is scarce or unreliable.
This is often the case when forecasting the demand for new products, assessing the impact of emerging technologies, or navigating geopolitical uncertainties. Understanding different kinds of qualitative forecasting methods is very important.
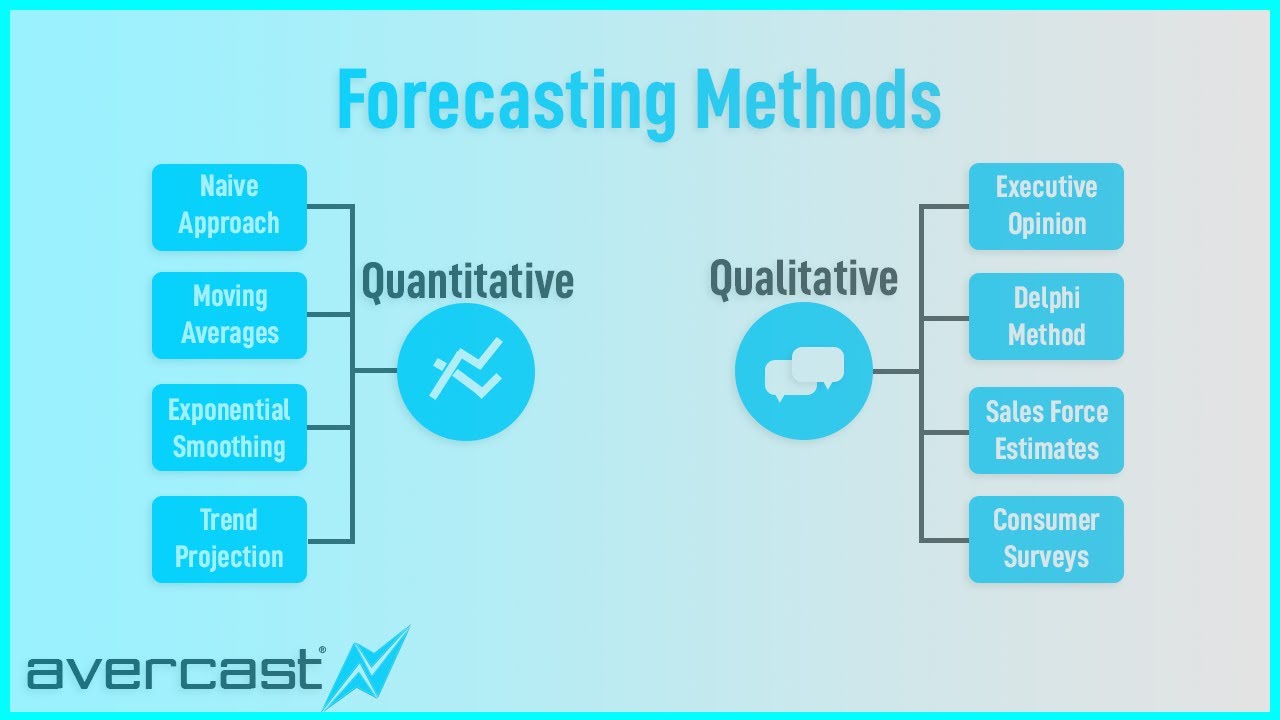
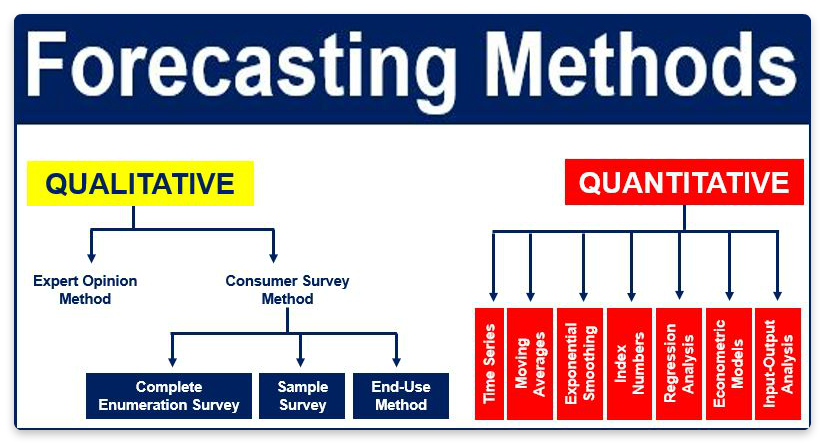
Key Qualitative Forecasting Methods
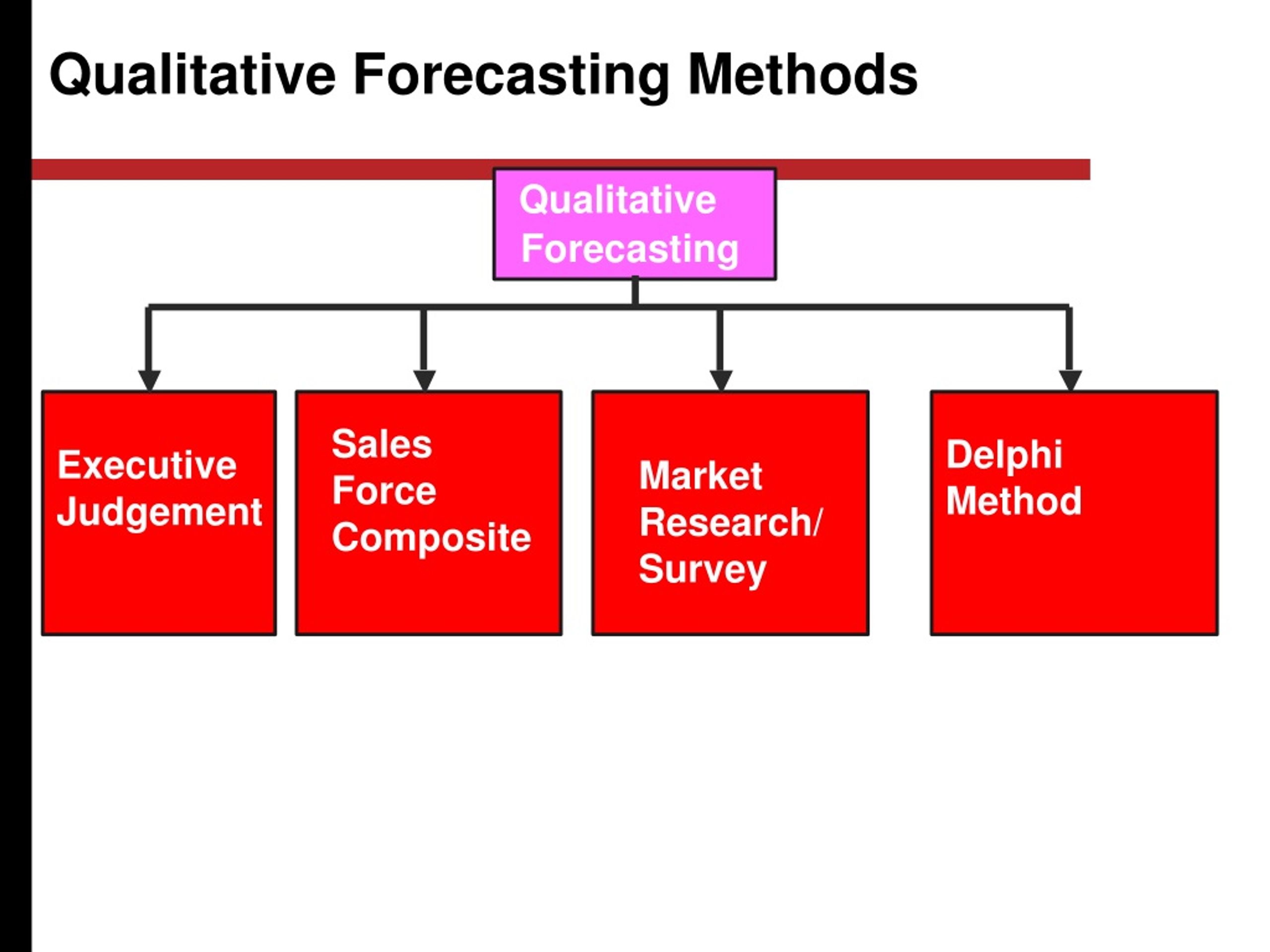
Several distinct qualitative forecasting methods are available, each offering unique strengths and applications. Here are some of the most common:
Delphi Method: This structured technique involves soliciting opinions from a panel of experts through multiple rounds of questionnaires. Anonymity is maintained to prevent bias, and feedback is provided after each round to refine the collective forecast. It is particularly useful for long-term forecasting and situations where diverse perspectives are needed.
Market Research: Involves gathering information directly from consumers or potential customers through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. This method helps understand consumer preferences, identify emerging trends, and assess the market potential for new products or services. Market research provides valuable insights into customer behavior and demand.
Executive Opinion: This approach relies on the collective wisdom and experience of high-level executives within an organization. Executives from various departments provide their individual assessments, which are then combined to form a comprehensive forecast. This method is often used for strategic planning and resource allocation decisions. Because of the limited group, it is prone to bias, therefore, it is critical to consider this limitation when evaluating the conclusions.
Sales Force Composite: This technique involves gathering individual sales forecasts from members of the sales team. These forecasts are then aggregated to create an overall sales forecast for the company. This method leverages the direct customer contact and market knowledge of the sales force.
Historical Analogy: This approach uses past events or trends to predict future outcomes. For example, a company might analyze the launch of a similar product in the past to estimate the demand for a new product. This method assumes that patterns from the past will repeat in the future.
Significance and Application
Qualitative forecasting plays a significant role in various sectors and industries. In situations where historical data is limited or nonexistent, qualitative methods provide a valuable alternative.
For example, when a company is launching a radically new product, there might be no existing data to base a quantitative forecast on. Instead, qualitative methods such as market research and expert opinions are used to estimate demand. Qualitative methods are frequently used to supplement quantitative techniques, providing a more well-rounded view of future trends.
Businesses can use qualitative forecasting to anticipate changes in consumer tastes. Governments can use qualitative forecasts to prepare for changes in the needs of the population. Economists can use qualitative forecasting to create more accurate economic models.
Impact on Audience and Society
The use of qualitative forecasting methods has a wide-ranging impact on both businesses and society. Accurate forecasts can lead to better resource allocation, reduced waste, and improved profitability for companies. However, qualitative methods are not without limitations.
They can be subjective and prone to bias, and their accuracy depends heavily on the expertise and judgment of the individuals involved. It is important to use them in conjunction with quantitative forecasts and to acknowledge their inherent limitations.
Poorly made forecasts can lead to over or under production and negatively affect customers, while successful forecasts can bring new, efficient, and effective solutions. The effective application of qualitative forecasting can contribute to economic stability, societal well-being, and enhanced quality of life.
Conclusion
Qualitative forecasting methods are valuable tools for predicting future trends and making informed decisions. Market research, executive opinions, the Delphi method, the sales force composite, and historical analogy each offer unique advantages and are suited for different situations.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of these methods is essential for effectively applying them in various contexts. As businesses and policymakers continue to navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain world, qualitative forecasting will remain a vital component of strategic planning and decision-making.
By embracing the insights gained from qualitative methods, organizations can better anticipate future challenges and opportunities, ultimately contributing to greater success and societal well-being. Qualitative methods are not perfect, but they can be a valuable tool when applied correctly.