Which Of The Following Is An Anabolic Reaction

In the intricate dance of life, where molecules are constantly being built up and broken down, lies the crucial concept of metabolism. Understanding the specific reactions within this process is paramount for fields ranging from medicine to athletic performance. The question, "Which of the following is an anabolic reaction?" serves as a gateway to unraveling the complex processes of biosynthesis within living organisms.
This article delves into the heart of anabolic reactions, providing a clear understanding of what defines them. It will distinguish anabolic reactions from their counterparts, catabolic reactions, and highlight key examples. By examining these processes, readers will gain a foundational understanding of how living organisms synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones, fueling growth, repair, and maintenance.
Anabolism: Building Blocks of Life
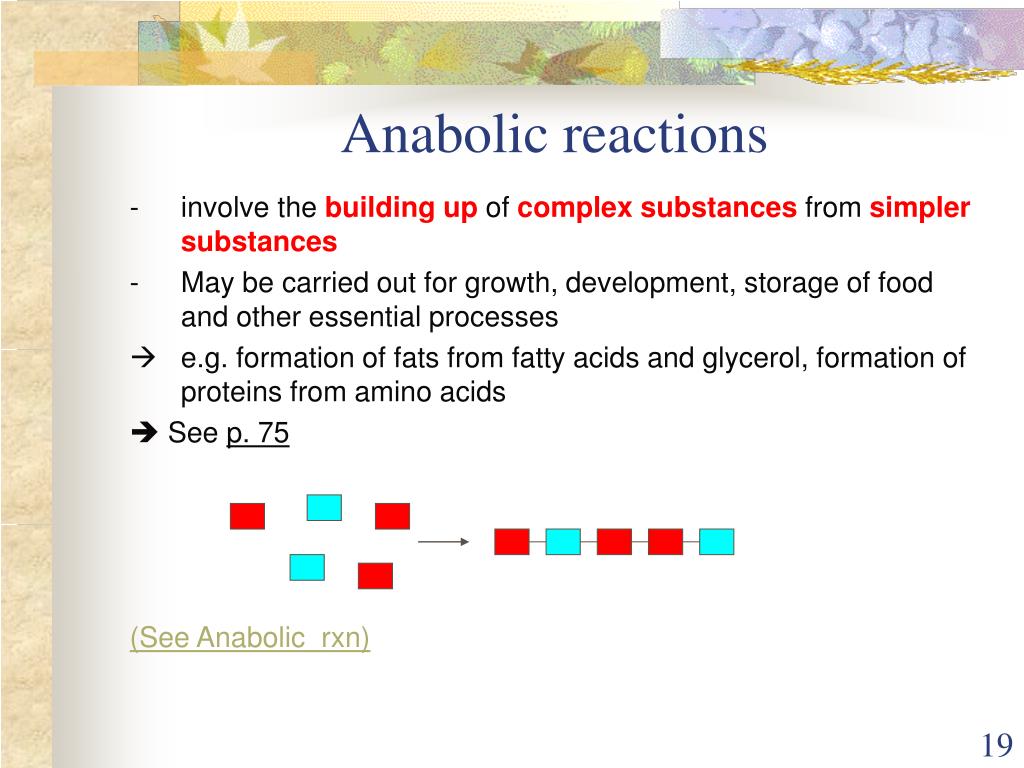
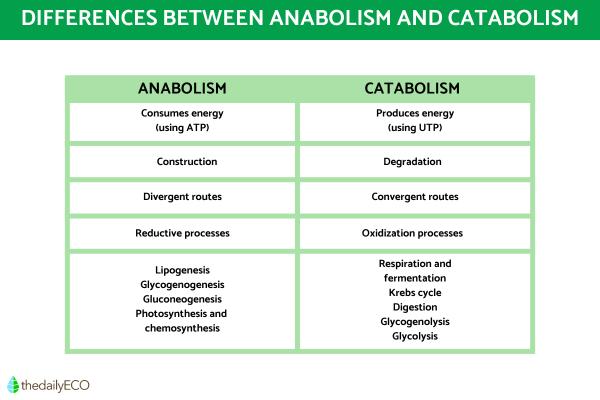
Anabolism, derived from the Greek word "anabole," meaning "a raising up," refers to the set of metabolic processes where complex molecules are synthesized from simpler precursors. This process requires energy input, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), to drive the formation of new chemical bonds. Anabolic reactions are fundamental to growth, development, and tissue repair.
In essence, anabolism is the constructive phase of metabolism. It is the process by which our bodies build and maintain their structures.
Distinguishing Anabolism from Catabolism
To fully grasp anabolism, it is crucial to differentiate it from catabolism. Catabolism involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. Think of catabolism as the demolition crew and anabolism as the construction crew within the body.
While anabolism builds, catabolism breaks down.
These two processes are intricately linked and work in concert to maintain homeostasis within a living organism.
Examples of Anabolic Reactions
Several key biological processes exemplify anabolic reactions. These include protein synthesis, photosynthesis, and bone mineralization.
Protein Synthesis
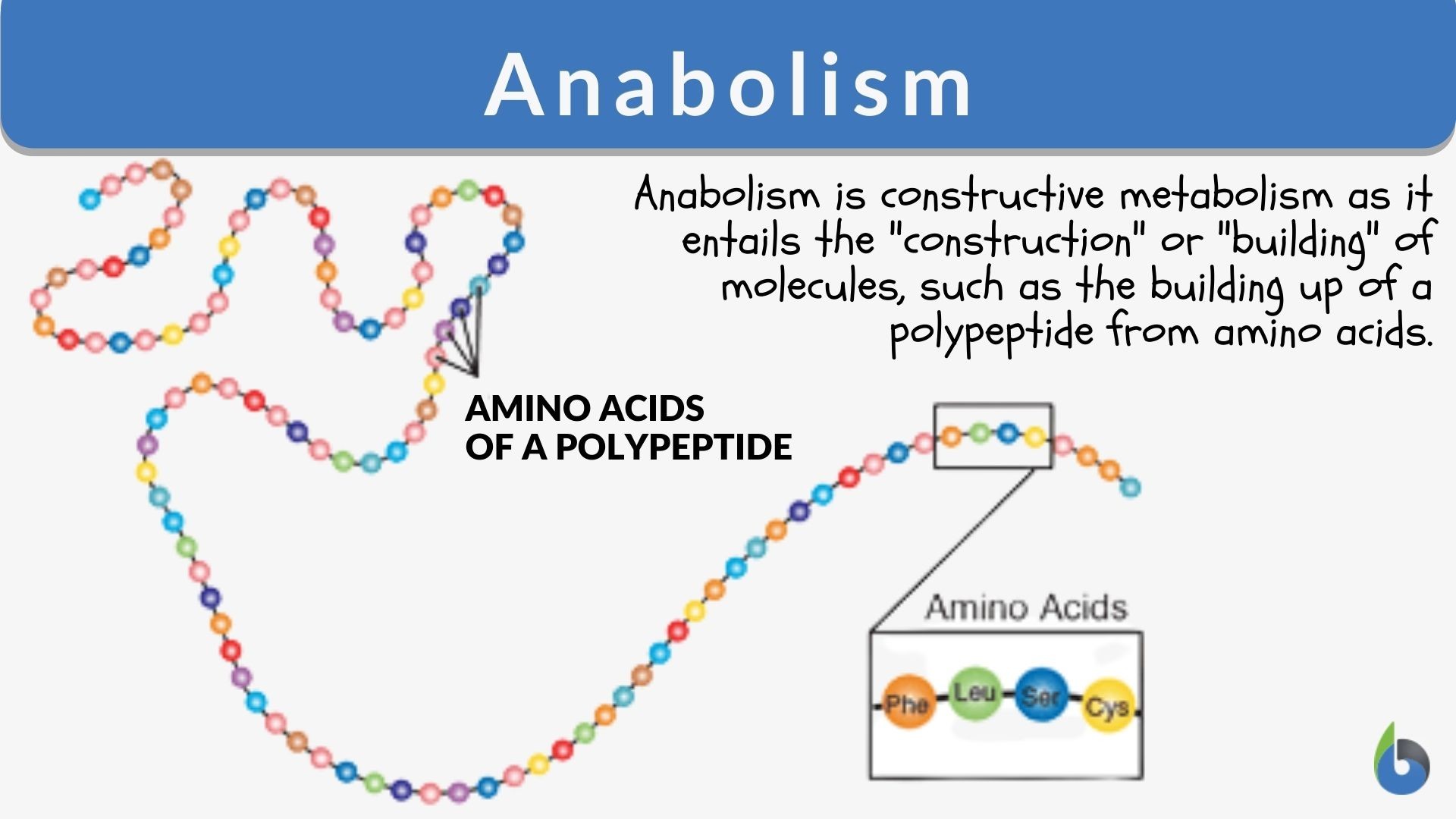
One of the most important anabolic processes is protein synthesis. This process involves linking amino acids together to form polypeptide chains, which then fold into functional proteins. Ribosomes are the molecular machines responsible for carrying out this complex task, using mRNA as a template to dictate the sequence of amino acids.
This intricate process is fundamental for building and repairing tissues, as well as producing enzymes, hormones, and other essential molecules.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, is another prime example of anabolism. Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to synthesize glucose, a simple sugar. This glucose serves as the primary energy source for the plant and also provides the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates, like cellulose.
Photosynthesis forms the foundation of most food chains on Earth.
Bone Mineralization
The formation of bone tissue is also an anabolic process. Bone mineralization involves the deposition of minerals, primarily calcium and phosphate, onto a collagen matrix. Osteoblasts, specialized bone-forming cells, are responsible for this process.
This process increases bone density and provides structural support to the skeleton.
Factors Influencing Anabolic Reactions
Various factors can influence the rate and efficiency of anabolic reactions. These include hormones, nutrition, and exercise.
Hormones
Hormones play a critical role in regulating anabolism. For instance, growth hormone stimulates protein synthesis and bone growth. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, promotes glucose uptake and protein synthesis. Testosterone, primarily in males, promotes muscle growth and bone density.
These hormones act as signaling molecules, instructing cells to increase anabolic activity.
Nutrition
Adequate nutrition is essential for anabolism. Providing the necessary building blocks, such as amino acids, carbohydrates, and fats, ensures that the body has the raw materials needed to synthesize complex molecules. A balanced diet is crucial for supporting anabolic processes.
Deficiencies in essential nutrients can impair anabolic activity and lead to health problems.
Exercise
Exercise, particularly resistance training, can stimulate anabolic reactions in muscle tissue. When muscles are stressed during exercise, they respond by increasing protein synthesis and muscle growth. This process is known as muscle hypertrophy.
Regular exercise, combined with adequate nutrition, is a powerful way to promote anabolism and improve overall health.
Clinical Significance of Anabolic Reactions
Anabolic reactions are essential for maintaining health and treating various medical conditions. Understanding these processes can inform treatment strategies for malnutrition, muscle wasting, and bone disorders.
For example, anabolic steroids, synthetic derivatives of testosterone, are sometimes used to promote muscle growth in patients with muscle-wasting diseases. However, the use of anabolic steroids is controversial due to potential side effects.
Furthermore, nutritional interventions aimed at providing adequate protein and calories can help to support anabolic processes in malnourished individuals.
The Future of Anabolic Research
Research into anabolic reactions continues to advance, with potential implications for improving human health and performance. Scientists are exploring novel strategies to enhance anabolism, such as developing new anabolic agents and optimizing exercise protocols.
Future research may also focus on understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms that regulate anabolic processes. This knowledge could lead to personalized interventions that maximize anabolic potential.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of anabolism will contribute to developing more effective strategies for preventing and treating a wide range of health conditions.
In conclusion, understanding anabolic reactions and their importance is pivotal. By recognizing that anabolic reactions are those that build complex molecules from simpler ones, fueled by energy, we can appreciate their significance in growth, repair, and overall health.