Which Of The Following Is Not A Benefit Of Rfid

The pervasive use of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology across diverse industries, from retail to healthcare, has spurred widespread discussion regarding its purported benefits. While proponents tout advantages such as enhanced inventory management and improved security, a critical examination reveals that not all frequently cited "benefits" withstand scrutiny.
This article delves into the often-misunderstood realities of RFID, specifically identifying claims that do not hold up as genuine advantages. We aim to provide a balanced perspective on RFID technology, separating fact from fiction in the ongoing debate about its efficacy and value.
Understanding RFID Technology
RFID utilizes radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information, which can be read wirelessly by an RFID reader.
This technology allows for item-level tracking, data collection, and automated processes that are intended to improve efficiency and accuracy.
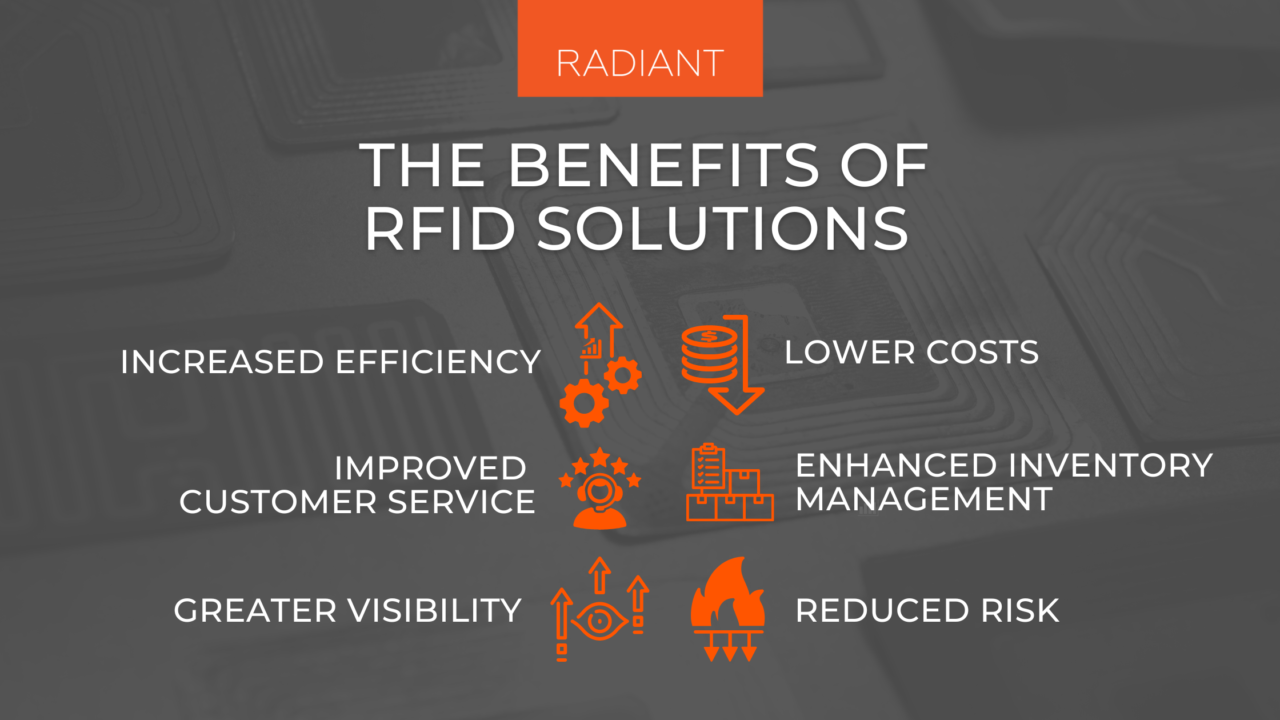
Commonly Cited Benefits and Their Realities
Several benefits are commonly associated with RFID, but a closer look reveals nuances and limitations that challenge their universal applicability.
Increased Profit Margins: A Conditional Advantage
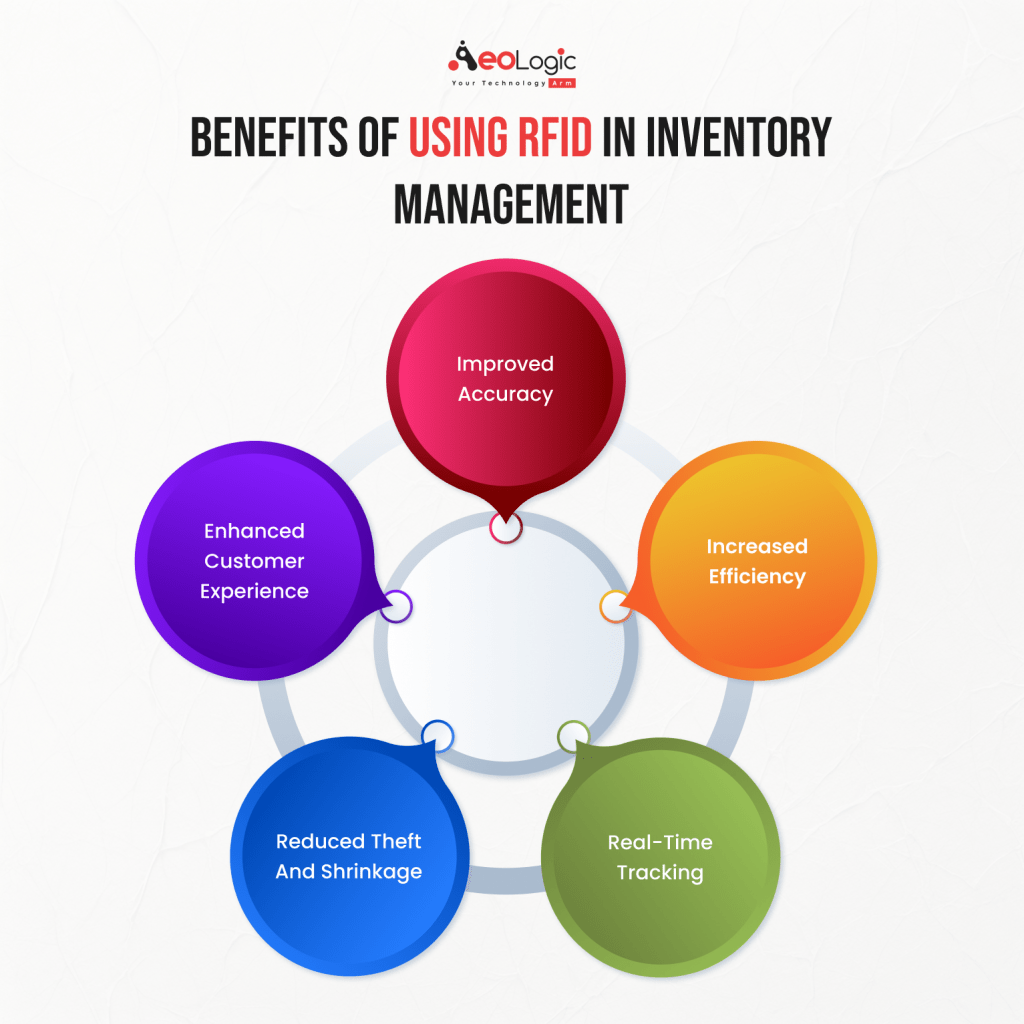
One frequently cited benefit is that RFID automatically increases profit margins. While improved inventory accuracy and reduced labor costs can potentially lead to higher profits, this outcome is not guaranteed.
The initial investment in RFID infrastructure, including tags, readers, and software, can be substantial. Furthermore, realizing profit gains depends on effectively leveraging the data collected and optimizing business processes accordingly, which requires strategic planning and skilled personnel.
The effectiveness of RFID in boosting profits is heavily dependent on the specific context and the company's ability to integrate the technology into its broader operational strategy. A poorly implemented system can easily lead to increased costs and minimal returns.
Guaranteed Error-Free Data: An Overstatement
Another claim is that RFID systems provide error-free data collection. While RFID offers significant improvements over manual data entry methods, it is not immune to errors.
Factors such as tag collisions (when multiple tags are read simultaneously), signal interference, and damaged tags can lead to inaccurate or incomplete data. The quality of the tags themselves and the reader's sensitivity also influence data accuracy.
Robust system design, proper tag placement, and regular system maintenance are crucial to minimizing errors. Data validation and reconciliation processes are also necessary to ensure data integrity.
Complete Supply Chain Visibility in All Situations: An Exaggeration
RFID is often touted as providing complete supply chain visibility. While RFID can significantly enhance visibility, it does not provide complete coverage in all situations.
The effectiveness of RFID tracking is limited to the areas where readers are deployed. Gaps in coverage, particularly in transit or at locations without RFID infrastructure, can result in blind spots.
Furthermore, relying solely on RFID for supply chain visibility may not be sufficient. Integration with other data sources, such as GPS tracking and transportation management systems, is often necessary for a truly comprehensive view.
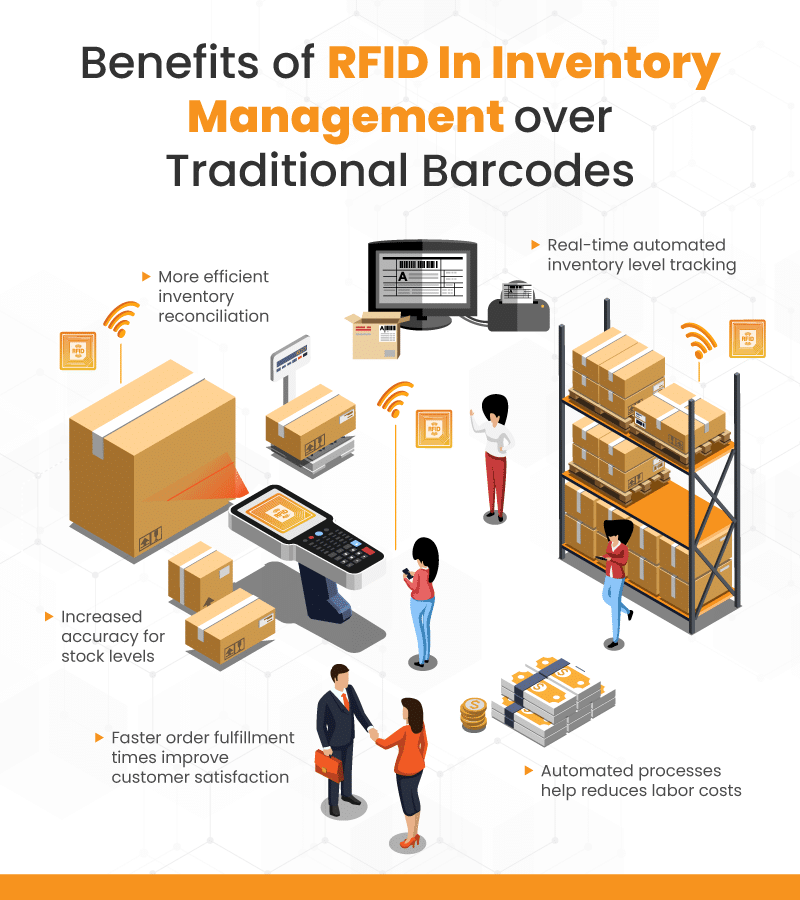
Elimination of Manual Inventory Counts: A Partial Truth
It's frequently said that RFID eliminates the need for manual inventory counts. While RFID greatly reduces the need for physical stocktaking, it does not completely eliminate it.
Periodic physical audits are still necessary to verify the accuracy of the RFID system and to address discrepancies caused by factors such as misplaced items, data errors, or system malfunctions. Furthermore, for items that are difficult to tag or are not consistently tagged, manual counts may still be required.
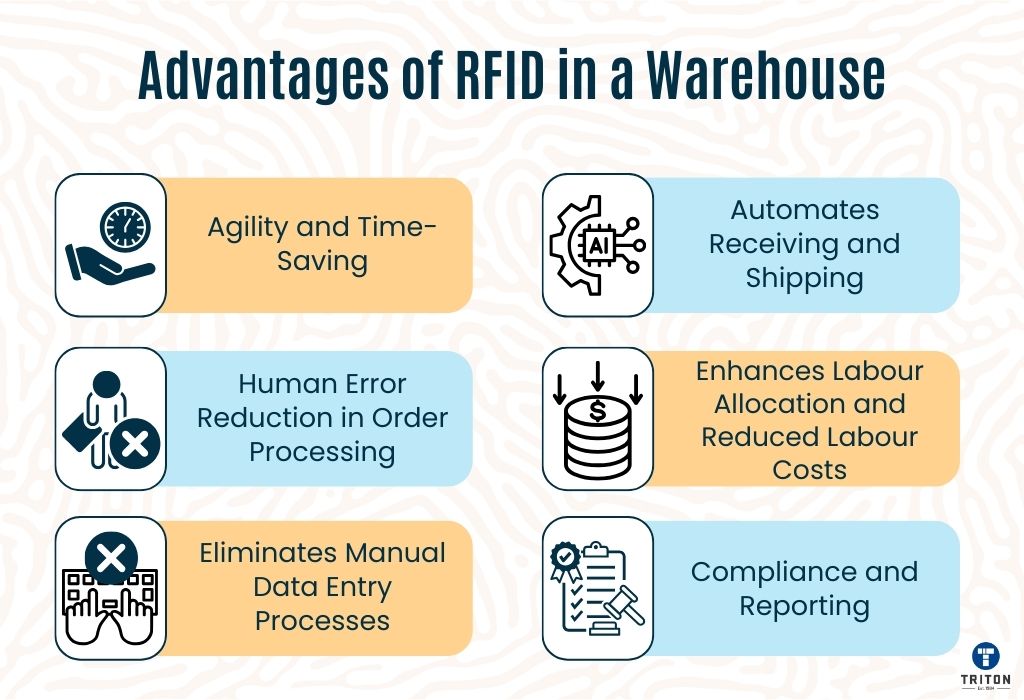
RFID automates much of the inventory management process, significantly reducing the time and labor required. But complete dependence on RFID without any manual oversight can lead to inaccuracies and inventory management issues.
The Importance of Realistic Expectations
The true value of RFID lies in its potential to improve efficiency, accuracy, and visibility when implemented strategically and managed effectively. Setting realistic expectations is crucial for successful implementation.
Companies must carefully evaluate their specific needs and challenges before investing in RFID. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, a well-defined implementation plan, and ongoing system monitoring are essential.
By understanding the limitations and potential pitfalls of RFID, organizations can make informed decisions and maximize the return on their investment. The hype surrounding RFID needs to be tempered with a healthy dose of realism.