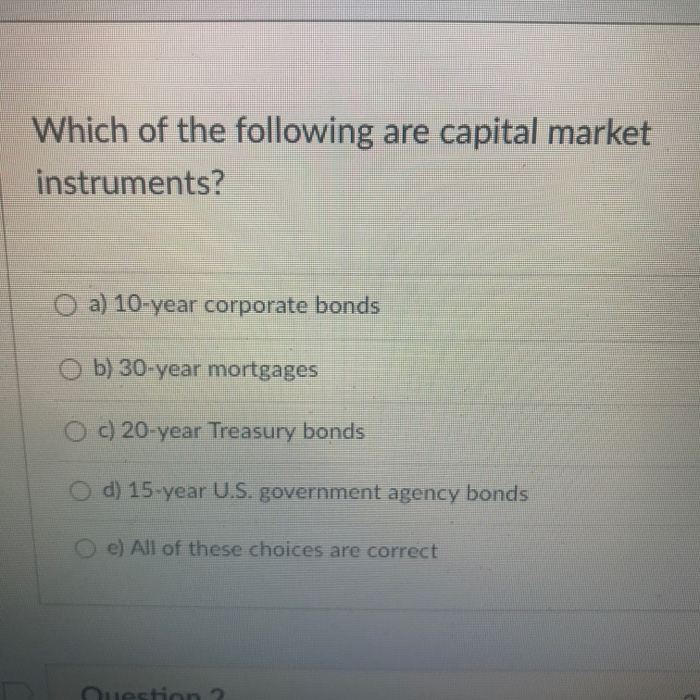
Which Of The Following Is Not A Capital Market Instrument
Imagine stepping into a bustling marketplace, not one filled with fruits and vegetables, but with financial instruments. Buyers and sellers converge, exchanging assets with the hope of future returns. The air crackles with anticipation, each transaction a thread woven into the larger tapestry of the global economy.
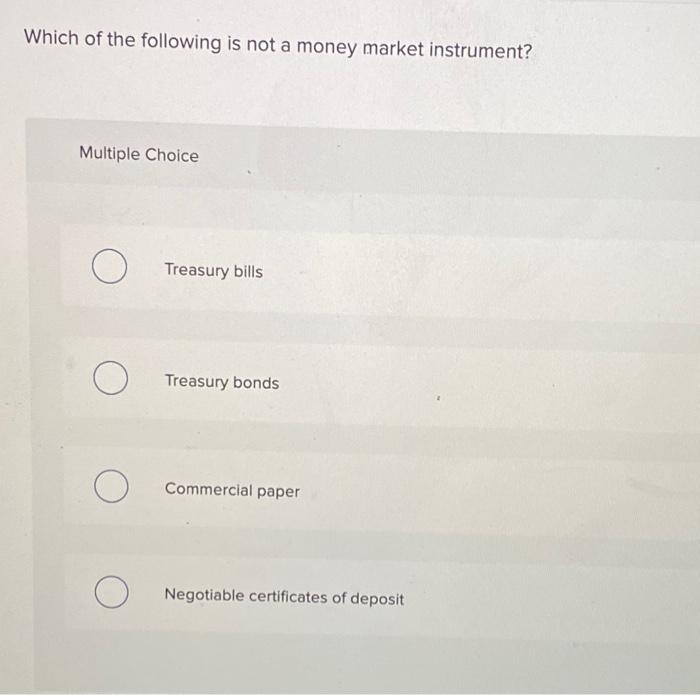
At the heart of this financial ecosystem lies the capital market, a crucial engine for economic growth. Understanding which instruments belong, and which don't, is key to navigating this complex landscape. This article will clarify that crucial distinction by explaining that the instrument that does not belong in the capital market is Commercial Paper. Commercial Paper is a short-term money market instrument, unlike the others which are capital market instruments.
What Are Capital Markets?
Capital markets are financial marketplaces where long-term debt and equity-backed securities are bought and sold. They channel savings and investments between suppliers of capital, such as retail investors and institutional investors, and those who are in need of capital, such as companies, governments, and individuals.
These markets are vital for funding long-term projects and supporting economic development. Think of them as the engine that fuels significant infrastructural projects or the expansion of businesses, ultimately creating jobs and driving innovation.
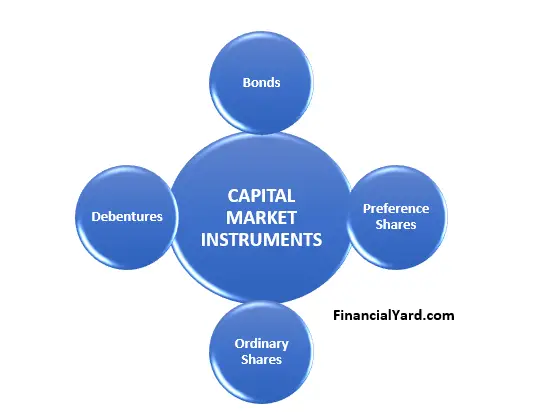
Key Capital Market Instruments
Several key instruments form the backbone of capital markets. Understanding each one is essential for any investor or anyone keen on grasping how the global economy functions.
Stocks, also known as equities, represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you're essentially buying a small piece of that company and are entitled to a portion of its profits and assets.
Bonds are debt instruments where an investor loans money to an entity (corporate or governmental) which borrows the funds for a defined period of time at a fixed interest rate. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks, providing a steady income stream.
Mortgages are loans specifically for purchasing real estate. These are a significant part of the capital market, especially when packaged and sold as mortgage-backed securities.
Mortgage-backed securities allow investors to indirectly invest in real estate. It helps lenders to free up capital for future loans.
The Odd One Out: Commercial Paper
While stocks, bonds, and mortgages are all integral parts of the capital market, commercial paper stands apart. This is the answer to our original question: which of the following is not a capital market instrument?
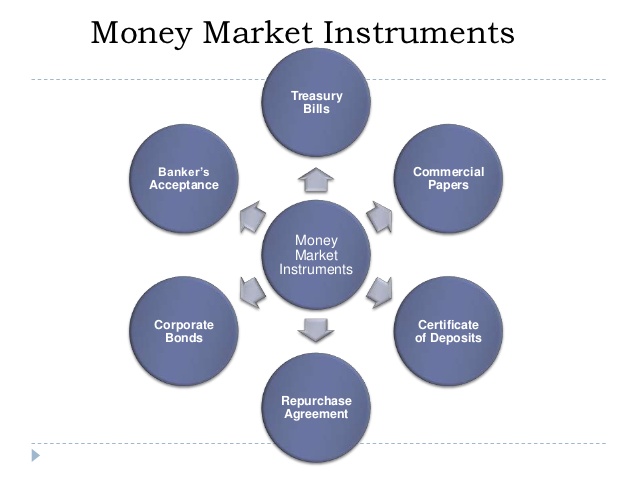
Commercial paper is a short-term, unsecured promissory note issued by large corporations to finance short-term liabilities such as accounts payable and inventory. It's a money market instrument, not a capital market one.
Its maturity typically ranges from a few days to nine months, making it a very liquid and short-term investment. It's generally considered a relatively safe investment, although not entirely without risk, because it is issued by creditworthy companies.
Money Market vs. Capital Market
To fully understand why commercial paper doesn't belong in the capital market, it's important to distinguish between the money market and the capital market.
The money market deals with short-term debt instruments, usually with maturities of less than one year. It is focused on providing liquidity and managing short-term cash flows.
The capital market, as we've discussed, focuses on long-term investments, with maturities of more than one year. It’s where capital is raised for long-term projects and investments.
Therefore, commercial paper's short-term nature firmly places it in the money market, distinct from the long-term focus of capital market instruments.
Significance and Implications
Understanding the differences between these financial instruments and the markets they operate in is vital for several reasons. For investors, it helps in diversifying portfolios and managing risk effectively.
Knowing the characteristics of both the capital and money markets facilitates informed decision-making aligned with specific financial goals. For businesses, it helps in choosing the right funding sources for different needs.
Companies can use the capital markets to fund long-term expansions and the money market to manage their working capital effectively. It also provides a better understanding of the overall economic health and stability, which is invaluable for policymakers.
By analyzing the activity in both money and capital markets, governments and central banks can get insights into economic conditions and calibrate their policies accordingly.
Conclusion
The world of finance can seem daunting, but with a little understanding, it becomes much more navigable. The difference between capital market instruments and money market instruments like commercial paper is a key piece of that understanding.
Capital markets are the foundation upon which long-term economic growth is built. The stocks, bonds, and mortgages are essential tools to facilitate wealth creation and economic development.
Next time you hear about the stock market or a new bond offering, remember the bigger picture. You are now one step closer to understanding the forces that shape our economic world.