Which Of The Following Processes Requires The Use Of Energy
In a world increasingly focused on energy conservation and sustainability, understanding the fundamental principles of energy consumption is crucial. Many everyday processes, often taken for granted, require energy input to occur. Distinguishing between processes that require energy and those that don't is vital for optimizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
This article will delve into several common processes, identifying those that require energy and providing context for why energy is necessary. Understanding the energy requirements of various processes is essential for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions about resource allocation, technological development, and environmental stewardship.
Processes Requiring Energy
Numerous processes across diverse fields fundamentally depend on the input of energy to proceed. From the biological to the industrial, energy drives change and facilitates essential functions.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, absolutely requires energy. This energy comes in the form of sunlight. Without sunlight, plants cannot create food and sustain life.
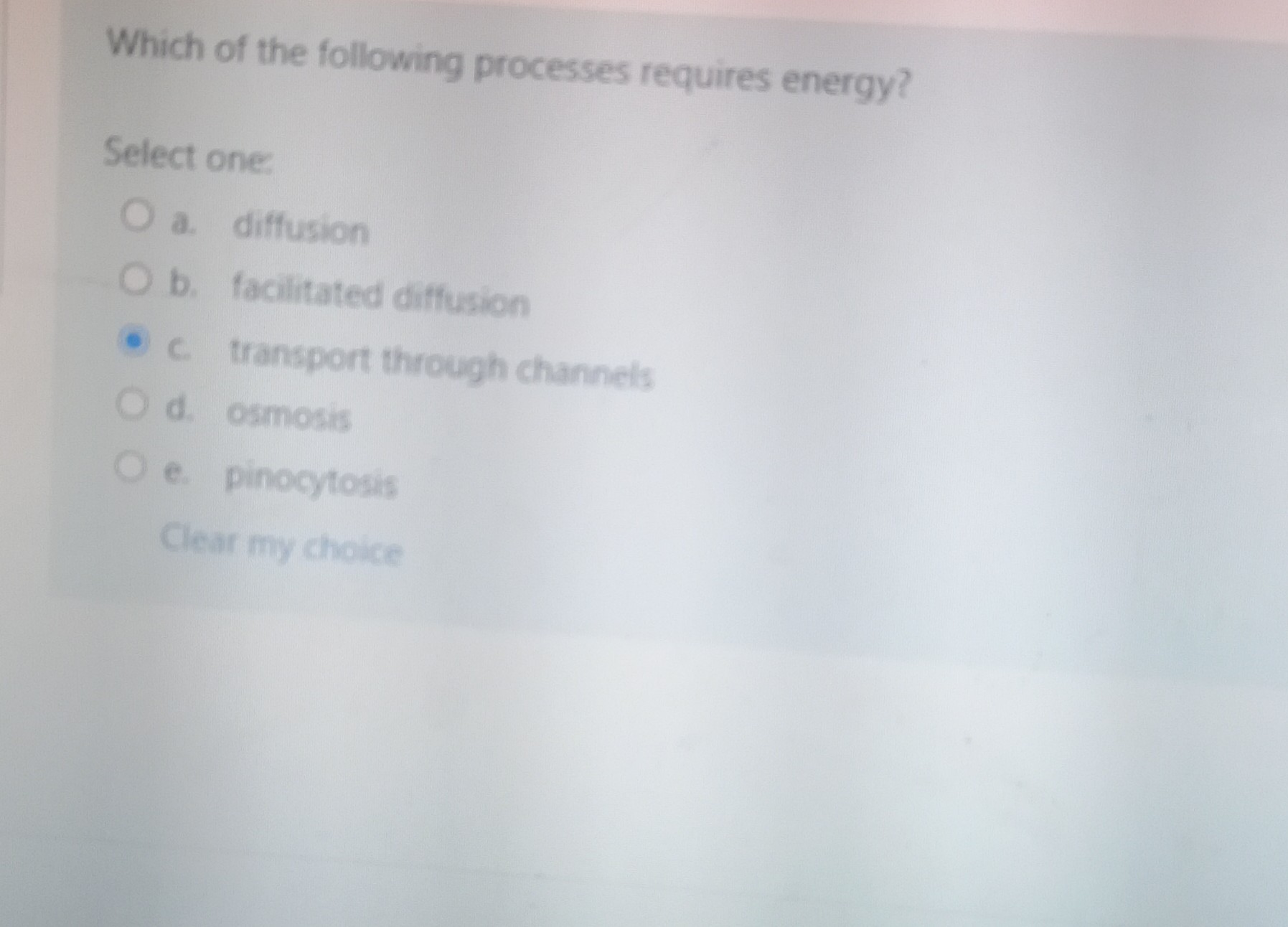
Active Transport
In biological systems, active transport, is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient. This movement requires energy, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This process is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and performing essential functions.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis, the process of using electrical current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, undeniably requires energy. It’s used in various industries, including the production of aluminum and the separation of water into hydrogen and oxygen. The amount of energy required depends on the specific reaction and the efficiency of the electrolytic cell.
Heating Water
Heating water, a common task for cooking or cleaning, necessitates a significant input of energy. Energy is needed to increase the kinetic energy of the water molecules. The required energy amount is determined by the mass of the water and the desired temperature increase.
Manufacturing Processes
Most manufacturing processes, from assembling electronics to producing textiles, rely heavily on energy. Energy is required to power machinery, heat materials, and transport goods. The push for energy efficiency has driven innovations in manufacturing technology and strategies.
Processes That Don't Require Additional Energy (After Initial Input)
While many processes require continuous energy input, some can sustain themselves or occur naturally after an initial input.
Diffusion
Diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, doesn't require continuous energy input. It occurs spontaneously due to the kinetic energy of the molecules themselves. Though it may start with some initial kinetic energy, it does not continuously need it.
Passive Transport
Passive transport, the movement of molecules across a cell membrane without the need for energy, is another example. This includes processes like facilitated diffusion and osmosis. These movements occur down the concentration gradient and utilize the inherent properties of the molecules and the membrane.
A Rock Rolling Downhill
Once initiated, a rock rolling downhill requires no additional energy to continue its descent (ignoring air resistance and friction). Gravity acts as the driving force, and the initial potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as the rock moves downward. The initial push to get it rolling is the only energy input.
Significance and Impact
Understanding which processes require energy is fundamental to addressing pressing issues. This includes climate change and resource management.
By identifying energy-intensive processes, we can develop strategies to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency. Investing in renewable energy sources is key to fulfilling the energy demands of essential processes in a sustainable manner. This creates a more resilient and environmentally responsible society.
Moreover, it raises individual awareness about energy usage, leading to more conscious choices in daily life. Recognizing the energy cost of various activities empowers consumers to make eco-friendly decisions. This can include simple actions like turning off lights to investing in energy-efficient appliances.
Conclusion
The identification of processes requiring energy is crucial for a sustainable and efficient future. By understanding the energy demands of different processes, individuals, businesses, and governments can make informed decisions. These decisions will lead to reduced environmental impact and improved resource management.
Ongoing research and innovation in energy-efficient technologies are essential for minimizing the energy footprint of our activities. Emphasizing energy awareness and conservation principles can promote a more sustainable and responsible way of living.

![Which Of The Following Processes Requires The Use Of Energy [ANSWERED] Which of the following processes requires the most energy](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220505153159421269-4566174.jpg?h=512)




![Which Of The Following Processes Requires The Use Of Energy [ANSWERED] Which of the following processes requires more heat energy](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220617014158069949-4548477.jpg?h=512)



+ENERGY+Living+things+have+the+ability+to+use+energy+for+different+processes..jpg)
