Which Of The Following Represents An Isotope Of Lithium

The fundamental question of what defines an isotope, especially in the context of elements like lithium, frequently surfaces in introductory chemistry and physics courses. Understanding this concept is crucial, not just for academic purposes, but also for various applications in nuclear medicine, archaeology, and energy production.
At the heart of the matter lies the atomic structure of an element. While all atoms of a specific element share the same number of protons, variations in the number of neutrons within the nucleus give rise to isotopes. The question, "Which of the following represents an isotope of lithium?" is therefore not simply about identifying lithium, but identifying a version of it with a different neutron count.
Isotopes: The Basics
An element's identity is defined by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. Lithium (Li), for example, always has three protons. However, the number of neutrons can vary.
This variation leads to different isotopes of lithium, each with a different mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons).
Key Concepts: Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus and uniquely identifies an element. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
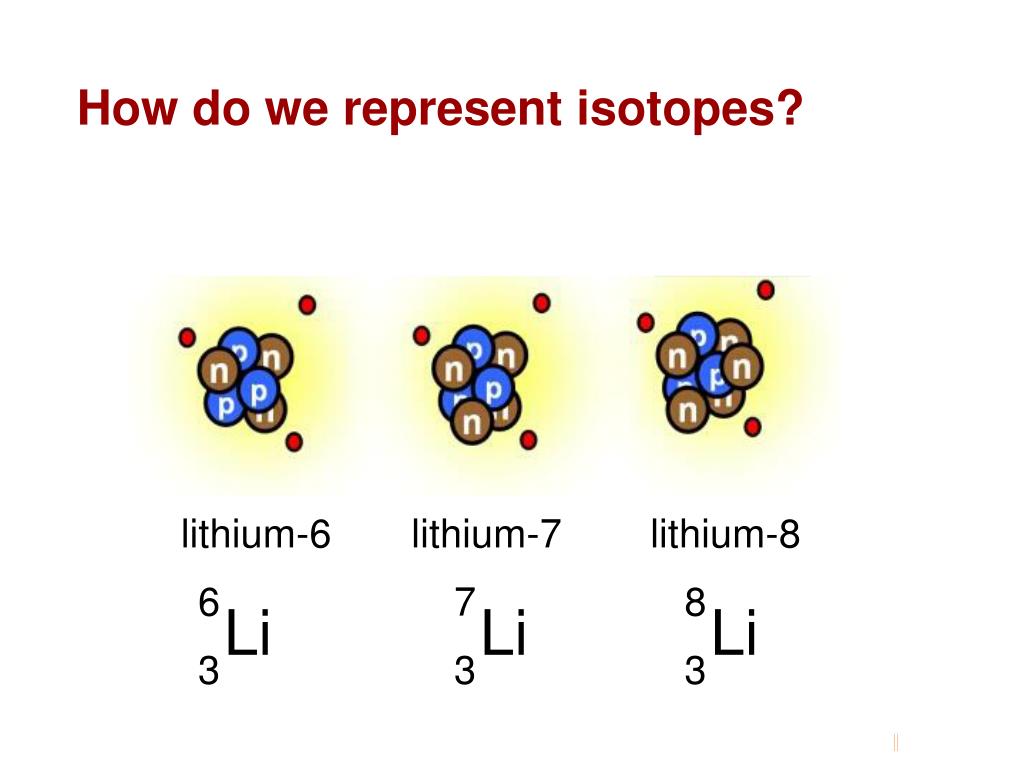
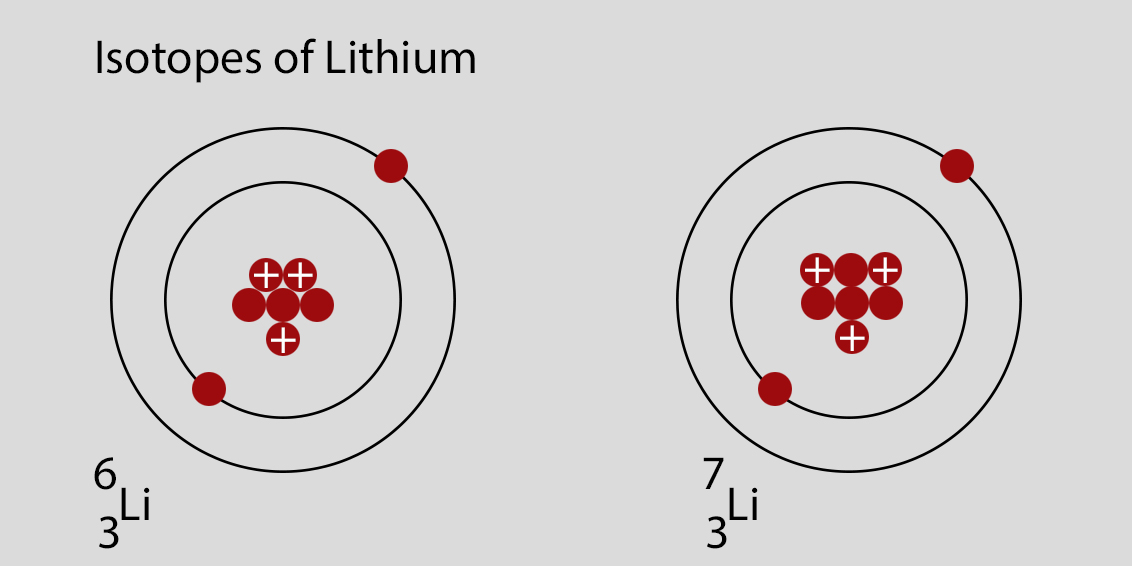
For example, Lithium-6 (6Li) has 3 protons and 3 neutrons, while Lithium-7 (7Li) has 3 protons and 4 neutrons. The chemical properties of different isotopes of the same element are virtually identical.
Identifying Lithium Isotopes
So, how do we identify an isotope of lithium? We look for an atom with 3 protons but a different number of neutrons compared to the most common form of lithium.
The most stable and abundant isotope of lithium is 7Li, comprising about 92.5% of naturally occurring lithium. 6Li is another stable isotope, making up the remaining 7.5%.
Consider the following scenarios: If you see an atom with 3 protons and 4 neutrons, it's 7Li. If you see an atom with 3 protons and 3 neutrons, it's 6Li. Both are isotopes of lithium.
Unstable Isotopes: Radioactivity
Not all isotopes are stable. Some, like Lithium-8 and Lithium-9, are radioactive. These isotopes decay rapidly, transforming into other elements.
The decay process involves the emission of particles and energy from the nucleus, altering the composition of the atom.
The Significance of Understanding Isotopes
Understanding isotopes extends far beyond basic chemistry. Isotopes of various elements have wide-ranging applications.
In medicine, radioactive isotopes are used in diagnostic imaging and cancer therapy. In archaeology, carbon-14 dating utilizes the decay of a carbon isotope to determine the age of organic materials.
Lithium isotopes themselves have specific uses. 6Li is used in the production of tritium, a key component of nuclear weapons and fusion reactors.
7Li is used in pressurized water reactors in nuclear power plants to control the pH of the reactor coolant.
Furthermore, studies involving lithium isotopes, particularly the ratios of 6Li to 7Li, have helped scientists understand the origins of the universe and the processes within stars. By analyzing the isotopic composition of meteorites and other celestial bodies, researchers can gain insights into the conditions that prevailed during the early solar system.
"The ability to differentiate between isotopes is fundamental to understanding a wide range of scientific phenomena," says Dr. Emily Carter, a professor of chemistry at Princeton University. "From tracing the origins of elements to developing new medical treatments, isotopes play a critical role."
Conclusion
The question "Which of the following represents an isotope of lithium?" highlights a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. The key is to remember that isotopes of an element share the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons.
This understanding has implications in various fields, from nuclear energy to medical diagnostics. Mastering the concept of isotopes is essential for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the world around them.