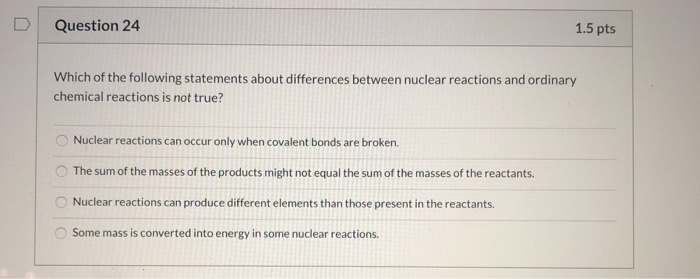
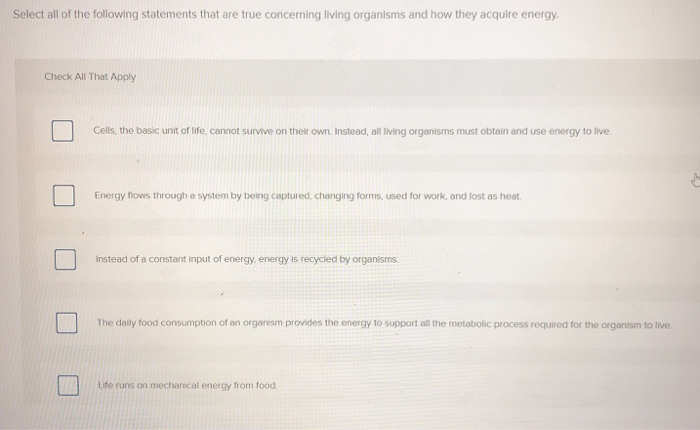
Which Of The Following Statements About Nuclear Energy Is True

The debate surrounding nuclear energy often sparks heated discussions, riddled with misconceptions and varying perspectives. Understanding the factual basis of nuclear power is crucial for informed decision-making, especially as global energy demands and climate change concerns intensify.
This article aims to clarify common questions and assess the validity of statements regarding nuclear energy, drawing on credible sources like the World Nuclear Association, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), and governmental reports. By examining different aspects of nuclear energy, from its safety and waste management to its role in carbon emissions and energy independence, this analysis will offer a balanced view.
Nuclear Energy: A Complex Landscape
Nuclear energy is generated through controlled nuclear fission, typically using uranium as fuel. This process releases immense heat, which is used to produce steam that drives turbines and generates electricity. Currently, nuclear power contributes a significant portion of the world's electricity supply.
There are several statements about nuclear energy circulating in public discourse. Understanding their truthfulness requires examining the evidence-based facts.
Is Nuclear Energy a Carbon-Free Source?
One of the most frequently discussed aspects of nuclear energy is its impact on carbon emissions. The claim that nuclear energy is a carbon-free energy source is generally true, but with some important nuances. Nuclear power plants themselves release virtually no greenhouse gases during operation.
However, the entire lifecycle of nuclear energy, including uranium mining, fuel processing, plant construction, and waste disposal, does involve some carbon emissions. Studies from the IAEA and other organizations suggest that these lifecycle emissions are significantly lower than those from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas, and are comparable to, or even lower than, some renewable energy sources like solar.
How Safe is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear safety is a major concern for many, understandably so. The incidents at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima have raised serious questions about the risks associated with nuclear power. However, it's vital to place these events in perspective.
The assertion that nuclear energy is inherently unsafe is an oversimplification. While accidents can happen, the nuclear industry has implemented rigorous safety protocols and technological advancements to minimize risks. Modern reactors have multiple layers of safety systems to prevent accidents and mitigate their consequences.
Data from various studies indicate that nuclear energy has one of the lowest fatality rates per unit of energy produced compared to other energy sources, including coal, oil, and even some renewables when accounting for manufacturing and installation risks. Improved reactor designs and safety regulations continue to enhance the safety profile of nuclear power.
What About Nuclear Waste?
Nuclear waste management is another key consideration. Nuclear power generates radioactive waste, which requires careful handling and long-term storage. The statement that nuclear waste is an insurmountable problem is not entirely accurate.
While the long-term disposal of nuclear waste remains a challenge, the volume of waste produced is relatively small compared to other industrial wastes. Moreover, significant advancements have been made in waste management technologies, including the development of advanced reactors that can recycle nuclear waste.
Currently, spent nuclear fuel is often stored in secure facilities, either on-site at reactor locations or at centralized storage facilities. The search for a permanent geological repository continues, with many countries exploring different options for safe and effective long-term storage.
Is Nuclear Energy Economically Viable?
The economic viability of nuclear energy is a complex issue with varying perspectives. The initial construction costs of nuclear power plants are high, but the operating costs are relatively low. The assertion that nuclear energy is always economically uncompetitive is not universally true.
The economic competitiveness of nuclear energy depends on several factors, including government policies, financing costs, and the availability of alternative energy sources. In some regions, nuclear energy can be a cost-effective option, particularly when considering its long operational lifespan and low fuel costs. Government subsidies and carbon pricing policies can also significantly impact the economic viability of nuclear power.
Nuclear Energy and Energy Independence
Energy independence is a growing concern for many nations. Nuclear energy can contribute to energy independence by reducing reliance on fossil fuel imports. The claim that nuclear energy enhances energy independence holds some truth.
Uranium, the primary fuel for nuclear reactors, is relatively abundant and can be sourced from various countries. By diversifying their energy mix and reducing dependence on volatile fossil fuel markets, countries can enhance their energy security and stability.
The World Nuclear Association emphasizes the role of nuclear energy in achieving a secure, clean, and affordable energy future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many common statements about nuclear energy require careful evaluation. While nuclear energy has inherent risks and challenges, it also offers significant benefits, including low carbon emissions, high energy density, and contribution to energy independence.
A balanced approach is essential, acknowledging both the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy. Further research, technological advancements, and international cooperation are crucial for ensuring the safe, secure, and sustainable use of nuclear power in the future energy mix.




![Which Of The Following Statements About Nuclear Energy Is True [Solved] Which of the following statement/(s) is/are true with regard](https://storage.googleapis.com/tb-img/production/21/06/nuclear_fuel_cycle112.png)