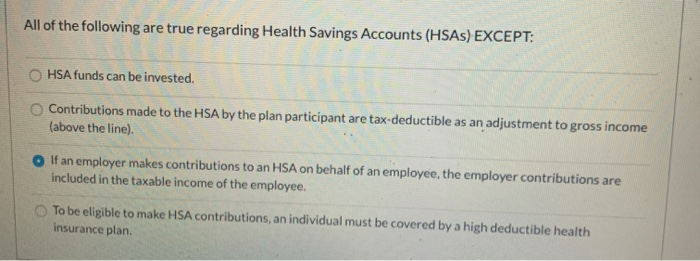
Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Health Insurance

The American healthcare landscape is a minefield of complexities, and navigating health insurance is often the most daunting part. Misinformation abounds, leading to confusion, financial strain, and potentially detrimental health outcomes. Understanding the fundamental truths about health insurance is not just beneficial; it's crucial for ensuring access to quality care and protecting your financial well-being.
This article aims to dissect common misconceptions and illuminate the realities of health insurance. We will explore various aspects, from plan types and coverage options to costs, regulations, and the future of the industry. The goal is to provide clarity and empower readers to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Understanding the Basics of Health Insurance
Health insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company. You pay a premium, and the insurer agrees to pay a portion of your medical expenses. There are various types of plans, each with its own set of rules and benefits.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your care. You usually need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist. HMOs often have lower premiums but less flexibility.
PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer more flexibility, allowing you to see specialists without a referral. However, premiums are generally higher than HMOs. You'll also pay less if you stay within the plan's network of providers.
EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations) are similar to HMOs in that you typically need to stay within the network to receive coverage. However, they don't usually require you to choose a PCP or get referrals.
POS (Point of Service) plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. You typically need a PCP and referrals, but you have the option to go out-of-network for care, although at a higher cost.
Debunking Common Myths About Health Insurance
A pervasive myth is that all health insurance plans are created equal. This is demonstrably false. Plans vary significantly in coverage, costs, and provider networks.
Another misconception is that cheaper plans are always better. While a lower premium might seem appealing, these plans often have higher deductibles, copays, and coinsurance, leading to significant out-of-pocket expenses when you need care.
It's also untrue that pre-existing conditions are no longer a factor in obtaining health insurance. While the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurers from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions, certain short-term plans may not offer the same protections. Also, some grandfathered plans may not fully comply with ACA provisions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plan
When selecting a health insurance plan, consider your individual healthcare needs. How often do you typically see a doctor? Do you have any chronic conditions that require ongoing treatment?
Assess your risk tolerance. Are you comfortable with a higher deductible and lower premium, or would you prefer a lower deductible and higher premium? Consider also your typical annual spending on healthcare and whether you can afford to pay potentially high out-of-pocket cost.
Carefully review the plan's formulary, which is the list of covered prescription drugs. Ensure that your medications are included and understand the cost-sharing arrangements.
The Role of the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The ACA has significantly impacted the health insurance landscape. It expanded access to coverage, prohibited discrimination based on pre-existing conditions, and established minimum essential benefits.
The ACA also created health insurance marketplaces where individuals and families can purchase subsidized coverage. These marketplaces offer a variety of plans from different insurers, making it easier to compare options.
The ACA remains a subject of political debate, and its future is uncertain. However, its core provisions have had a lasting impact on access to healthcare in the United States.
Understanding Costs: Premiums, Deductibles, and More
Premiums are the monthly payments you make to maintain your health insurance coverage. These are generally fixed costs, but can vary greatly between plans.
The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance company starts to pay for covered services. It's important to choose a plan with a deductible you can afford. Usually plans with higher deductibles have lower premiums.
Copays are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor's visits or prescription drugs. Coinsurance is the percentage of the cost of covered services that you pay after you've met your deductible.
"Understanding these cost-sharing arrangements is critical for budgeting for healthcare expenses," says Dr. Emily Carter, a health policy expert at the National Institutes of Health.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Health Insurance
The health insurance landscape is constantly evolving. Technological advancements, policy changes, and demographic shifts are all shaping the future of the industry.
One trend is the increasing adoption of value-based care models. These models focus on improving patient outcomes and reducing costs by incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality, efficient care.
Another trend is the rise of consumer-driven healthcare. Individuals are becoming more engaged in their healthcare decisions and demanding greater transparency and control over their costs.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of health insurance requires a thorough understanding of plan types, costs, and regulations. By debunking common myths and providing clear, accurate information, this article aims to empower readers to make informed decisions and secure the healthcare coverage they need. Continuous learning and staying informed about industry changes are vital for managing healthcare effectively.