Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Touch

In an era dominated by digital interactions, a resurgence of interest in the fundamental role of touch is emerging across diverse fields, from neuroscience to social psychology. A central question fueling this inquiry revolves around the myriad benefits and complexities of tactile interaction.
This article delves into the core understanding of touch, addressing a fundamental question: Which of the following statements is true of touch?
Understanding this is crucial not only for scientists and healthcare professionals, but also for educators, policymakers, and individuals navigating an increasingly disconnected world.
The Science of Touch: Beyond Simple Contact
Touch is not merely a sensation; it's a complex system that involves a wide array of sensory receptors in the skin. These receptors detect pressure, temperature, pain, and texture. They relay this information through the nervous system to the brain.
This sophisticated process allows us to perceive the world in nuanced ways, impacting our emotional well-being, social interactions, and cognitive development.
Key Functions and Characteristics of Touch
Several statements capture crucial aspects of touch. To determine which statement is true, let's examine some key considerations.
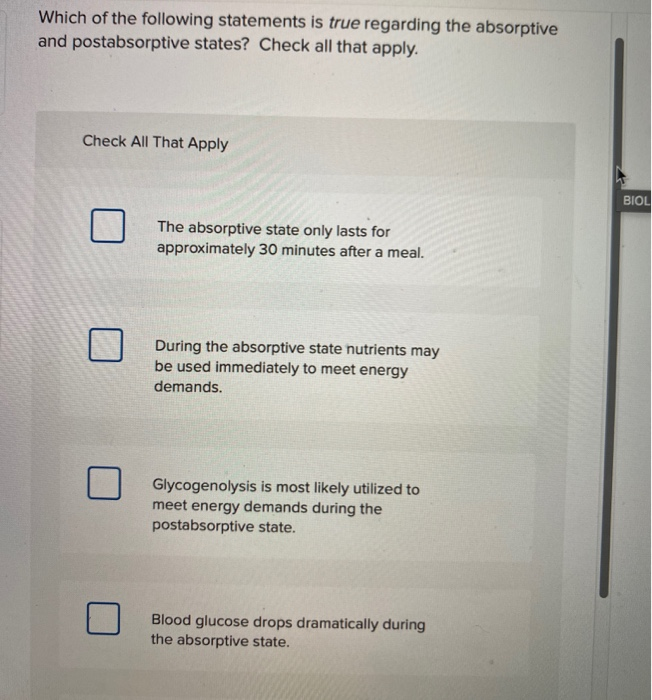
Touch is essential for infant development. Studies have shown that physical contact, such as skin-to-skin care, is vital for newborns. It promotes bonding, regulates their heart rate and breathing, and supports healthy growth.
"Touch is the first language of love," says Dr. Tiffany Field, director of the Touch Research Institute at the University of Miami.
Touch can influence our emotional state. Research consistently demonstrates the impact of touch on reducing stress and anxiety. A comforting touch can trigger the release of oxytocin. This is often called the "cuddle hormone," promoting feelings of trust and relaxation.
Touch perception varies across individuals. Factors such as age, gender, and cultural background can affect how we experience touch. Some individuals may be more sensitive to certain types of touch than others, and cultural norms dictate the appropriateness of touch in different contexts.
Touch plays a crucial role in social bonding. Physical contact helps us form and maintain relationships. Handshakes, hugs, and other forms of touch signal connection and intimacy.
Touch is not simply a passive process. It’s an active exploration of our environment. We use touch to identify objects, navigate spaces, and learn about the world around us.
Evaluating the Truth: A Comprehensive View
Considering these factors, it becomes clear that multiple statements about touch can be true. There is no single answer; instead, a more holistic understanding is required.
A true statement about touch would likely encompass its multifaceted nature. It should acknowledge its importance in development, emotional regulation, social interaction, and environmental exploration. It should also recognize individual differences in touch perception.
Therefore, rather than seeking a singular "true" statement, it’s more accurate to recognize that touch is a complex and dynamic sense. It contributes to our overall well-being in numerous ways.
The Implications of Understanding Touch
The deeper understanding of touch has profound implications across various sectors.
In healthcare, it can inform therapeutic interventions for infants, individuals with autism spectrum disorder, and those suffering from chronic pain. In education, it can guide the creation of more supportive and engaging learning environments. Dr. David Linden, a neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins University, emphasizes the need for more research on the therapeutic applications of touch.
In social policy, recognizing the importance of touch can lead to the development of programs that promote social connection and reduce loneliness. This is particularly relevant in an increasingly isolated society. Furthermore, it impacts our understanding of the ethics of touch, particularly in sensitive settings such as education and healthcare.
Moving Forward: Research and Application
Continued research into the neuroscience and psychology of touch is essential. This includes exploring the role of touch in different cultural contexts. It is also vital to examine the impact of technology on our tactile experiences.
By embracing a more nuanced understanding of touch, we can create environments and practices that foster human connection and well-being. This ensures that the power of touch is harnessed for positive social impact.
Ultimately, appreciating the complexity of touch allows us to better understand ourselves. It enriches our relationships, and navigates the world around us with greater awareness and empathy.