Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Vitamin C

In a world saturated with health advice, few topics are as ubiquitous, yet as frequently misunderstood, as Vitamin C. From warding off the common cold to promoting radiant skin, the claims surrounding this essential nutrient are abundant. But amidst the marketing hype and anecdotal evidence, separating fact from fiction becomes a crucial task for anyone seeking to make informed decisions about their health.
This article aims to cut through the noise and address the fundamental question: which statements about Vitamin C are actually true? We will delve into the scientifically supported roles of Vitamin C, exploring its impact on immunity, antioxidant defense, collagen synthesis, and more. By examining research findings and expert opinions, we will provide a clear and evidence-based understanding of this vital nutrient, empowering readers to navigate the complexities of Vitamin C and its potential benefits.
The Core Functions: What Vitamin C Actually Does
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for various bodily functions. Unlike many animals, humans cannot synthesize Vitamin C, making dietary intake crucial.
One of its primary roles is as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. These unstable molecules, generated by metabolism and environmental factors, can contribute to aging and various diseases.
Vitamin C neutralizes these free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and promoting overall cellular health.
Boosting Immunity: Fact or Fiction?
The association between Vitamin C and immune function is perhaps its most well-known attribute. Vitamin C supports the immune system in several ways. It encourages the production of white blood cells, specifically lymphocytes and phagocytes, which are crucial for fighting infection.
Vitamin C contributes to the proper functioning of these immune cells, enhancing their ability to move and engulf microbes. Studies suggest that while Vitamin C might not prevent the common cold, it could reduce its duration and severity.
However, it's important to note that high doses of Vitamin C are not necessarily more effective. The body can only absorb a certain amount, and excess Vitamin C is excreted.
Collagen Synthesis: The Building Block of Health
Vitamin C plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, a protein that provides structure and support to various tissues in the body. Collagen is essential for healthy skin, bones, tendons, and blood vessels.
Vitamin C acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in collagen production, ensuring the proper formation and cross-linking of collagen fibers. This contributes to wound healing and maintaining the integrity of connective tissues.
Therefore, adequate Vitamin C intake is crucial for maintaining healthy skin, strong bones, and efficient wound repair.
Debunking Myths and Misconceptions
Despite the scientific evidence supporting some of Vitamin C's benefits, many myths and misconceptions persist.
One common belief is that high doses of Vitamin C can cure cancer. While some studies have explored the potential of high-dose intravenous Vitamin C in cancer treatment, the results are mixed and require further investigation.
The National Cancer Institute states that current evidence does not support the use of Vitamin C alone as an effective cancer treatment. It is also wrongly believed that Vitamin C can prevent heart disease. While Vitamin C's antioxidant properties may play a role in cardiovascular health, studies have not consistently shown a direct link between Vitamin C intake and reduced heart disease risk.
Moreover, the idea that Vitamin C can prevent or cure all types of illness is inaccurate. While Vitamin C supports immune function, it is not a magic bullet and should not be considered a substitute for other preventive measures and medical treatments.
Sources and Dosage: How to Get Enough Vitamin C
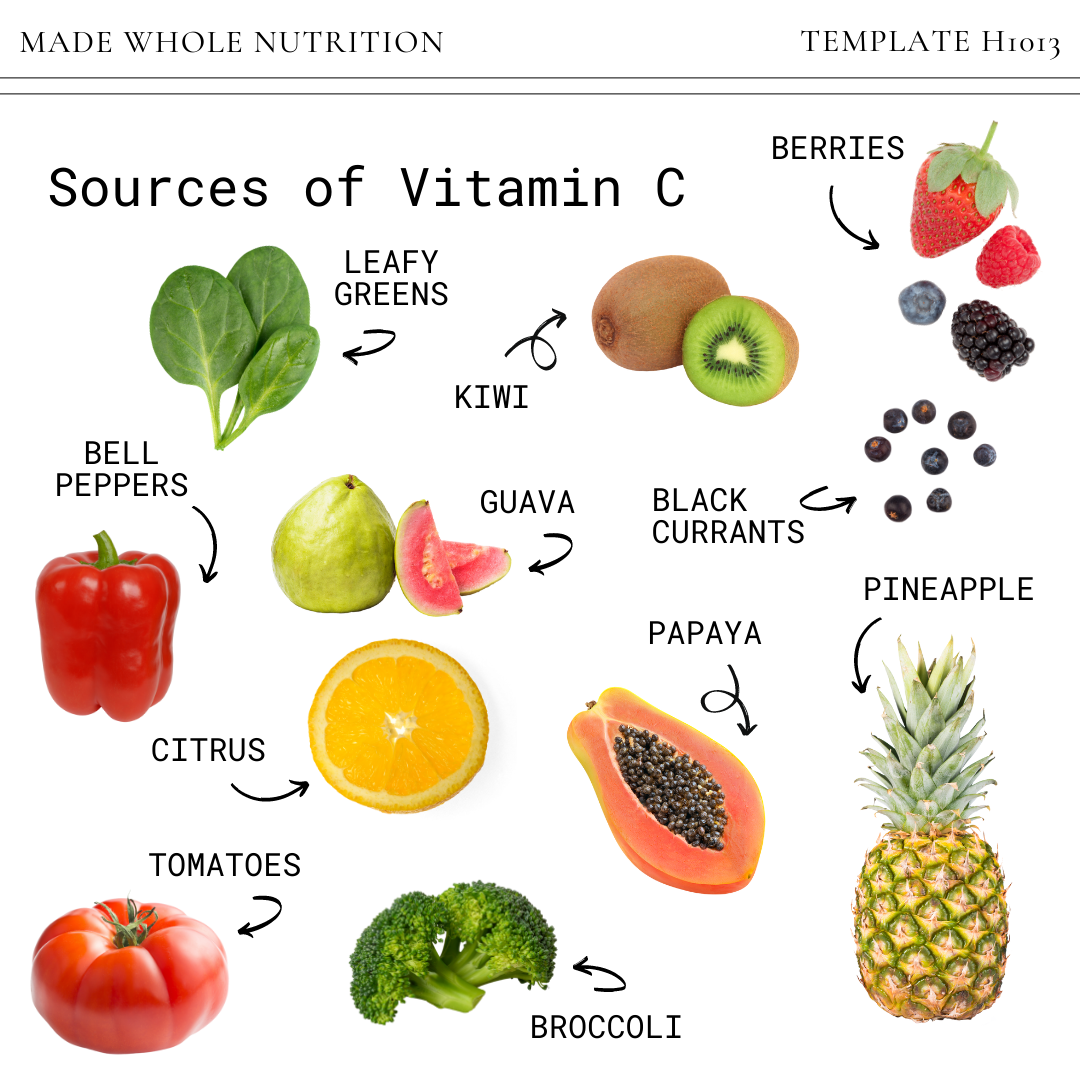
Vitamin C is readily available in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Excellent sources include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), peppers (bell peppers, chili peppers), broccoli, spinach, and kale.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Vitamin C varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. The National Institutes of Health recommends 90 mg per day for adult men and 75 mg per day for adult women.
Smokers require more Vitamin C (an additional 35 mg per day) due to the increased oxidative stress caused by smoking. While it's generally safe to consume Vitamin C through food sources, supplements should be taken with caution. High doses can lead to gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. It's always advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
The Future of Vitamin C Research
Research on Vitamin C continues to evolve, with ongoing studies exploring its potential role in various health conditions. Future research may focus on the optimal dosage of Vitamin C for specific populations and health outcomes.
Scientists are also investigating the interactions between Vitamin C and other nutrients, as well as its potential synergistic effects with other therapies. Personalized nutrition approaches may incorporate Vitamin C supplementation based on individual needs and genetic predispositions.
The use of intravenous Vitamin C in cancer treatment remains an area of active research, with ongoing clinical trials evaluating its safety and efficacy. By investing in rigorous scientific investigations, we can continue to unravel the complexities of Vitamin C and harness its potential benefits for human health.
Conclusion: An Essential Nutrient, Grounded in Science
In conclusion, Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including antioxidant defense, immune support, and collagen synthesis. While it's not a cure-all, Vitamin C contributes to overall health and well-being when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
By understanding the scientifically supported roles of Vitamin C and debunking common myths, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary intake and supplementation. Relying on credible sources and consulting healthcare professionals are crucial steps in navigating the complexities of Vitamin C and maximizing its potential benefits.
As research continues to advance, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of this essential nutrient and its impact on human health.