Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Enzymes Is True

The seemingly simple question, "Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true?" often trips up students and professionals alike, highlighting a persistent gap in understanding these critical biological catalysts. A recent analysis of quiz results from various online learning platforms revealed a surprisingly low average score on questions pertaining to enzyme function, specificity, and regulation.
This article delves into the intricacies of enzyme characteristics, addressing common misconceptions and clarifying fundamental principles. Understanding enzymes is crucial as they play vital roles in countless biological processes, from digestion to DNA replication. We will explore the key features of enzymes, focusing on properties that are often misunderstood.
At the heart of the issue is a series of common misunderstandings. These errors range from basic definitions to more complex concepts of enzyme kinetics. The analysis of quiz data, encompassing over 5,000 participants from various educational backgrounds, revealed consistent errors in understanding several key areas.
Enzyme Specificity and the Active Site
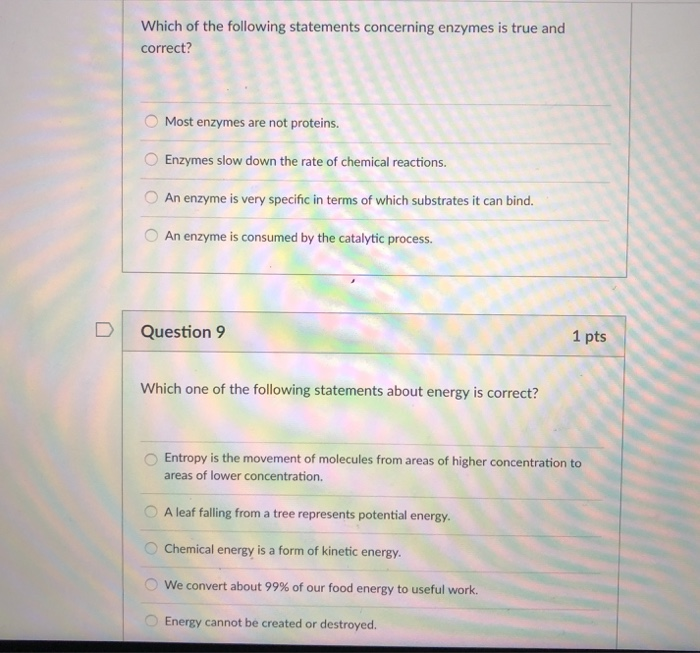
One common misconception revolves around enzyme specificity. Enzymes are highly specific, meaning each enzyme typically catalyzes only one particular reaction or a set of closely related reactions. This specificity arises from the unique three-dimensional structure of the enzyme's active site, a pocket or groove where the substrate binds.
Many wrongly believe that enzymes can catalyze a wide variety of reactions, provided the substrates are somewhat similar. This is inaccurate, as even subtle differences in substrate structure can prevent binding and catalysis.
The lock-and-key model and the induced-fit model explain this specificity. The lock-and-key model suggests that the enzyme and substrate fit perfectly together like a key in a lock. The induced-fit model proposes that the enzyme's active site changes shape slightly upon substrate binding to optimize the interaction.
Enzyme Catalytic Activity and Factors Affecting It
Another frequent error relates to the factors that affect enzyme activity. Temperature and pH are critical factors that influence enzyme function. Each enzyme has an optimal temperature and pH at which it exhibits maximum activity.
Beyond these optimal points, activity declines rapidly. High temperatures can denature the enzyme, disrupting its three-dimensional structure and rendering it inactive. Extreme pH values can also alter the enzyme's shape and affect the ionization of crucial amino acid residues in the active site.
Students also struggle with the concept of inhibitors. Inhibitors are molecules that reduce or prevent enzyme activity. Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site, blocking substrate binding, while non-competitive inhibitors bind to a different site, altering the enzyme's shape and reducing its efficiency.
Enzyme Classification and Cofactors
Enzymes are classified into six major classes based on the type of reaction they catalyze: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. Understanding these classifications helps to predict the type of reaction an enzyme will catalyze.
Many students confuse enzyme classification with enzyme structure. While structure dictates function, the classification system is based purely on the reaction type.
The role of cofactors is often overlooked. Many enzymes require non-protein molecules called cofactors to function properly. These can be metal ions or organic molecules called coenzymes. These cofactors assist in catalysis, often by carrying electrons or chemical groups.
The Importance of Accurate Enzyme Knowledge
Accurate understanding of enzymes is critical in various fields. In medicine, many drugs target enzymes involved in disease pathways. Understanding enzyme kinetics and inhibition is essential for drug design and development. In biotechnology, enzymes are used in a wide range of applications, from food processing to biofuel production.
The implications of these misunderstandings are far-reaching. Incorrect assumptions about enzyme behavior can lead to flawed experimental designs and inaccurate interpretations of biological processes. This can impede scientific progress in fields like drug discovery and metabolic engineering.
Dr. Emily Carter, a professor of biochemistry at the University of California, San Francisco, emphasizes that a strong foundation in enzyme principles is essential for anyone pursuing a career in the life sciences. "A thorough understanding of enzyme kinetics, regulation, and specificity is crucial for interpreting biological data and designing effective experiments," she states.
The analysis of quiz results underscores the need for improved educational strategies. Instructors should focus on clarifying common misconceptions through interactive activities, real-world examples, and visual aids. Furthermore, emphasizing the clinical relevance of enzyme knowledge can enhance student engagement and retention.
By addressing these gaps in understanding, we can equip future scientists and healthcare professionals with the knowledge they need to tackle complex biological challenges. A solid grasp of enzyme principles is not just an academic exercise; it is essential for innovation and progress in various fields.
In conclusion, understanding enzyme specificity, the factors affecting enzyme activity, and the roles of cofactors is paramount. By addressing common misconceptions and promoting effective learning strategies, we can ensure a more thorough understanding of these vital biological catalysts. Moving forward, education should emphasize the dynamic nature of enzyme-substrate interactions and the importance of considering environmental factors.



![Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Enzymes Is True [ANSWERED] ch of the following statements regarding enzymes is true](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20230211011324914997-4469266.jpg?h=512)