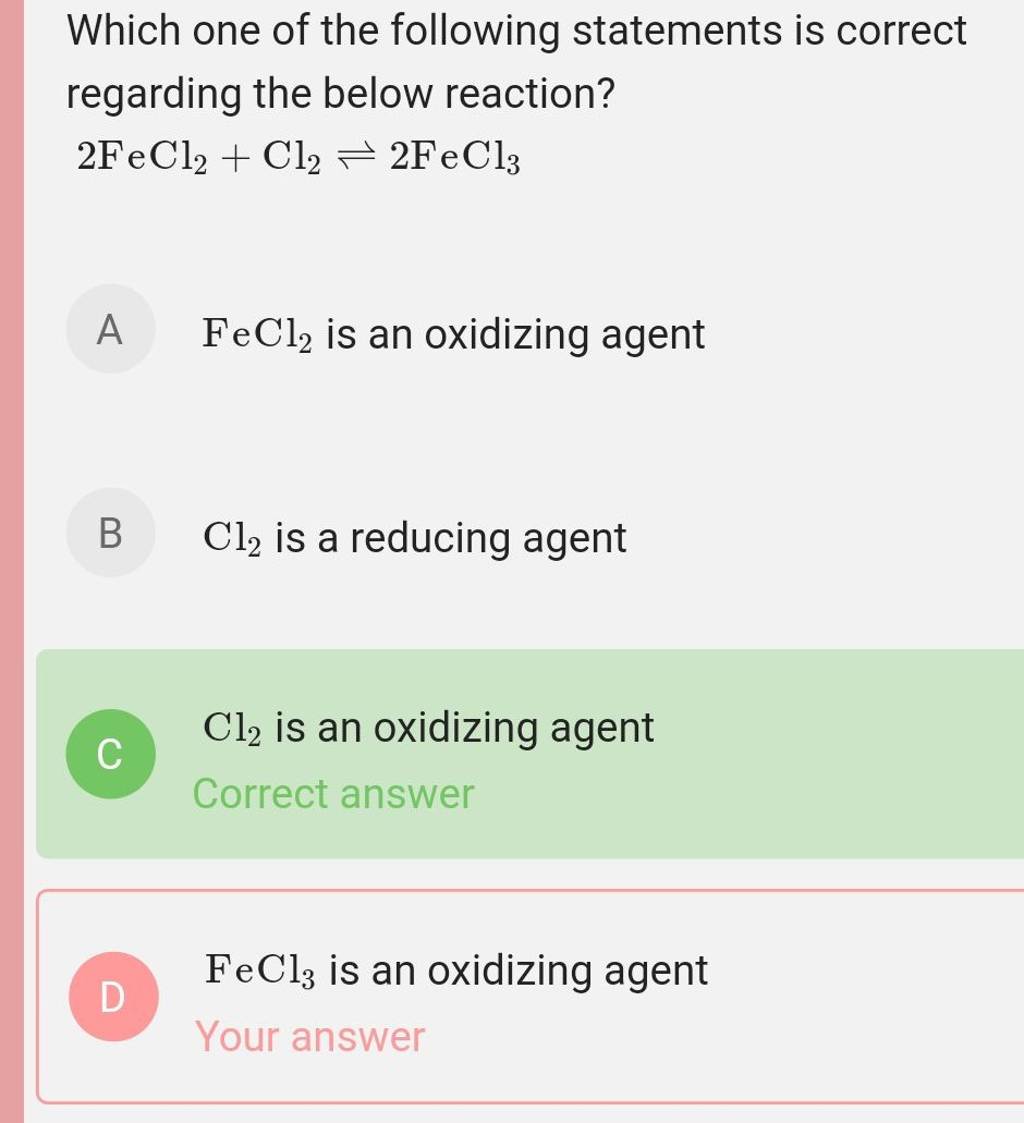
Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Plasma Is Correct

Imagine a crackling bolt of lightning illuminating the night sky, or the mesmerizing glow of a neon sign beckoning you from a bustling city street. These aren't just pretty phenomena; they offer a glimpse into the fascinating world of plasma, the fourth state of matter.
But what exactly *is* plasma? And which of the common perceptions about it are actually true? Let's delve into the heart of this superheated state to separate fact from fiction, revealing the truth about plasma's properties, behavior, and diverse applications in our modern world.
Understanding Plasma: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and Gas
We're all familiar with the three common states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. Plasma, however, is different. It's a state of matter where a gas becomes so energized that its electrons are stripped from their atoms, forming an ionized gas.
This mixture contains ions and free electrons, giving plasma unique properties that set it apart from ordinary gases.
The Ionization Process: Creating Plasma
Creating plasma requires significant energy. Typically, this involves heating a gas to extremely high temperatures, often thousands of degrees Celsius. The heat causes atoms to collide violently, knocking electrons loose.
This process of ionization creates the characteristic mixture of ions and electrons that defines plasma.
Key Properties of Plasma: Why It's Unique
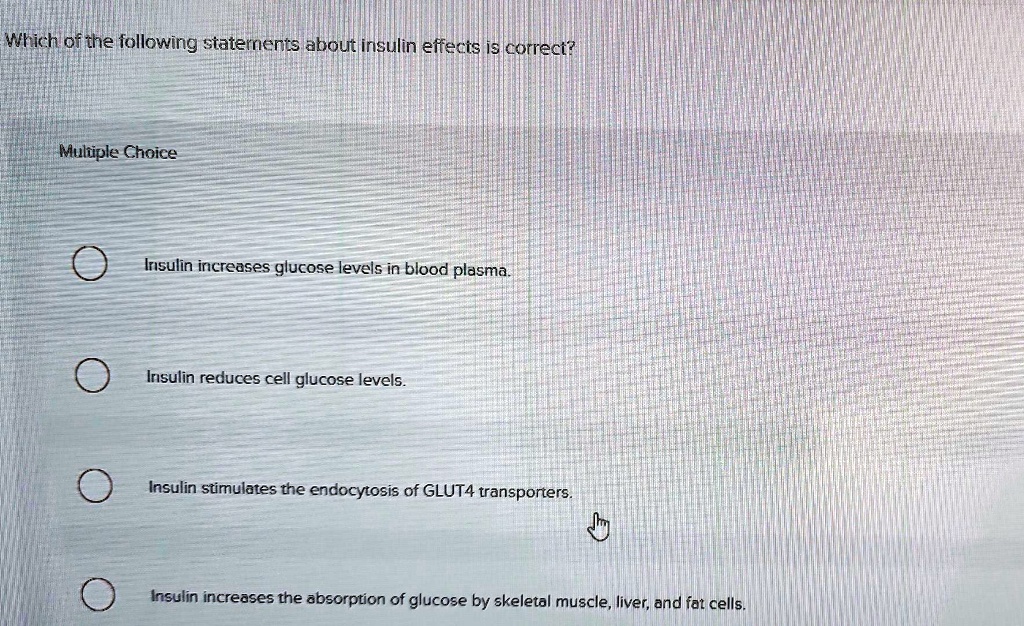
Plasma possesses several key properties that distinguish it from other states of matter. It's a good conductor of electricity, interacts strongly with magnetic fields, and emits electromagnetic radiation, including light. These properties make plasma incredibly versatile for a wide range of applications.
Common Misconceptions About Plasma
Many people have misconceptions about plasma, often associating it solely with exotic technologies or science fiction. Let's debunk some of these myths and focus on verifiable facts. This is particularly important when confronting a question like "Which of the following statements regarding plasma is correct?"
Plasma is Rare: Fact or Fiction?
While we might not encounter it in our everyday lives as often as solids, liquids, or gases, plasma is actually the most abundant state of matter in the universe. Stars, including our sun, are primarily composed of plasma. The solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the sun, is also a form of plasma.
Plasma is Always Hot: A Nuance to Consider
While high temperatures are often associated with plasma creation, it's important to distinguish between different types of plasma. Thermal plasmas, like those found in welding torches or lightning, are indeed extremely hot. However, non-thermal plasmas, used in some industrial applications and medical treatments, can exist at much lower temperatures.
Plasma is Just a Gas: A Fundamental Difference
Although plasma originates from a gas, it's not simply a gas at a higher temperature. The presence of free electrons and ions gives plasma unique electrical and magnetic properties that ordinary gases lack. This fundamental difference defines plasma as a distinct state of matter.
Applications of Plasma Technology: A World of Possibilities
The unique properties of plasma have led to its widespread use in various technological applications. From industrial manufacturing to medical treatments, plasma technology continues to revolutionize various fields. It's important to remember this broad applicability when evaluating statements about plasma.
Industrial Applications: Manufacturing and Beyond
Plasma is used extensively in industrial processes such as surface treatment, etching, and deposition of thin films. These processes are crucial in manufacturing semiconductors, creating durable coatings, and modifying material properties.
Medical Applications: Healing and Sterilization
Plasma is also finding increasing applications in medicine. Cold plasma is used for sterilization of medical instruments and wound healing, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods.
Energy and Environmental Applications: Clean and Efficient
Plasma technologies are being explored for energy production, waste treatment, and pollution control. Plasma gasification can convert waste into energy, while plasma torches can destroy hazardous materials.
Everyday Applications: From TVs to Lighting
We encounter plasma technology in everyday life more often than we realize. Plasma TVs, although largely replaced by other technologies, utilized plasma to create images. Fluorescent lights also rely on plasma to generate light.
Identifying Correct Statements About Plasma
Given our understanding of plasma, we can now confidently assess the validity of statements about it. A correct statement would accurately reflect plasma's composition, properties, behavior, or applications, and could be verifiable via credible sources. The most accurate answer will be informed by both theoretical understanding and observed phenomena.
A statement that "Plasma is always extremely hot" would be incorrect due to the existence of non-thermal plasmas. A statement that "Plasma does not interact with magnetic fields" would be false. The key lies in understanding plasma's core characteristics.
The Future of Plasma Research
Research into plasma science and technology continues to advance, unlocking new possibilities and applications. Scientists are exploring new ways to generate and control plasma, as well as developing innovative uses for this versatile state of matter.
As our understanding of plasma deepens, its potential to address global challenges in energy, medicine, and manufacturing becomes increasingly apparent.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Power of Plasma
Plasma, often overlooked in our daily lives, is a fundamental and incredibly versatile state of matter. From the stars that illuminate the cosmos to the technologies that power our modern world, plasma plays a vital role.
By understanding its properties and applications, we can appreciate the true power and potential of this fascinating phenomenon. It is this knowledge that allows us to discern fact from fiction, and confidently identify correct statements about plasma.
![Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Plasma Is Correct [Solved]: QUESTION 6 Refer to the figure. Which of the follo](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/59c/59caa71e-d773-48e0-8ce1-be3b1f817039/image.jpg)
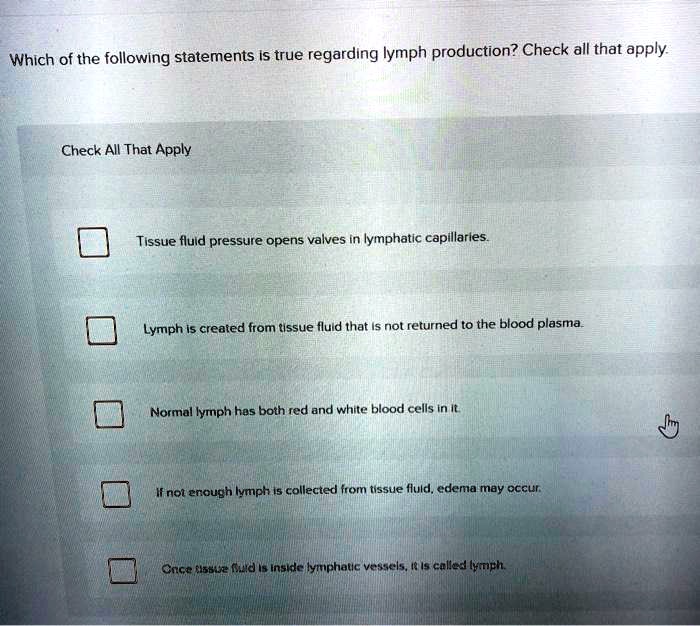




+Which+of+the+following+statements+concerning+unsaturated+fats+is+true..jpg)


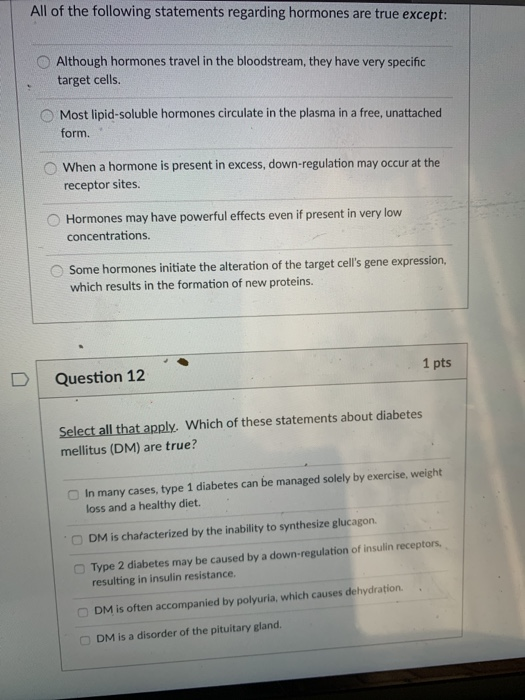
![Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Plasma Is Correct [ANSWERED] 27 Which of the following statements is correct regarding](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20200704172409918628-1835984.jpg?h=512)

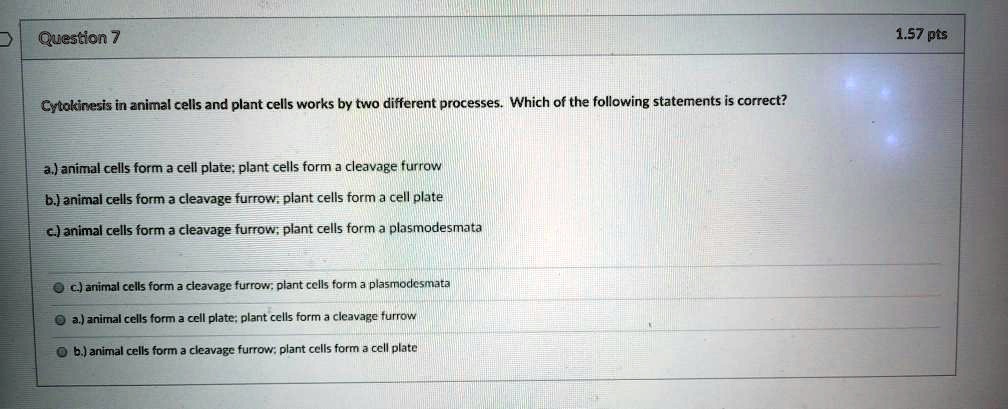
![Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Plasma Is Correct [ANSWERED] All of the following statements are correct regarding - Kunduz](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20211203063233722844-3475341.jpg?h=512)