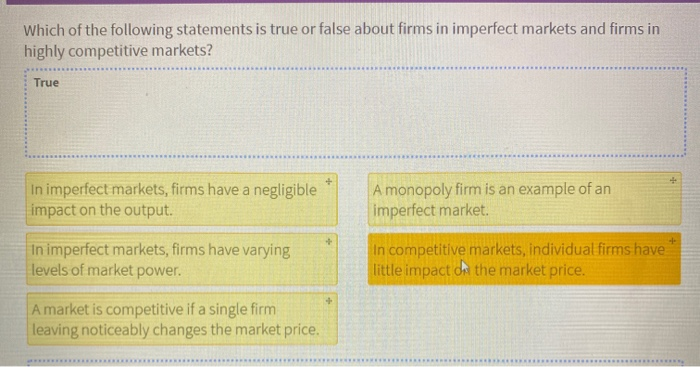
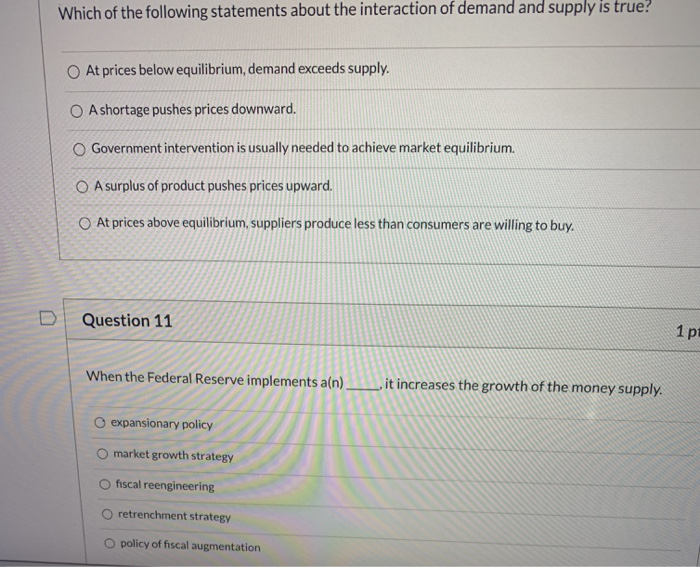
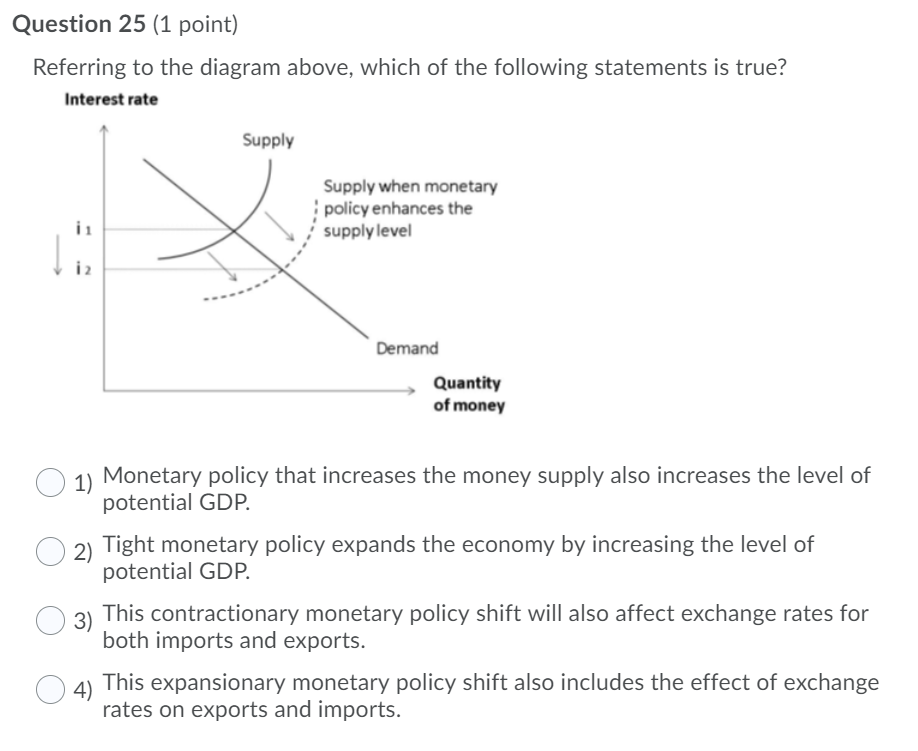
Which Of The Following Statements Relating To Supply Is True
The global economy is a complex interplay of factors, and at its heart lies the fundamental principle of supply. Misunderstandings about supply can lead to flawed policies, inaccurate business decisions, and distorted market expectations. The question, "Which of the following statements relating to supply is true?" is not merely an academic exercise, but a critical inquiry with real-world consequences.
This article aims to dissect the nuances of supply, clarifying common misconceptions and providing a solid understanding of its core principles. We will explore how supply interacts with demand, the factors that influence it, and its broader impact on market dynamics. Through careful analysis of economic data and expert opinions, we will strive to answer the question, "Which of the following statements relating to supply is true?" with clarity and precision.
Understanding the Basics of Supply
In economics, supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price during a specific period. It is crucial to distinguish between supply and the quantity supplied. A change in price only causes a change in the quantity supplied, while a change in any other factor leads to a shift in the entire supply curve.
The law of supply states that, all other things being equal, the quantity supplied of a good or service increases as its price increases. This positive relationship occurs because higher prices incentivize producers to allocate more resources to the production of that good or service, increasing their potential profits.
Factors Influencing Supply
Price is undoubtedly a key determinant of supply, but it is far from the only one. A multitude of other factors, often referred to as non-price determinants of supply, can significantly impact a producer's willingness and ability to supply goods or services.
Cost of Production
The cost of production, including raw materials, labor, energy, and capital, plays a crucial role. An increase in production costs, for example, due to rising energy prices, would decrease supply, shifting the supply curve to the left.
Technology
Technological advancements often lead to increased efficiency and reduced production costs. New technologies can enable firms to produce more goods or services with the same amount of resources, resulting in an increase in supply.
Number of Sellers
The number of sellers in a market directly influences the overall supply. More producers entering the market lead to a greater aggregate supply, while a decrease in the number of sellers reduces the total amount available.
Expectations of Future Prices
Producers' expectations about future prices can influence their current supply decisions. If producers expect prices to rise in the future, they may reduce their current supply, holding back inventory to sell at a higher price later.
Government Policies
Government policies, such as taxes and subsidies, can significantly impact supply. Taxes increase the cost of production, thus decreasing supply. Subsidies, on the other hand, reduce the cost of production and encourage increased supply.
Other Factors
Other factors, such as weather conditions (especially for agricultural products), natural disasters, and political instability, can also disrupt supply chains and affect the availability of goods and services.
Supply vs. Quantity Supplied: A Critical Distinction
A common mistake is confusing supply with quantity supplied. Supply refers to the entire relationship between price and the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer. Quantity supplied refers to the specific amount offered at a given price.
Movement along the supply curve represents a change in the quantity supplied, caused only by a change in price. A shift of the entire supply curve, to the left or right, represents a change in supply, caused by factors other than price.
Statements Relating to Supply: Which is True?
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario where we are presented with several statements related to supply. For example:
- An increase in the price of a good will always increase its supply.
- Supply is the same as quantity supplied.
- A decrease in the cost of raw materials will decrease supply.
- Government subsidies typically lead to an increase in supply.
Based on our understanding of supply principles, we can evaluate each statement.
Statement 1 is false. An increase in the price of a good increases the quantity supplied, not the overall supply. Supply only changes when factors other than price change.
Statement 2 is false. Supply and quantity supplied are distinct concepts, as discussed above.
Statement 3 is false. A decrease in the cost of raw materials will increase supply, as it reduces the cost of production.
Statement 4 is true. Government subsidies reduce the cost of production, thereby encouraging producers to supply more of the good or service.
The Interplay of Supply and Demand
Supply doesn't operate in isolation; it interacts constantly with demand. The interaction of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. When supply exceeds demand, there is a surplus, leading to downward pressure on prices. When demand exceeds supply, there is a shortage, leading to upward pressure on prices.
Understanding the dynamics of both supply and demand is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and investment.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends Affecting Supply
Several future trends are likely to significantly affect supply across various industries. These include:
Technological Disruptions: Continued advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and other technologies will further transform production processes and supply chains.
Climate Change: Increasingly frequent and severe weather events will disrupt agricultural production, supply chains, and infrastructure, creating challenges for maintaining stable supply.
Geopolitical Instability: Political conflicts, trade wars, and other forms of geopolitical instability can disrupt global supply chains and create uncertainty for businesses.
Resource Scarcity: Growing populations and increased consumption will place greater pressure on natural resources, potentially leading to resource scarcity and higher production costs, impacting supply.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of supply is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern economy. The statement "Which of the following statements relating to supply is true?" highlights the need for careful analysis and a clear grasp of economic principles. By considering the factors that influence supply, differentiating between supply and quantity supplied, and understanding the interplay of supply and demand, businesses and policymakers can make more informed decisions and promote economic stability.
Moving forward, anticipating future trends and adapting to changing conditions will be crucial for ensuring stable and resilient supply chains in an increasingly uncertain world. Staying informed and continuously refining our understanding of supply is paramount for economic success.