Which Of The Following Will Increase During Strenuous Muscular Activity
During strenuous muscular activity, several physiological changes occur within the body to meet the increased energy demands. Understanding these changes is crucial for optimizing athletic performance, managing medical conditions, and comprehending the body's response to physical stress.
This article examines the various factors that increase during intense exercise, drawing upon scientific research and expert opinions. It sheds light on the complex interplay of physiological processes that enable the body to function under demanding conditions.
The Primary Players in Physiological Upregulation
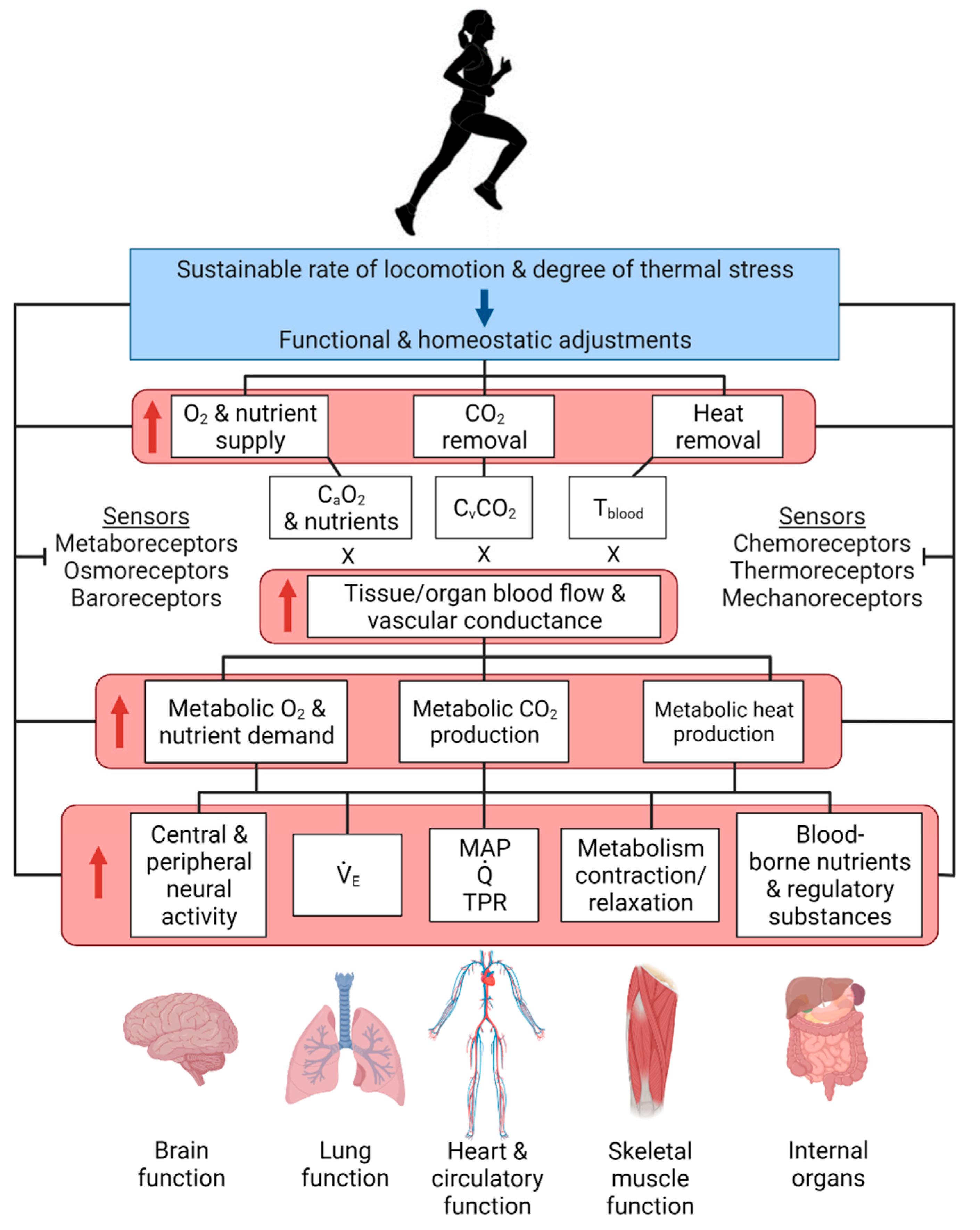
Several key factors experience a notable increase during strenuous muscular activity. Among these, increased heart rate, respiration rate, body temperature, and blood lactate levels are perhaps the most significant.
These changes are essential for providing working muscles with the necessary oxygen and energy, while also removing waste products.
Heart Rate: The Engine's Throttle
The heart rate, measured in beats per minute (bpm), is a direct indicator of cardiovascular exertion. During strenuous exercise, the heart pumps blood more rapidly to deliver oxygen and nutrients to active muscles.
According to the American Heart Association, a person's maximum heart rate can be estimated by subtracting their age from 220. The increase in heart rate is proportional to the intensity of the muscular activity.
This response is mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, which releases hormones like adrenaline to accelerate the heart's contractions.
Respiration Rate: The Oxygen Pipeline
Respiration rate, or breathing rate, increases dramatically during intense exercise. This is driven by the body's need to take in more oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
Muscles use oxygen to generate energy through cellular respiration, producing carbon dioxide as a byproduct. The body responds by increasing the depth and frequency of breaths.
The American Lung Association states that a normal resting respiration rate for adults is between 12 and 20 breaths per minute, but this number can significantly increase during physical exertion.
Body Temperature: The Heat is On
Strenuous muscular activity generates heat as a byproduct of energy production. Consequently, body temperature rises during exercise.
The body regulates its temperature through mechanisms such as sweating and vasodilation (widening of blood vessels). Sweating helps dissipate heat through evaporation, while vasodilation allows more blood to flow to the skin's surface, promoting heat loss.
However, if the rate of heat production exceeds the rate of heat dissipation, body temperature can rise to dangerous levels, leading to heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
Blood Lactate Levels: The Anaerobic Indicator
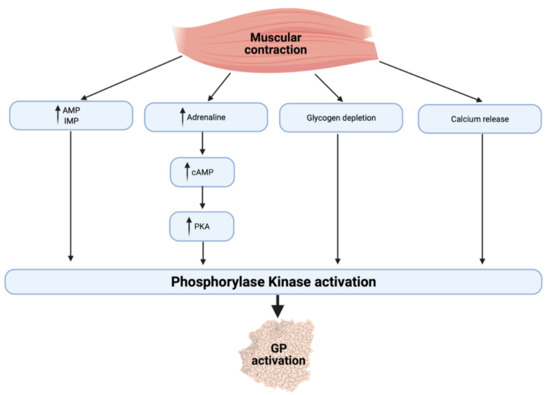
When muscles work intensely, they may not receive enough oxygen to meet their energy demands. This leads to anaerobic metabolism, which produces lactate as a byproduct.
Blood lactate levels increase during strenuous muscular activity, particularly when the exercise intensity exceeds the individual's aerobic threshold. This threshold represents the point at which the body can no longer clear lactate from the blood as quickly as it is produced.
Lactate was once thought to cause muscle fatigue, but it is now recognized as a valuable fuel source for muscles and other tissues.
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to the primary factors mentioned above, other physiological variables also increase during strenuous muscular activity. These include blood pressure, ventilation rate, and hormone levels.
Blood pressure increases to facilitate blood flow to working muscles. Ventilation rate (the volume of air inhaled and exhaled per minute) increases to meet the body's oxygen demands. Various hormones, such as epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol, are released to mobilize energy stores and support the stress response.
Furthermore, muscle glycogen breakdown accelerates to provide glucose for energy production. Oxygen consumption increases dramatically to fuel the metabolic processes required for muscle contraction.
Implications and Considerations
Understanding the physiological changes that occur during strenuous muscular activity is important for several reasons. It can inform training programs, help diagnose and manage medical conditions, and improve overall health and well-being.
For athletes, monitoring heart rate, respiration rate, and lactate levels can help optimize training intensity and prevent overtraining. For individuals with cardiovascular disease, understanding the effects of exercise on blood pressure and heart rate is crucial for safe participation in physical activity.
Healthcare professionals can use this knowledge to assess patients' fitness levels, identify potential risks associated with exercise, and develop personalized exercise recommendations.
"The body's response to strenuous muscular activity is a complex and finely tuned process. By understanding these physiological adaptations, we can better optimize our health and performance." - Dr. Emily Carter, Sports Medicine Physician.
In conclusion, numerous physiological factors increase during strenuous muscular activity, reflecting the body's remarkable ability to adapt to demanding conditions. Heart rate, respiration rate, body temperature, and blood lactate levels are among the most prominent, each playing a crucial role in supporting muscle function and maintaining homeostasis.
By understanding these changes, we can gain valuable insights into the body's response to physical stress and improve our approach to exercise, health, and well-being.