Which Statement About Circadian Rhythm Is Accurate

Confusion reigns as public health officials grapple with widespread misunderstandings about circadian rhythms. A recent survey reveals alarming inaccuracies in public knowledge, prompting urgent calls for clearer educational initiatives.
The accuracy of statements about circadian rhythms is under intense scrutiny as misinterpretations impact sleep hygiene, health decisions, and overall well-being. This article breaks down the facts, dispels myths, and highlights what you need to know now.
The Core Misconception: What is Actually True?
A common misconception is that circadian rhythms are solely dictated by the 24-hour day. This is false.
While the Earth's rotation is a significant influence, our internal clock is primarily endogenous, meaning it's generated within the body.
Environmental cues, known as zeitgebers, like sunlight and meal times, synchronize this internal clock to the external world.
Key Facts About Circadian Rhythms: Setting the Record Straight
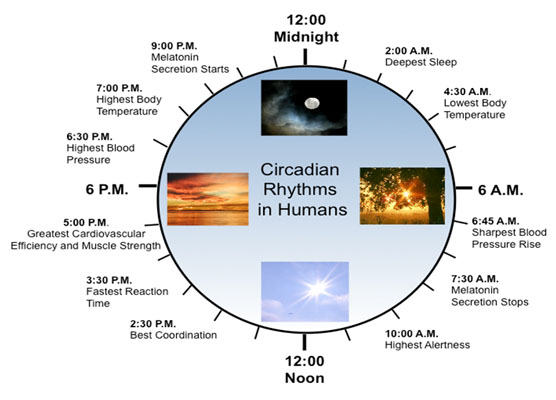
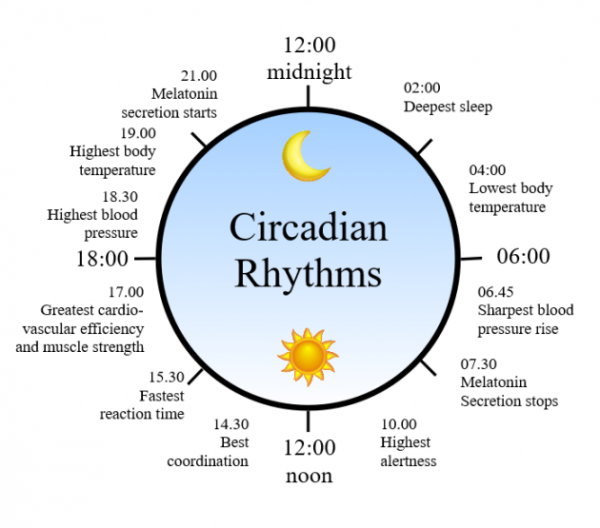
Circadian rhythms aren't just about sleep. They regulate a vast array of physiological processes.
These include hormone release, body temperature, blood pressure, and even gene expression.
Disruptions to these rhythms, caused by shift work, jet lag, or inconsistent sleep schedules, can have serious health consequences.
The Master Clock: Location and Function
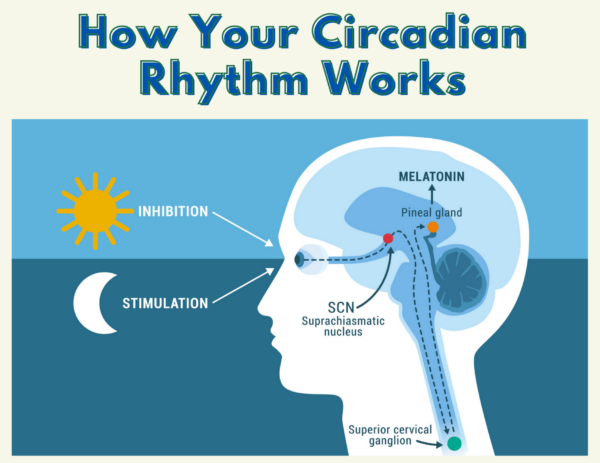
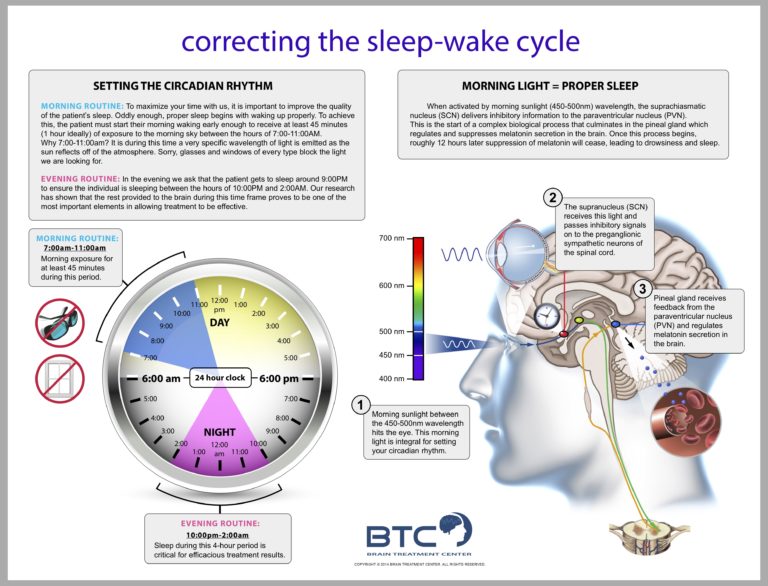
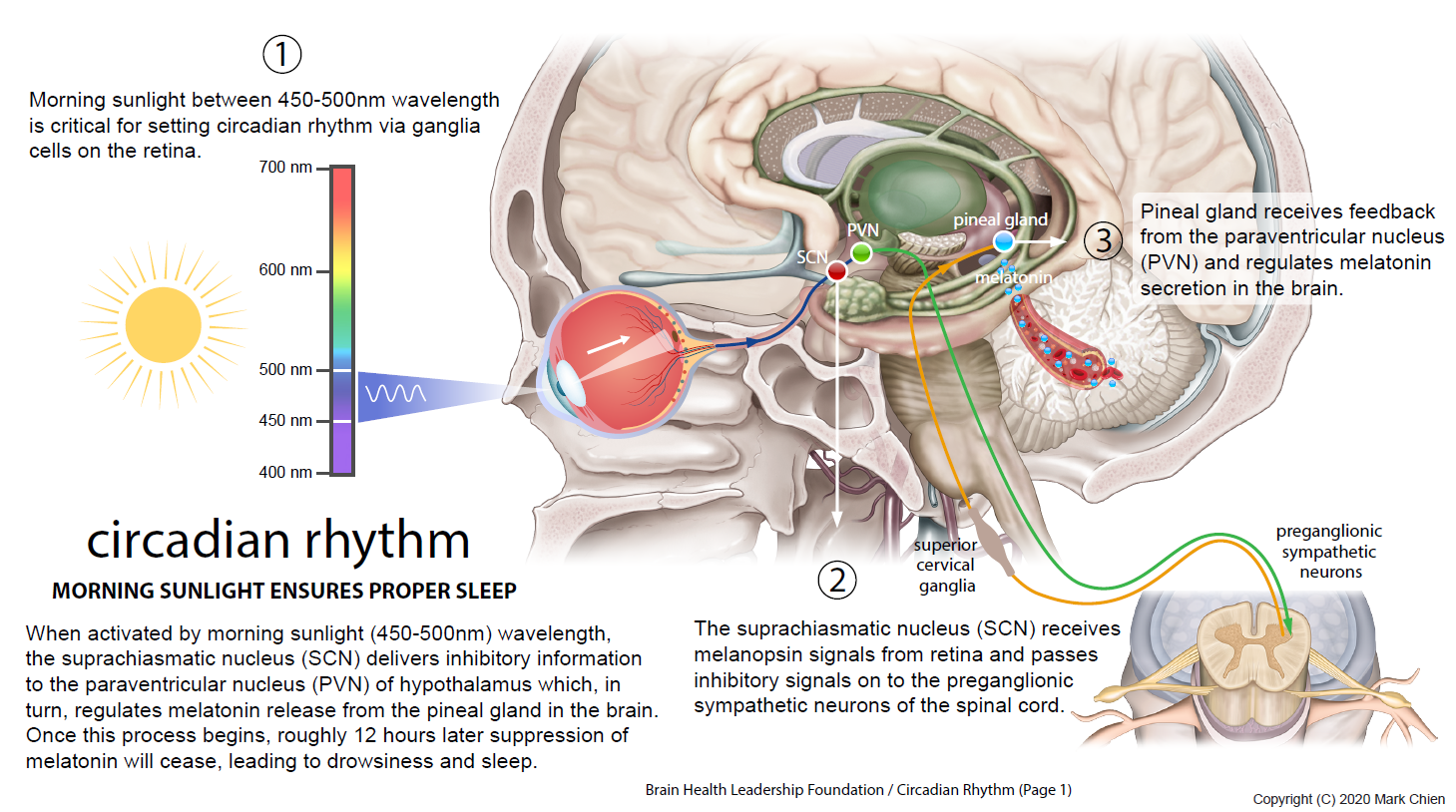
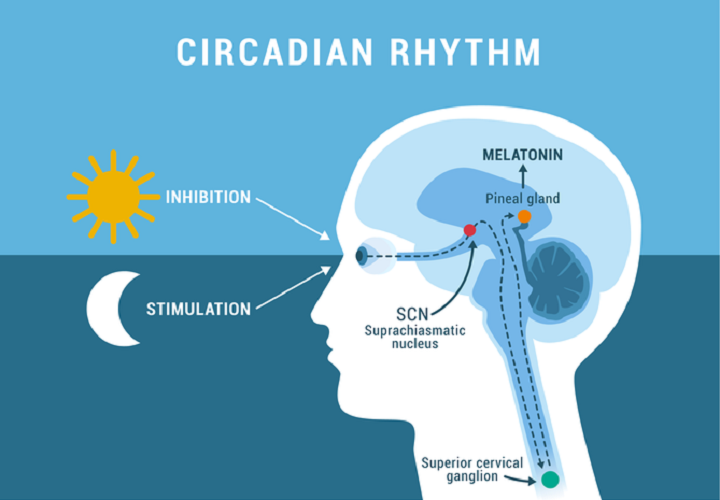
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), located in the hypothalamus of the brain, is the master circadian pacemaker.
The SCN receives light information from the retina via the retinohypothalamic tract.
This light input allows the SCN to synchronize the body's internal clock with the external environment.
Light's Crucial Role: More Than Just Seeing
Light exposure, particularly blue light, is a powerful regulator of the circadian rhythm.
Exposure to blue light in the evening can suppress melatonin production, delaying sleep onset.
Conversely, morning light exposure helps to advance the circadian rhythm, promoting wakefulness and alertness.
Melatonin: The Sleep Hormone, But Not the Whole Story
Melatonin is often mistakenly considered the "sleep hormone" and the sole determinant of sleep.
While melatonin plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles, it is only one piece of the puzzle.
Other neurotransmitters and hormones, such as cortisol and adenosine, also contribute to sleep regulation.
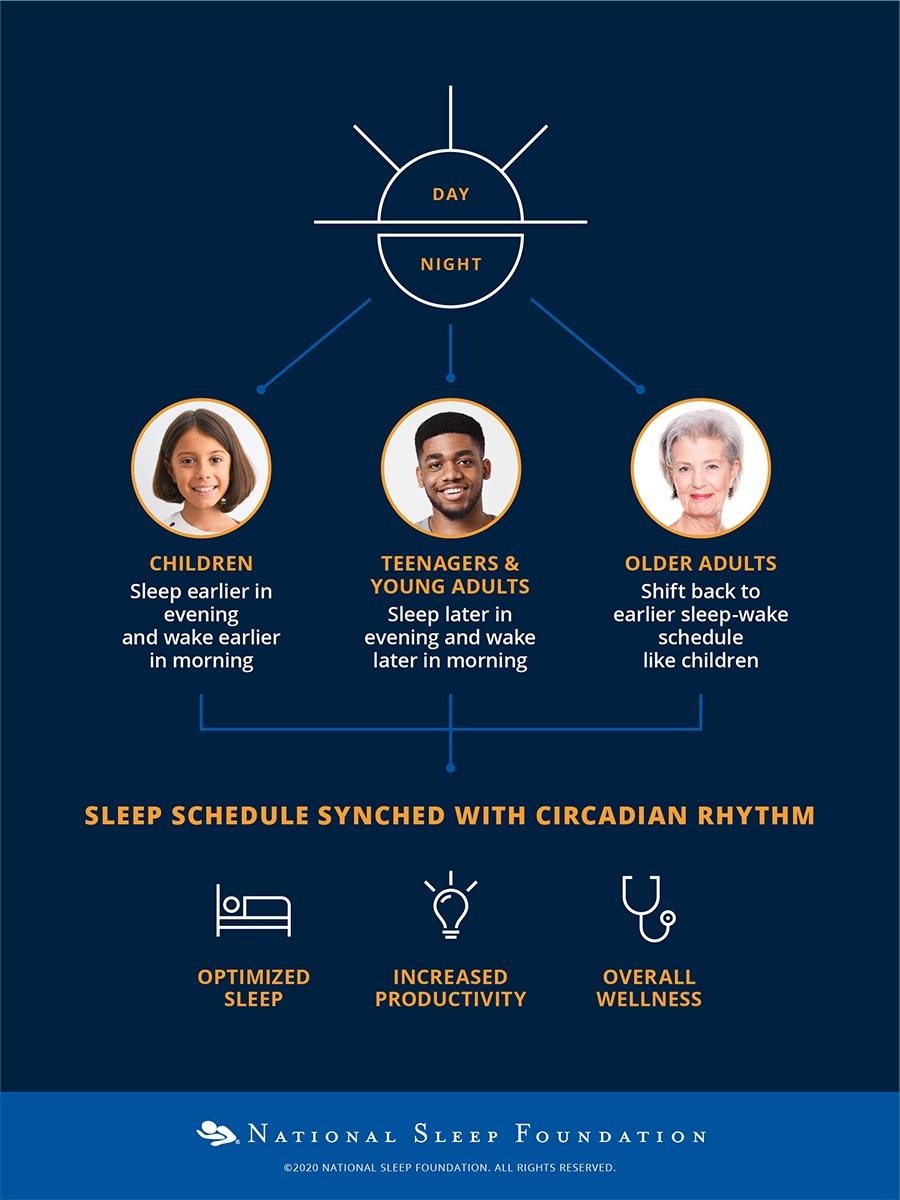
Individual Differences: Chronotypes and Their Impact
Not everyone operates on the same circadian schedule. Chronotypes, often referred to as "morning larks" or "night owls," describe individual differences in sleep timing preferences.
These differences are partly genetically determined, influencing optimal times for sleep, wakefulness, and cognitive performance.
Understanding your chronotype can help you optimize your daily schedule to align with your natural rhythms.
Consequences of Disrupted Rhythms: Health Risks and Real-World Impact
Chronic disruption of circadian rhythms has been linked to a range of health problems.
These include increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
Shift workers, who frequently work irregular hours, are particularly vulnerable to these health risks.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions: What's Next?
Researchers are actively investigating the intricate mechanisms of circadian rhythms.
They are exploring potential therapeutic interventions for circadian rhythm disorders.
Future research aims to develop personalized strategies for optimizing sleep and health based on individual circadian profiles. Stay tuned for updates.

![Which Statement About Circadian Rhythm Is Accurate Circadian Rhythm: What is it? [Plus 6 Ways to Fix Yours]– Carex](https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0240/6504/8681/t/34/assets/circadian_rhythm_diagram01-1647270124517_1200x.jpg?v=1647270126)



+–+Alan’s+Answer.jpg)