Which Statement Is Consistent With The Law Of Demand

Imagine strolling through a bustling farmer's market on a sunny Saturday morning. The air is filled with the aroma of fresh produce, and colorful displays tempt you at every turn. You notice a vendor selling juicy red strawberries. As the day wears on, and the sun climbs higher, the vendor drops the price of the strawberries. Shoppers, who were hesitant earlier, now eagerly line up, baskets in hand, ready to snag a bargain.
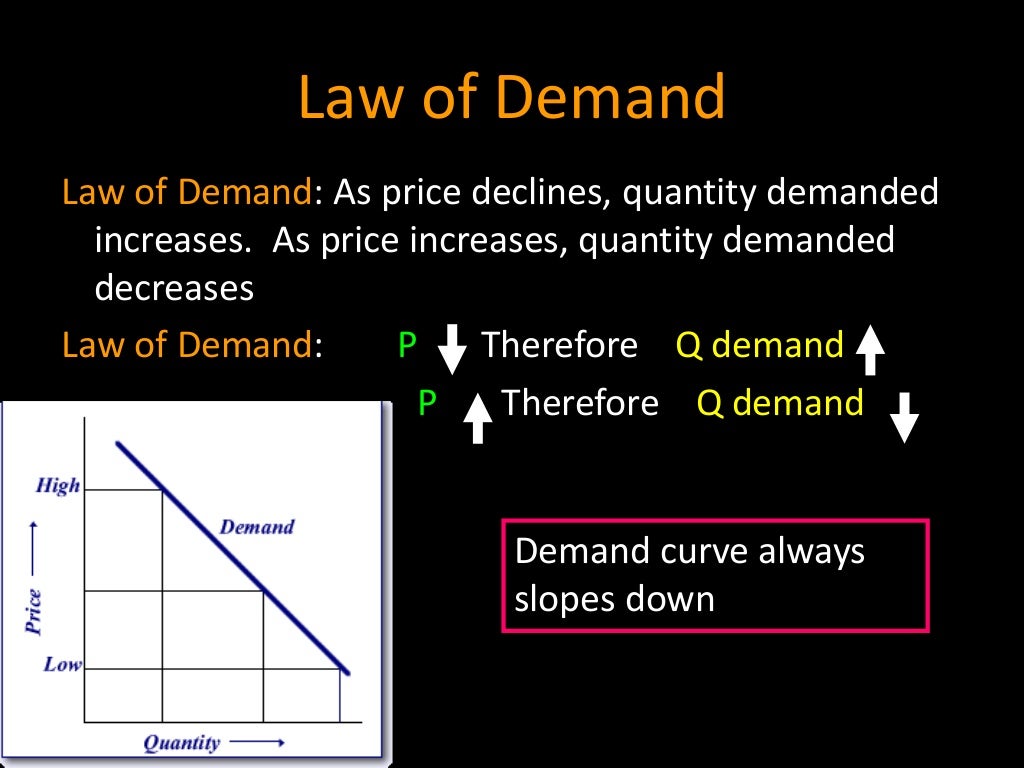
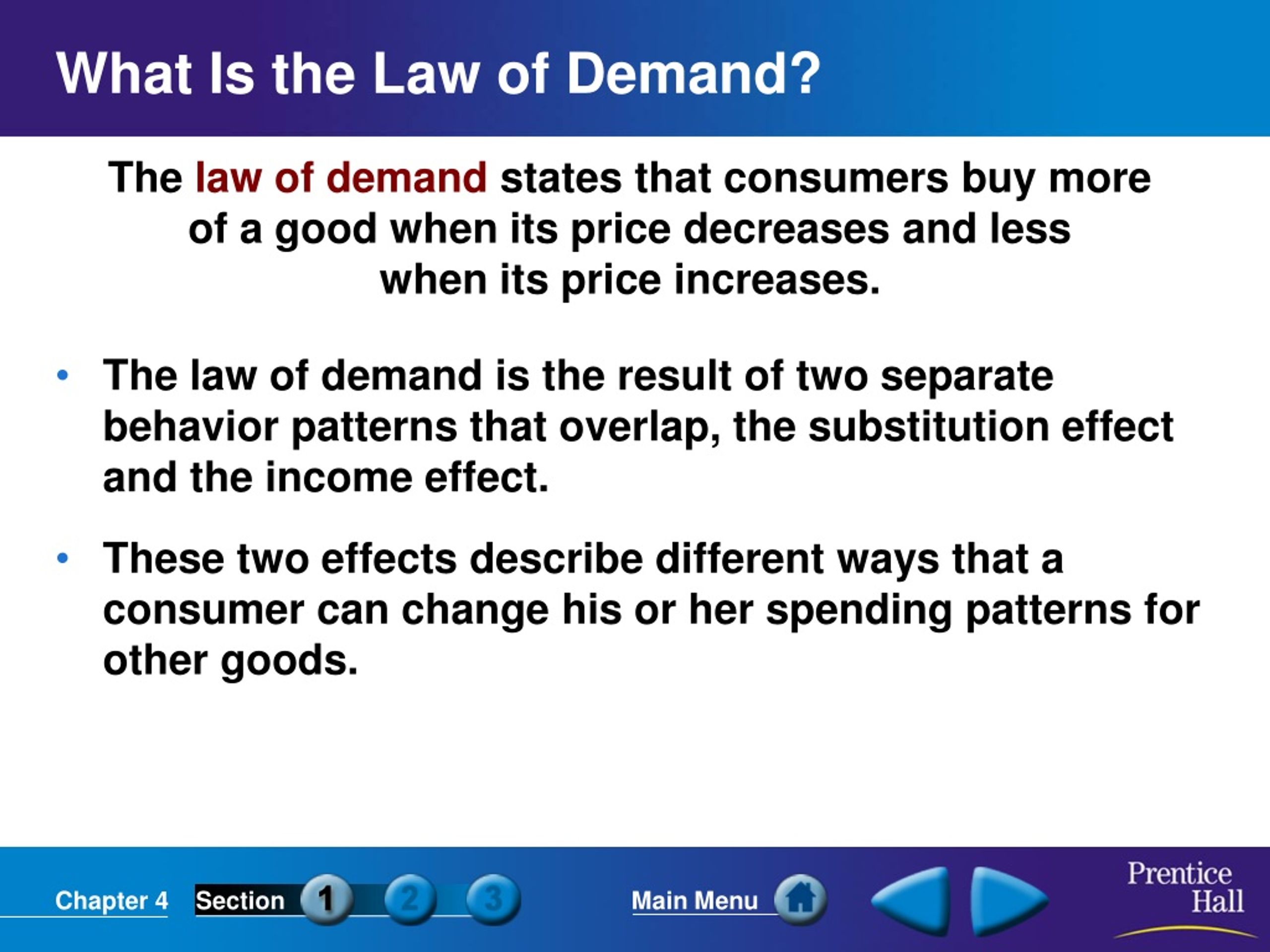
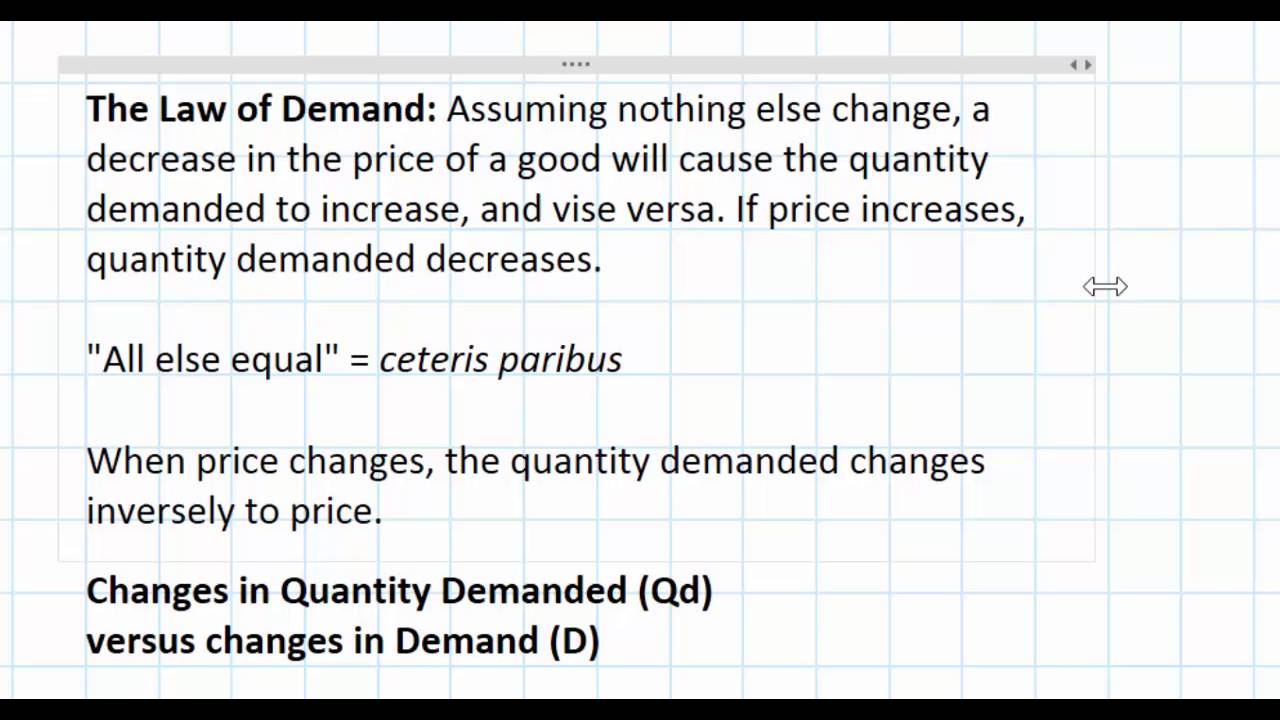
This simple scenario illustrates a fundamental principle in economics: the law of demand. In essence, it states that, all other things being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and conversely, as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases.
Understanding the Law of Demand
At its core, the law of demand is about the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. This isn't just some abstract theory; it's a reflection of how consumers behave in the real world. When something becomes cheaper, we tend to want more of it, and when it becomes more expensive, we tend to want less.
However, it's crucial to understand the caveat: "all other things being equal," often referred to as ceteris paribus. This means that we're isolating the effect of price on demand, assuming that factors like income, tastes, and the prices of related goods remain constant. In reality, these factors can and do change, influencing demand in complex ways.
Factors Influencing Demand
Several factors can shift the entire demand curve, meaning that at any given price, consumers will demand a different quantity than before. These factors are known as determinants of demand.
Consumer income plays a significant role. For most goods (known as normal goods), as income increases, demand also increases. Conversely, for inferior goods (like generic brands), demand may decrease as income rises, as consumers switch to higher-quality alternatives.
Tastes and preferences are another crucial determinant. A sudden trend or change in consumer sentiment can dramatically alter demand for a product. Think of the rise in popularity of plant-based diets and the corresponding surge in demand for vegan products.
The prices of related goods also matter. If the price of a substitute good (like tea) increases, the demand for the original good (coffee) might increase. Conversely, if the price of a complementary good (like coffee filters) increases, the demand for the original good (coffee) might decrease.
Illustrating the Law of Demand in Action
To truly grasp the law of demand, consider several examples. Take gasoline, for instance. When gas prices soar, people tend to drive less, carpool more, and explore public transportation options. This behavior reflects the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Another example can be seen with seasonal fruits and vegetables. When strawberries are in season and abundant, their price is typically lower, leading to increased demand. Conversely, during the off-season, when supply is limited, the price rises, and demand decreases.
Even in the realm of digital goods, the law of demand holds. When a video game goes on sale, downloads and purchases typically increase. This highlights the pervasive nature of this fundamental economic principle.
Statements Consistent with the Law of Demand
So, which statement is consistent with the law of demand? The answer lies in identifying a scenario where a decrease in price leads to an increase in quantity demanded, or vice versa.
"As the price of apples decreases, consumers buy more apples." This is a direct application of the law of demand. If the price of apples falls, consumers are likely to purchase a greater quantity.
Consider other options: "As consumer income increases, demand for luxury cars increases." While this may be true, it relates to the influence of income on demand, not the law of demand itself.
Similarly, "A popular celebrity endorses a new product, and demand increases." This illustrates the effect of tastes and preferences on demand, not price.
Finally, "A new technology makes producing computers cheaper, and supply increases." This describes the law of supply, which is a related but distinct economic principle.
Real-World Applications and Limitations
The law of demand is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in business and policy-making. Businesses use it to make pricing decisions, forecast demand, and plan production.
Governments rely on it when formulating tax policies and regulations that affect prices and consumption. For example, taxes on cigarettes are often implemented to discourage smoking, based on the principle that higher prices will reduce demand.
However, it's important to acknowledge the limitations of the law of demand. It doesn't always hold true in every situation. For example, in the case of Veblen goods, which are luxury items where demand increases as price increases (because the higher price is associated with status), the law of demand is violated.
Furthermore, in situations of extreme necessity, such as during a natural disaster, demand for essential goods like water and food may remain high regardless of price, as people prioritize survival.
Conclusion
The law of demand, with its simple yet powerful premise, serves as a cornerstone of economic analysis. It helps us understand how consumers respond to changes in price and provides a framework for making informed decisions in business and policy.
While real-world situations often involve a complex interplay of factors, understanding the fundamental relationship between price and quantity demanded remains essential for navigating the ever-changing economic landscape. Just like those strawberries at the farmer's market, the law of demand is a constant presence in our daily lives.